7 to 8¶
Gdsfactory v8, based on KFactory, offers enhanced routing functions and additional features from KLayout, including DRC, dummy fill, and connectivity checks.
For those still using gdsfactory v7, it is hosted in https://
Benefits of Migrating:¶
- Integrated Data: Ports, information, and settings are stored within the GDS file, eliminating the need for separate files.
- Improved Booleans: Booleans are more robust with integer-based polygons, removing slivers of less than 1nm.
- Enhanced Features: More robust booleans, DRC, LVS, and connectivity checks.
- Active Maintenance: KLayout is more actively maintained with frequent updates than gdstk.
- Advanced Routing Algorithms: Better routing algorithms for efficient design. Thanks to Kfactory.
- Grid Alignment: Ports and polygons snap to grid by default, reducing the likelihood of 1nm gaps.
Drawbacks of Migrating:¶
- Potential Errors: As with any code changes, undesired errors may be introduced. It is recommended to have regression tests for all your components before you migrate.
- Non-Manhattan Placement: Slightly more difficult to define non-manhattan references, routes, or port. Manhattan Components (at 0, 90, 180 and 270) work the same way.
- Incomplete Functionality: Some features, such as
route_path_length_match, are not yet implemented.
Major Differences:¶
- Port units:
port.x,port.x,port.widthhave changed to Database Units (1nm by default). To set/get them in um, used(decimal) e.g.,port.dxminport.dcenterorport.dwidthwhich are floats. - LayerMap: Now an Enum of integers.
- Routing Functions: New functions do not require starting ports to be in the same orientation and monitor for self-intersections.
get_routeis nowroute_single, andget_bundleis nowroute_bundle. - Grid Snapping: All polygon points snap to grid, mitigating 1nm gaps.
Minor Differences:¶
- Replace
from gdsfactory.cell import cellwithfrom gdsfactory import cell.
LayerMap¶
In v7 or below, a LayerMap needs to be called
from gdsfactory.technology import LayerMap
class LayerMapFab(LayerMap):
WG = (1, 0)
LAYER = LayerMapFab()However in v8 it has a different type and does not need to be called
from gdsfactory.technology import LayerMap
class LayerMapFab(LayerMap):
WG = (1, 0)
LAYER = LayerMapFabSee below:
import gdsfactory as gf
from gdsfactory.technology import LayerMap
class LayerMapFab(LayerMap):
WG = (1, 0)
LAYER = LayerMapFab
type(LAYER)aenum._enum.EnumTypeLAYER.WG<LayerMapFab.WG: 1>tuple(LAYER.WG)(1, 0)str(LAYER.WG)'WG'Ports¶
Ports are now stored in the GDS file and are not stored in a separate file.
Ports are snapped to grid, and therefore, width, x and y is in DBU (1nm by default).
c = gf.components.straight(length=10)
print(c.ports["o2"].width, "in DBU")
print(c.ports["o2"].dwidth, "in um")0.5 in DBU
0.5 in um
print(c.ports["o2"].dx, "in DBU")
print(c.ports["o2"].x, "in um")10.0 in DBU
10.0 in um
Component.bbox is now a function¶
Both Components and Instances have a bbox and dbbox that are now functions.
c = gf.c.straight(length=10)
c.bbox()(0,-0.25;10,0.25)dir(c.dbbox())['__add__',
'__and__',
'__class__',
'__copy__',
'__deepcopy__',
'__delattr__',
'__dict__',
'__dir__',
'__doc__',
'__eq__',
'__format__',
'__ge__',
'__getattribute__',
'__getstate__',
'__gsi_id__',
'__gt__',
'__hash__',
'__init__',
'__init_subclass__',
'__le__',
'__lt__',
'__module__',
'__mul__',
'__ne__',
'__new__',
'__reduce__',
'__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__',
'__rmul__',
'__setattr__',
'__setstate__',
'__sizeof__',
'__str__',
'__sub__',
'__subclasshook__',
'__weakref__',
'_const_cast',
'_create',
'_destroy',
'_destroyed',
'_is_const_object',
'_manage',
'_to_const_object',
'_unmanage',
'area',
'assign',
'bbox',
'bottom',
'center',
'contains',
'create',
'destroy',
'destroyed',
'dup',
'empty',
'enlarge',
'enlarged',
'from_ibox',
'from_s',
'hash',
'height',
'inside',
'is_const_object',
'is_point',
'left',
'move',
'moved',
'new',
'overlaps',
'p1',
'p2',
'perimeter',
'right',
'to_itype',
'to_s',
'top',
'touches',
'transformed',
'width',
'world']c.dbbox().right10.0For the old bbox behavior you can use c.bbox_np which returns the bbox as a numpy array.
c.bbox_np()array([[ 0. , -0.25],
[10. , 0.25]])Component.get_polygons()¶
Component.get_polygons() returns all the Polygons and can be slow.
Component.get_polygons_points() is the equivalent to Component.get_polygons() in gdsfactory7 where we return the polygon edges.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.pack([gf.components.seal_ring_segmented()] * 200)[0]
c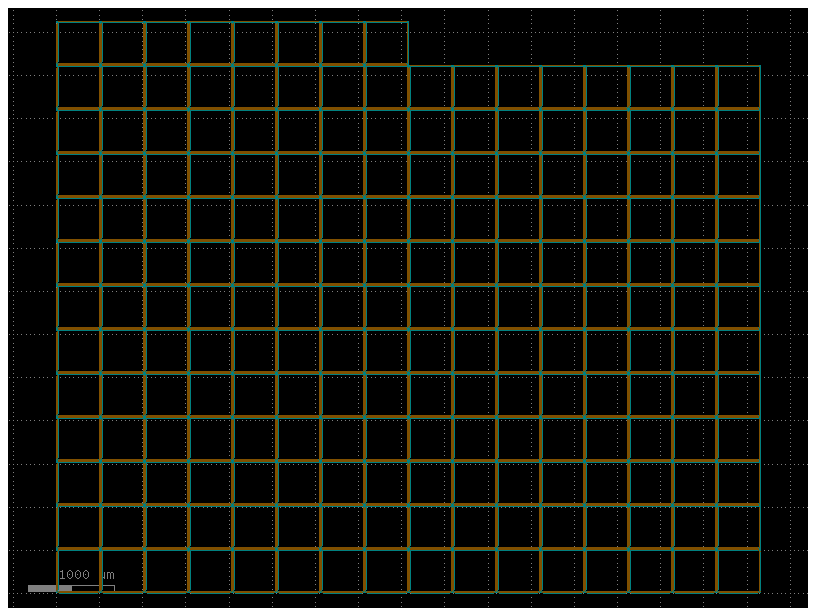
%time
p = c.get_polygons_points()CPU times: user 3 μs, sys: 0 ns, total: 3 μs
Wall time: 7.15 μs
If you only care about the polygons from one layer you can also only extract those.
%time
p = c.get_polygons_points(layers=("M3",))CPU times: user 4 μs, sys: 0 ns, total: 4 μs
Wall time: 8.11 μs
ref.get_ports_list¶
Reference does not have get_ports_list. You can use
- ref.ports to get all ports
- ref.ports.filter(...) to filter all ports with angle, port_type, orientation ...
- gf.port.get_ports_list(b, ...) for backwards compatibility.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.Component()
bend = gf.components.bend_euler()
b = c.add_ref(bend)
b.ports.filter(orientation=90)[DPort(self.name='o2', self.width=0.5, trans=r90 *1 10,10, layer=WG (1/0), port_type=optical)]gf.port.get_ports_list(b, orientation=90)[DPort(self.name='o2', self.width=0.5, trans=r90 *1 10,10, layer=WG (1/0), port_type=optical)]Routing functions¶
Routing functions NO longer return the route Instances but they place the instances in a Component, so you have to pass a Component as the first argument.
c = gf.Component()
w = gf.components.straight(cross_section="rib")
top = c << w
bot = c << w
bot.move((0, -2))
p0 = top.ports["o2"]
p1 = bot.ports["o2"]
r = gf.routing.route_single(
c,
p0,
p1,
cross_section="rib",
)
c
🚀 The new routing functions allow the starting ports ports1 to have different orientations.
The end ports ports2 still require to have the same orientation.
c = gf.Component()
top = c << gf.components.nxn(north=8, south=0, east=0, west=0)
bot = c << gf.components.nxn(north=2, south=2, east=2, west=2, xsize=10, ysize=10)
top.movey(100)
routes = gf.routing.route_bundle(
c,
ports1=bot.ports,
ports2=top.ports,
radius=5,
sort_ports=True,
cross_section="strip",
)
c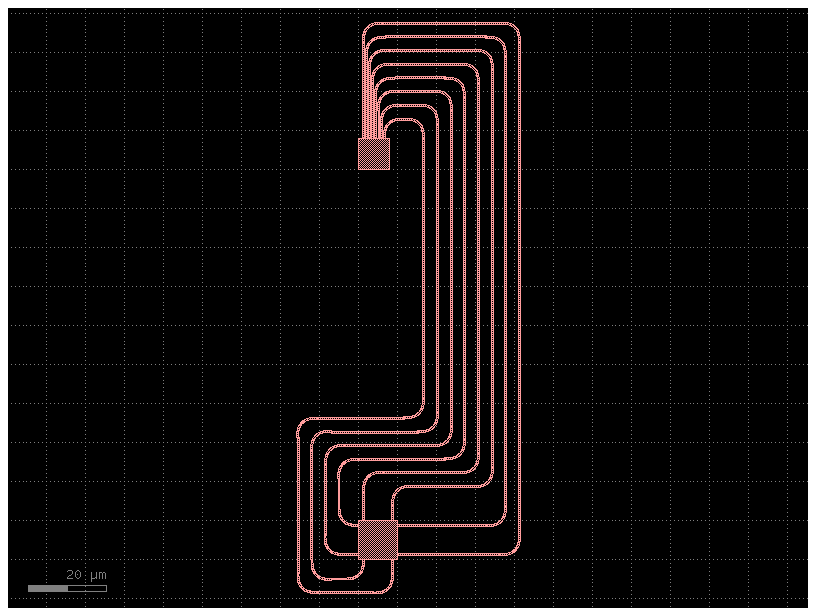
Built in connectivity checks¶
gdsfactory8 includes connectivity checks to ensure things are properly connected. no
This can help you find any:
- Gaps between ports.
- Width mismatches.
- Unconnected ports.
c = gf.Component()
s = c << gf.components.straight(width=1)
b1 = c << gf.components.bend_euler()
b1.connect("o1", s["o2"], allow_width_mismatch=True)
b2 = c << gf.components.bend_euler(radius=5)
b2.connect("o1", s["o1"], allow_width_mismatch=True)
gc = gf.components.grating_coupler_elliptical_te()
gc1 = c << gc
gc2 = c << gc
gc1.connect("o1", b1.ports["o2"])
gc2.connect("o1", b2.ports["o2"])
c.plot()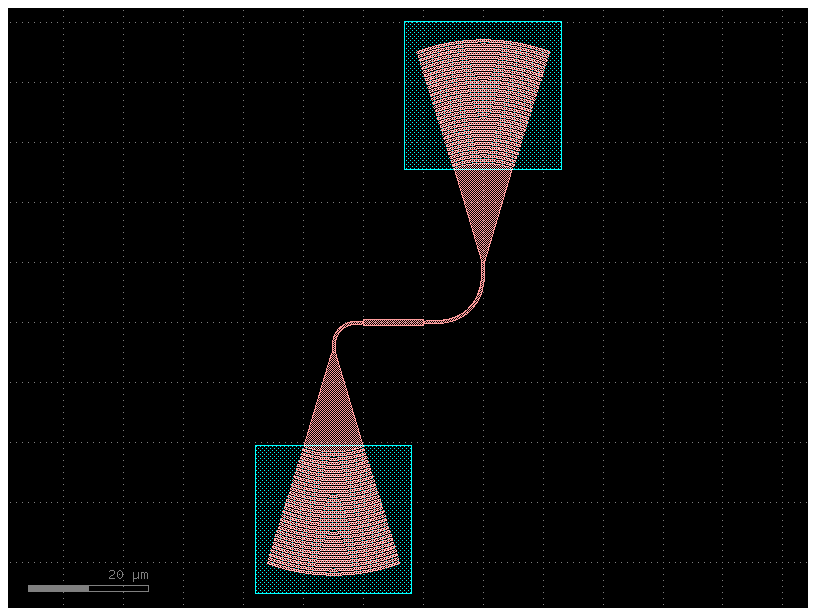
lyrdb = c.connectivity_check(port_types=("optical", "electrical"))
filepath = gf.config.home / "errors.lyrdb"
lyrdb.save(filepath)
gf.show(c, lyrdb=filepath)