Parametric Cells for the Generic PDK.
Consider them a foundation from which you can draw inspiration. Feel free to modify their cross-sections and layers to tailor a unique PDK suited for any foundry of your choice.
By doing so, you’ll possess a versatile, retargetable PDK, empowering you to design your circuits with speed and flexibility.
components¶
analog¶
- gdsfactory.components.analog.interdigital_capacitor(fingers: int = 4, finger_length: float | int = 20.0, finger_gap: float | int = 2.0, thickness: float | int = 5.0, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG')Component
Generates an interdigital capacitor with ports on both ends.
See for example Zhu & Wu (2000).
- Parameters
fingers– total fingers of the capacitor.finger_length– length of the probing fingers.finger_gap– length of gap between the fingers.thickness– Thickness of fingers and section before the fingers.layer– spec.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.interdigital_capacitor(fingers=4, finger_length=20, finger_gap=2, thickness=5, layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()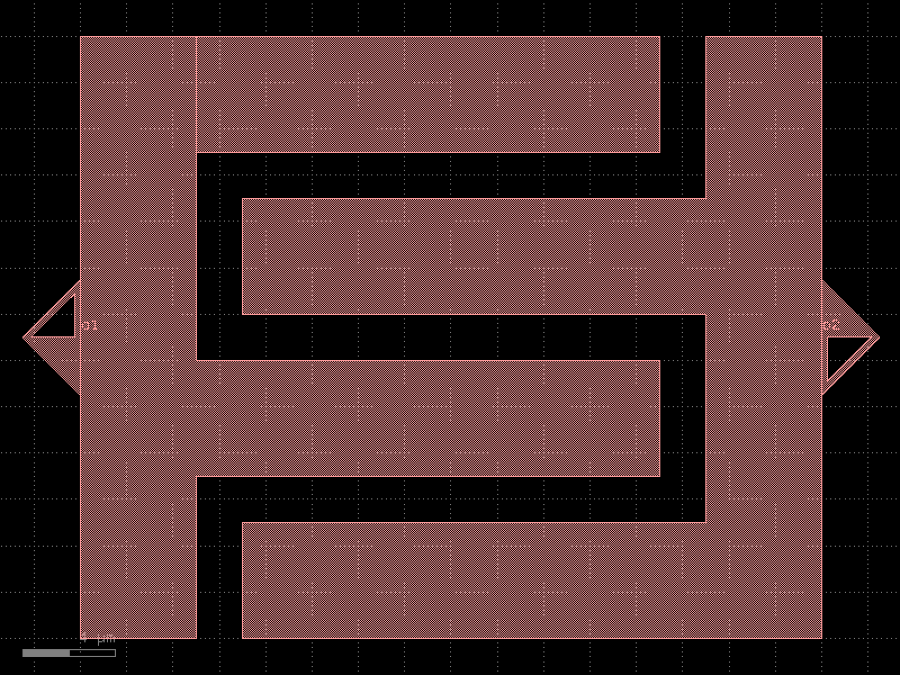
bends¶
- gdsfactory.components.bends.bend_circular(radius: float | None = None, angle: float = 90.0, npoints: int | None = None, layer: gf.typings.LayerSpec | None = None, width: float | None = None, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', allow_min_radius_violation: bool = False)Component
Returns a radial arc.
- Parameters
radius– in um. Defaults to cross_section_radius.angle– angle of arc (degrees).npoints– number of points.layer– layer to use. Defaults to cross_section.layer.width– width to use. Defaults to cross_section.width.cross_section– spec (CrossSection, string or dict).allow_min_radius_violation– if True allows radius to be smaller than cross_section radius.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.bend_circular(angle=90, cross_section='strip', allow_min_radius_violation=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()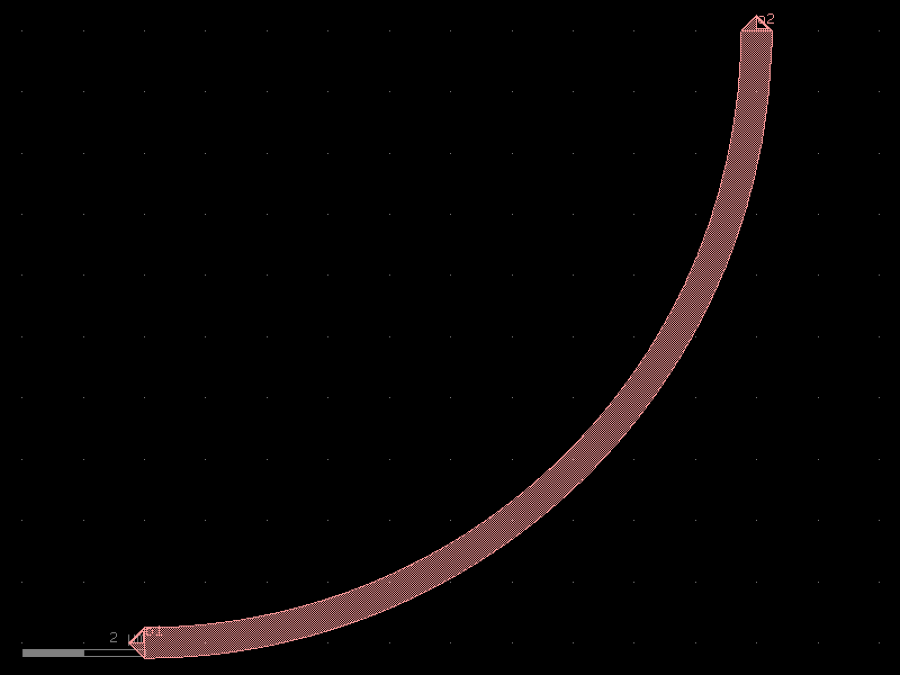
- gdsfactory.components.bends.bend_circular_heater(radius: float | None = None, angle: float = 90, npoints: int | None = None, heater_to_wg_distance: float = 1.2, heater_width: float = 0.5, layer_heater: LayerSpec = 'HEATER', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', allow_min_radius_violation: bool = False)Component
Creates an arc of arclength theta starting at angle start_angle.
- Parameters
radius– in um. Defaults to cross_section.radius.angle– angle of arc (degrees).npoints– Number of points used per 360 degrees.heater_to_wg_distance– in um.heater_width– in um.layer_heater– for heater.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).allow_min_radius_violation– if True allows radius to be smaller than cross_section radius.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.bend_circular_heater(angle=90, heater_to_wg_distance=1.2, heater_width=0.5, layer_heater='HEATER', cross_section='strip', allow_min_radius_violation=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()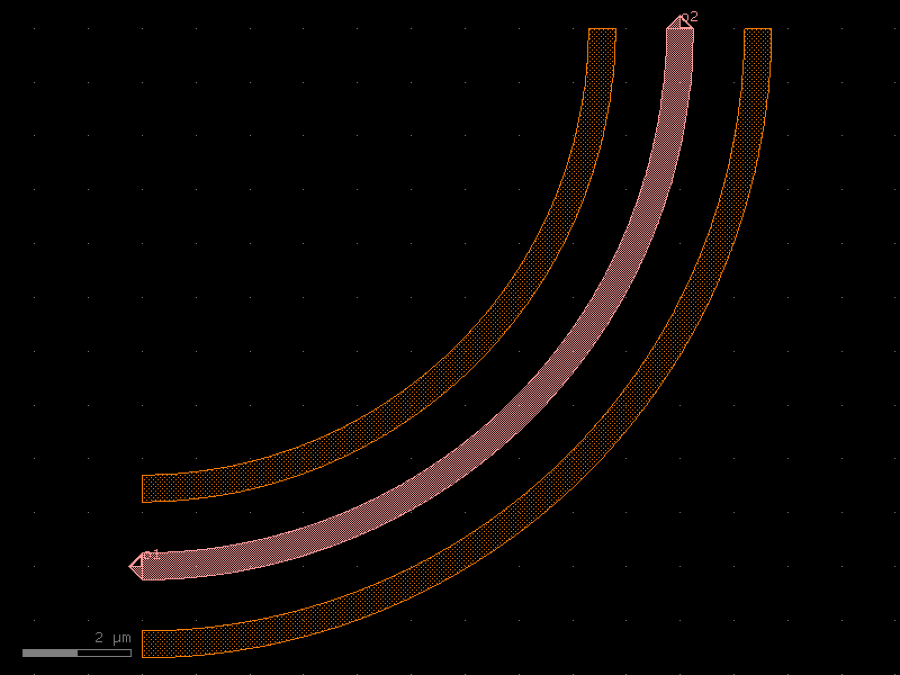
- gdsfactory.components.bends.bend_euler(radius: float | None = None, angle: float = 90.0, p: float = 0.5, with_arc_floorplan: bool = True, npoints: int | None = None, layer: LayerSpec | None = None, width: float | None = None, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', allow_min_radius_violation: bool = False)Component
Regular degree euler bend.
- Parameters
radius– in um. Defaults to cross_section_radius.angle– total angle of the curve.p– Proportion of the curve that is an Euler curve.with_arc_floorplan– if True the size of the bend will be adjusted to match an arc bend with the specified radius. If False: radius is the minimum radius of curvature.npoints– Number of points used per 360 degrees.layer– layer to use. Defaults to cross_section.layer.width– width to use. Defaults to cross_section.width.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).allow_min_radius_violation– if True allows radius to be smaller than cross_section radius.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.bend_euler(angle=90, p=0.5, with_arc_floorplan=True, cross_section='strip', allow_min_radius_violation=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()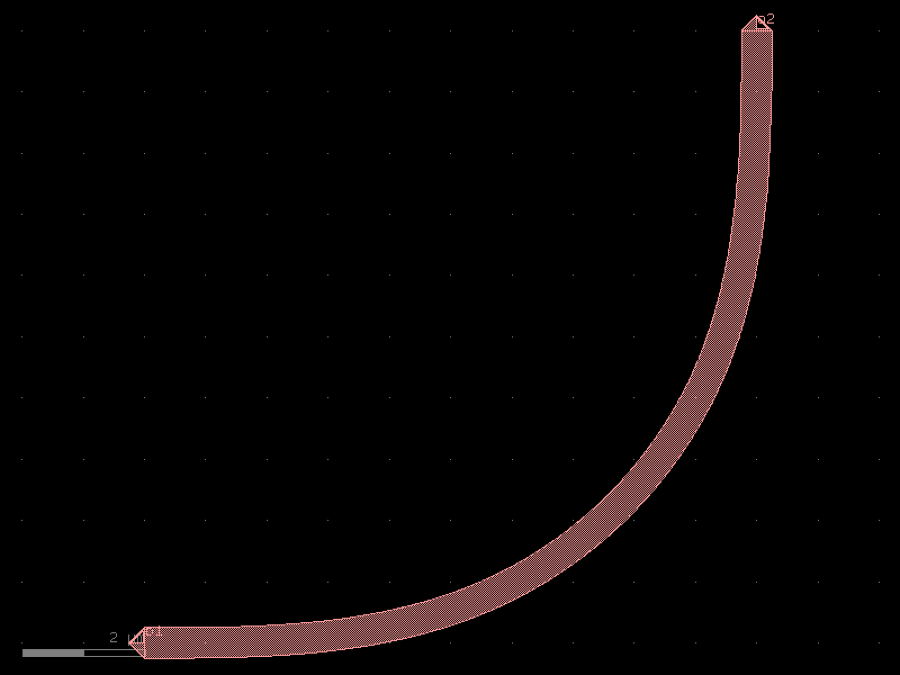
- gdsfactory.components.bends.bend_euler_s(radius: float | None = None, p: float = 0.5, with_arc_floorplan: bool = True, npoints: int | None = None, layer: LayerSpec | None = None, width: float | None = None, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', allow_min_radius_violation: bool = False, port1: str = 'o1', port2: str = 'o2')Component
Sbend made of 2 euler bends.
- Parameters
radius– in um. Defaults to cross_section_radius.p– Proportion of the curve that is an Euler curve.with_arc_floorplan– If False: radius is the minimum radius of curvature.npoints– Number of points used per 360 degrees.layer– layer to use. Defaults to cross_section.layer.width– width to use. Defaults to cross_section.width.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).allow_min_radius_violation– if True allows radius to be smaller than cross_section radius.port1– input port name.port2– output port name.
_____ o2 / / / / | / / / o1_____/
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.bend_euler_s(p=0.5, with_arc_floorplan=True, cross_section='strip', allow_min_radius_violation=False, port1='o1', port2='o2').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()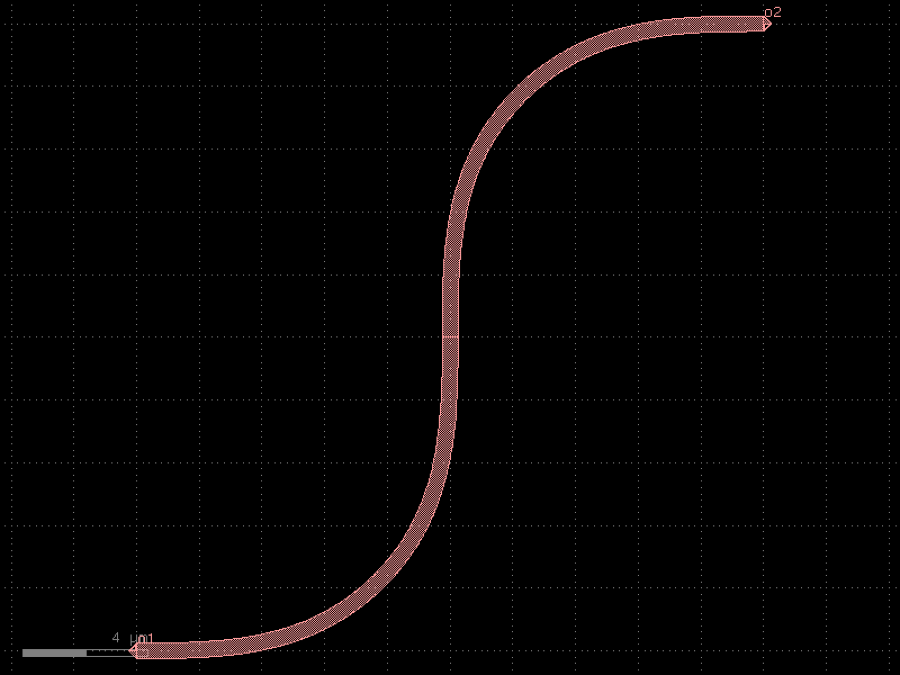
- gdsfactory.components.bends.bend_s(size: Size = (11.0, 1.8), npoints: int = 99, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', allow_min_radius_violation: bool = False, width: float | None = None)Component
Return S bend with bezier curve.
stores min_bend_radius property in self.info[‘min_bend_radius’] min_bend_radius depends on height and length
- Parameters
size– in x and y direction.npoints– number of points.cross_section– spec.allow_min_radius_violation– bool.width– width to use. Defaults to cross_section.width.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.bend_s(size=(11, 1.8), npoints=99, cross_section='strip', allow_min_radius_violation=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()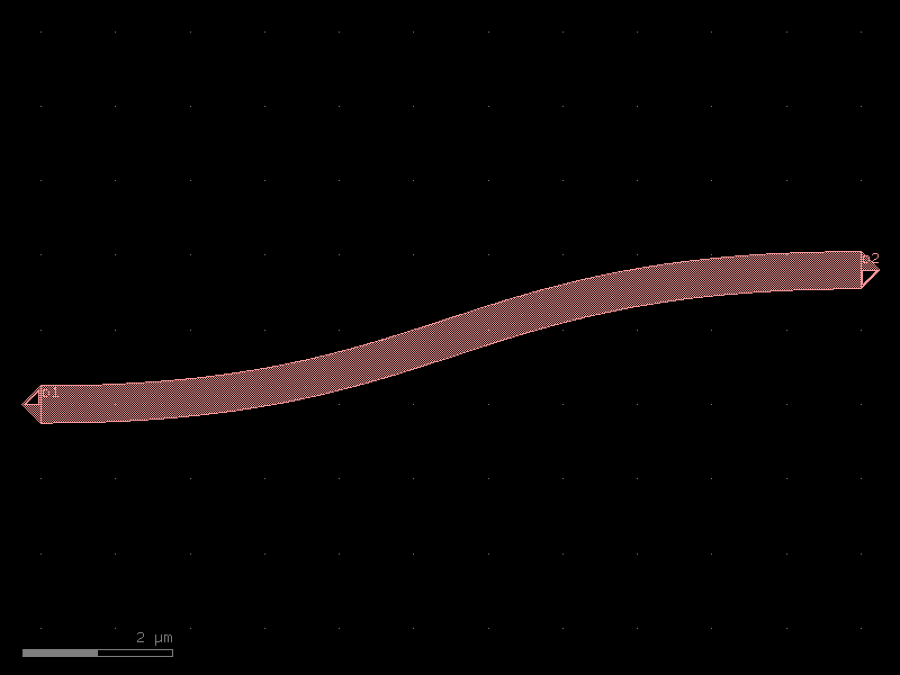
- gdsfactory.components.bends.bend_s_offset(offset: float = 40.0, radius: float | None = 10.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', width: float | None = None, with_euler: bool = True)gf.Component
Return S bend made of two euler bends with a straight section.
stores min_bend_radius property in self.info[‘min_bend_radius’] min_bend_radius depends on height and length
- Parameters
offset– in um.radius– in um. if None, uses cross_section_radius.cross_section– spec.width– width to use. Defaults to cross_section.width.with_euler– use euler bend instead of arc bend.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.bend_s_offset(offset=40, radius=10, cross_section='strip', with_euler=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()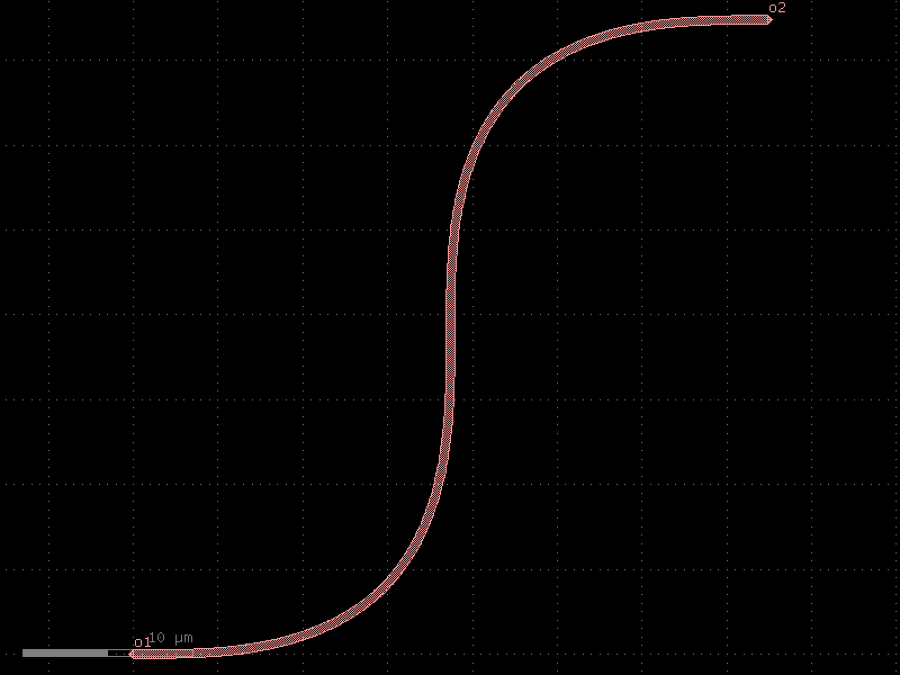
- gdsfactory.components.bends.bezier(control_points: Coordinates = ((0.0, 0.0), (5.0, 0.0), (5.0, 1.8), (10.0, 1.8)), npoints: int = 201, with_manhattan_facing_angles: bool = True, start_angle: int | None = None, end_angle: int | None = None, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', bend_radius_error_type: ErrorType | None = None, allow_min_radius_violation: bool = False, width: float | None = None)Component
Returns Bezier bend.
- Parameters
control_points– list of points.npoints– number of points varying between 0 and 1.with_manhattan_facing_angles– bool.start_angle– optional start angle in deg.end_angle– optional end angle in deg.cross_section– spec.bend_radius_error_type– error type.allow_min_radius_violation– bool.width– width to use. Defaults to cross_section.width.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.bezier(control_points=((0, 0), (5, 0), (5, 1.8), (10, 1.8)), npoints=201, with_manhattan_facing_angles=True, cross_section='strip', allow_min_radius_violation=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()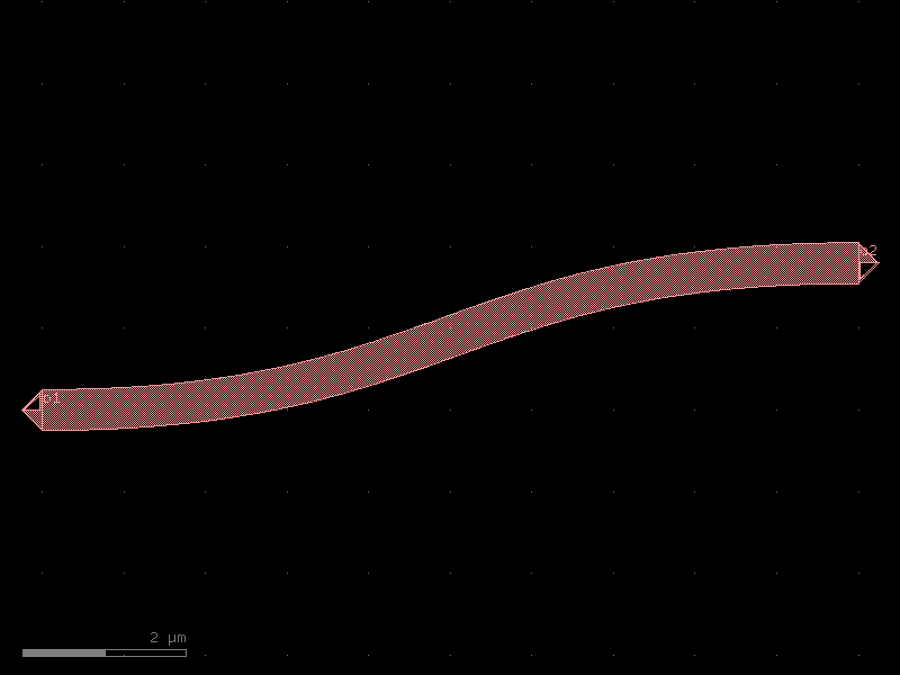
containers¶
- gdsfactory.components.containers.add_fiber_array_optical_south_electrical_north(component: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell, pad: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell, grating_coupler: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell, cross_section_metal: CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection, with_loopback: bool = True, pad_pitch: float = 100.0, pitch: float = 127.0, pad_gc_spacing: float = 250.0, electrical_port_names: list[str] | None = None, electrical_port_orientation: float | None = 90, npads: int | None = None, port_types_grating_couplers: list[str] | None = None, **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns a fiber array with Optical gratings on South and Electrical pads on North.
This a test configuration for DC pads.
- Parameters
component– component spec to add fiber and pads.pad– pad spec.grating_coupler– grating coupler function.cross_section_metal– metal cross section.with_loopback– whether to add a loopback port.pad_pitch– spacing between pads.pitch– spacing between grating couplers.pad_gc_spacing– spacing between pads and grating couplers.electrical_port_names– list of electrical port names. Defaults to all.electrical_port_orientation– orientation of electrical ports. Defaults to 90.npads– number of pads. Defaults to one per electrical_port_names.port_types_grating_couplers– port types for grating couplers. Defaults to vertical TE, TM, and dual.kwargs– additional arguments.
- Keyword Arguments
layer_label– layer for settings label.measurement– measurement name.measurement_settings– measurement settings.analysis– analysis name.doe– Design of Experiment.anchor– anchor point for the label. Defaults to south-west “sw”. Valid options are: “n”, “s”, “e”, “w”, “ne”, “nw”, “se”, “sw”, “c”.gc_port_name– grating coupler input port name.gc_port_labels– grating coupler list of labels.component_name– optional for the label.select_ports– function to select ports.cross_section– cross_section function.get_input_labels_function– function to get input labels. None skips labels.layer_label– optional layer for grating coupler label.bend– bend spec.straight– straight spec.taper– taper spec.get_input_label_text_loopback_function– function to get input label test.get_input_label_text_function– for labels.fanout_length– if None, automatic calculation of fanout length.max_y0_optical– in um.with_loopback– True, adds loopback structures.straight_separation– from edge to edge.list_port_labels– None, adds TM labels to port indices in this list.connected_port_list_ids– names of ports only for type 0 optical routing.nb_optical_ports_lines– number of grating coupler lines.force_manhattan– Falseexcluded_ports– list of port names to exclude when adding gratings.grating_indices– list of grating coupler indices.routing_straight– function to route.routing_method– route_single.gc_rotation– fiber coupler rotation in degrees. Defaults to -90.input_port_indexes– to connect.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.add_fiber_array_optical_south_electrical_north(with_loopback=True, pad_pitch=100, pitch=127, pad_gc_spacing=250, electrical_port_orientation=90).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()- gdsfactory.components.containers.add_termination(component: str | ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], ~gdsfactory.component.Component] | dict[str, ~typing.Any] | ~kfactory.kcell.DKCell = 'straight', port_names: tuple[str, ...] | None = None, terminator: str | ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], ~gdsfactory.component.Component] | dict[str, ~typing.Any] | ~kfactory.kcell.DKCell = functools.partial(<function taper>, width2=0.1), terminator_port_name: str | None = None)Component
Returns component with terminator on some ports.
- Parameters
component– to add terminator.port_names– ports to add terminator.terminator– factory for the terminator.terminator_port_name– for the terminator to connect to the component ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.add_termination(component='straight').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.containers.add_trenches(component: ComponentSpec = 'coupler', layer_component: LayerSpec = 'WG', layer_trench: LayerSpec = 'DEEP_ETCH', width_trench: float = 2.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'rib_with_trenches', top: float | None = None, bot: float | None = None, right: float | None = 0, left: float | None = 0, **kwargs: Any)gf.Component
Return component with trenches.
- Parameters
component– component to add to the trenches.layer_component– layer of the component.layer_trench– layer of the trenches.width_trench– width of the trenches.cross_section– spec (CrossSection, string or dict).top– width of the trench on the top. If None uses width_trench.bot– width of the trench on the bottom. If None uses width_trench.right– width of the trench on the right. If None uses width_trench.left– width of the trench on the left. If None uses width_trench.kwargs– component settings.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.add_trenches(component='coupler', layer_component='WG', layer_trench='DEEP_ETCH', width_trench=2, cross_section='rib_with_trenches', right=0, left=0).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()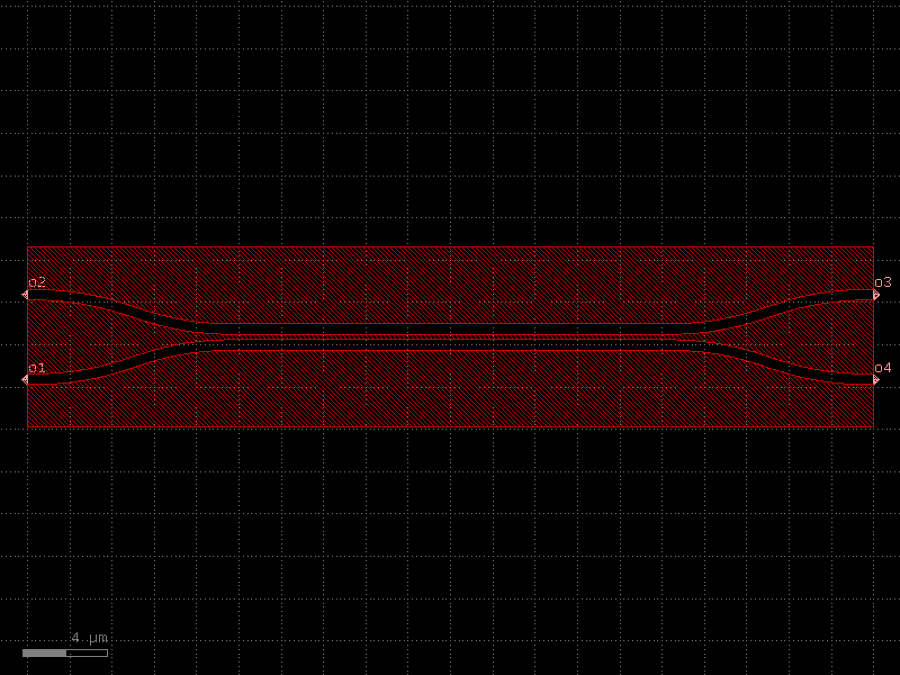
- gdsfactory.components.containers.add_trenches90(*, component: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', layer_component: LayerSpec = 'WG', layer_trench: LayerSpec = 'DEEP_ETCH', width_trench: float = 2.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'rib_with_trenches', top: float | None = 0, bot: float | None = None, right: float | None = None, left: float | None = 0, **kwargs: Any)gf.Component
Return component with trenches.
- Parameters
component– component to add to the trenches.layer_component– layer of the component.layer_trench– layer of the trenches.width_trench– width of the trenches.cross_section– spec (CrossSection, string or dict).top– width of the trench on the top. If None uses width_trench.bot– width of the trench on the bottom. If None uses width_trench.right– width of the trench on the right. If None uses width_trench.left– width of the trench on the left. If None uses width_trench.kwargs– component settings.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.add_trenches90(component='bend_euler', layer_component='WG', layer_trench='DEEP_ETCH', width_trench=2, cross_section='rib_with_trenches', top=0, left=0).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()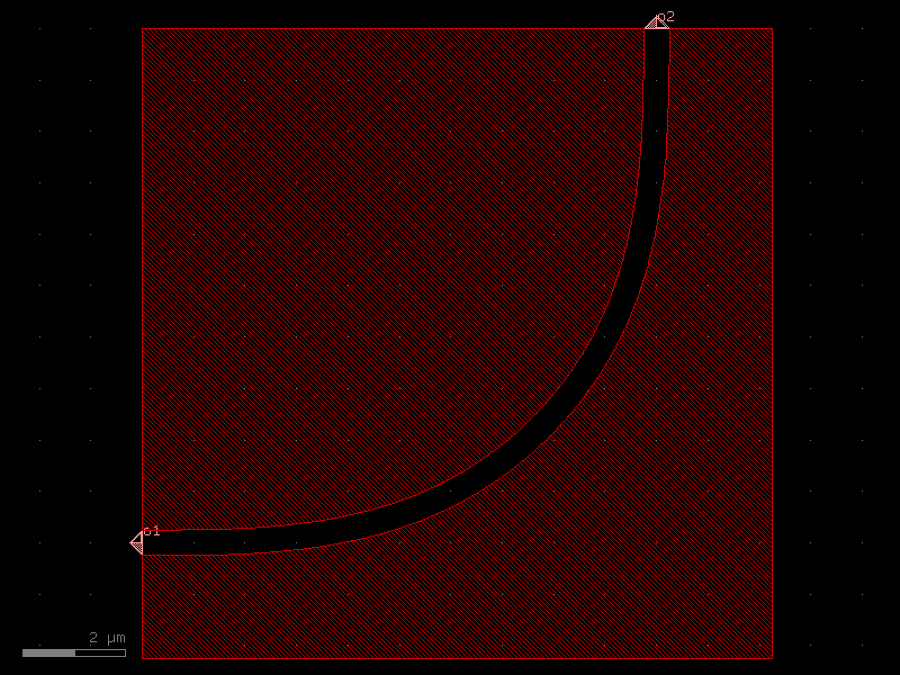
- gdsfactory.components.containers.array(component: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'pad', columns: int = 6, rows: int = 1, column_pitch: float = 150, row_pitch: float = 150, add_ports: bool = True, size: tuple[float, float] | None = None, centered: bool = False, post_process: Sequence[_PostProcess | Callable[[Component], None] | partial[Component]] | None = None, auto_rename_ports: bool = False)Component
Returns an array of components.
- Parameters
component– to replicate.columns– in x.rows– in y.column_pitch– pitch between columns.row_pitch– pitch between rows.auto_rename_ports– True to auto rename ports.add_ports– add ports from component into the array.size– Optional x, y size. Overrides columns and rows.centered– center the array around the origin.post_process– function to apply to the array after creation.
- Raises
ValueError– If columns > 1 and spacing[0] = 0.ValueError– If rows > 1 and spacing[1] = 0.
2 rows x 4 columns column_pitch <----------> ___ ___ ___ ___ | | | | | | | | |___| |___| |___| |___| ___ ___ ___ ___ | | | | | | | | |___| |___| |___| |___|
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.array(component='pad', columns=6, rows=1, column_pitch=150, row_pitch=150, add_ports=True, centered=False, auto_rename_ports=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()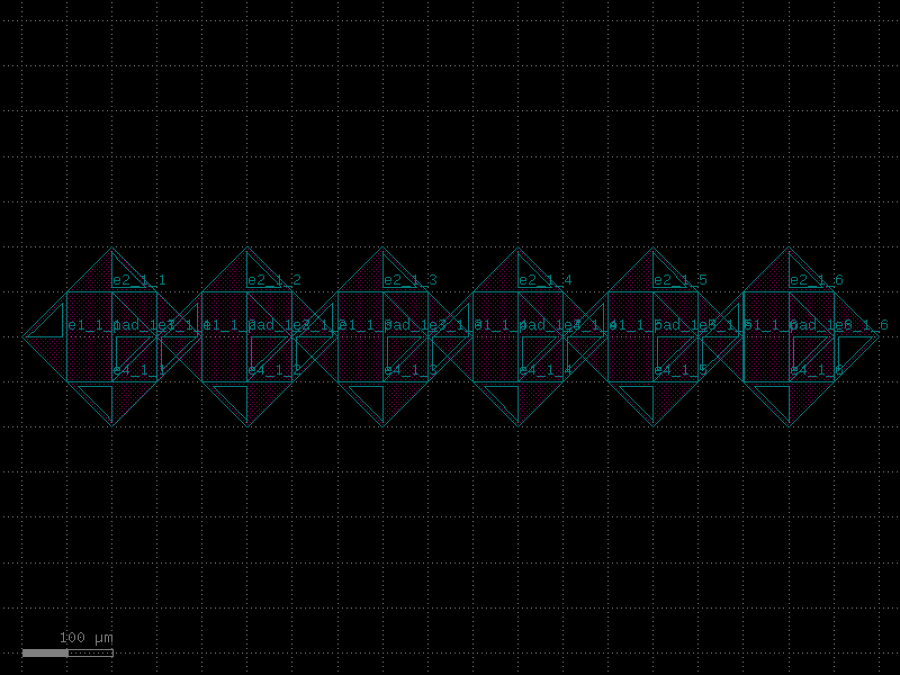
- gdsfactory.components.containers.component_sequence(sequence: str, symbol_to_component: dict[str, tuple[Component, str, str]], ports_map: dict[str, tuple[str, str]] | None = None, port_name1: str = 'o1', port_name2: str = 'o2', start_orientation: float = 0.0)Component
Returns component from ASCII sequence.
if you prefix a symbol with ! it mirrors the component
- Parameters
sequence– a string or a list of symbols.symbol_to_component– maps symbols to (component, input, output).ports_map– (optional) extra port mapping using the convention. {port_name: (alias_name, port_name)}port_name1– input port_name.port_name2– output port_name.start_orientation– in degrees.
- Returns
- containing the sequence of sub-components
instantiated and connected together in the sequence order.
- Return type
component
import gdsfactory as gf bend180 = gf.components.bend_circular180() wg_pin = gf.components.straight_pin(length=40) wg = gf.components.straight() # Define a map between symbols and (component, input port, output port) symbol_to_component = { "A": (bend180, 'o1', 'o2'), "B": (bend180, 'o2', 'o1'), "H": (wg_pin, 'o1', 'o2'), "-": (wg, 'o1', 'o2'), } # Each character in the sequence represents a component s = "AB-H-H-H-H-BA" c = gf.components.component_sequence(sequence=s, symbol_to_component=symbol_to_component) c.plot()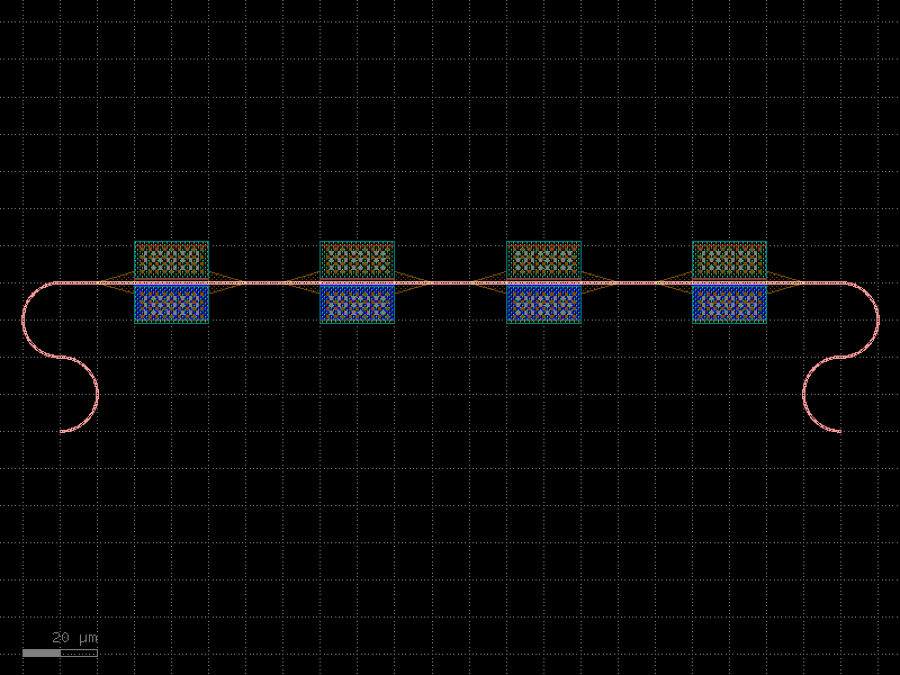
- gdsfactory.components.containers.copy_layers(factory: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'cross', layers: Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum] = ((1, 0), (2, 0)), **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns a component with the geometry copied in different layers.
- Parameters
factory– component spec.layers– iterable of layers.kwargs– keyword arguments.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.copy_layers(factory='cross', layers=((1, 0), (2, 0))).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()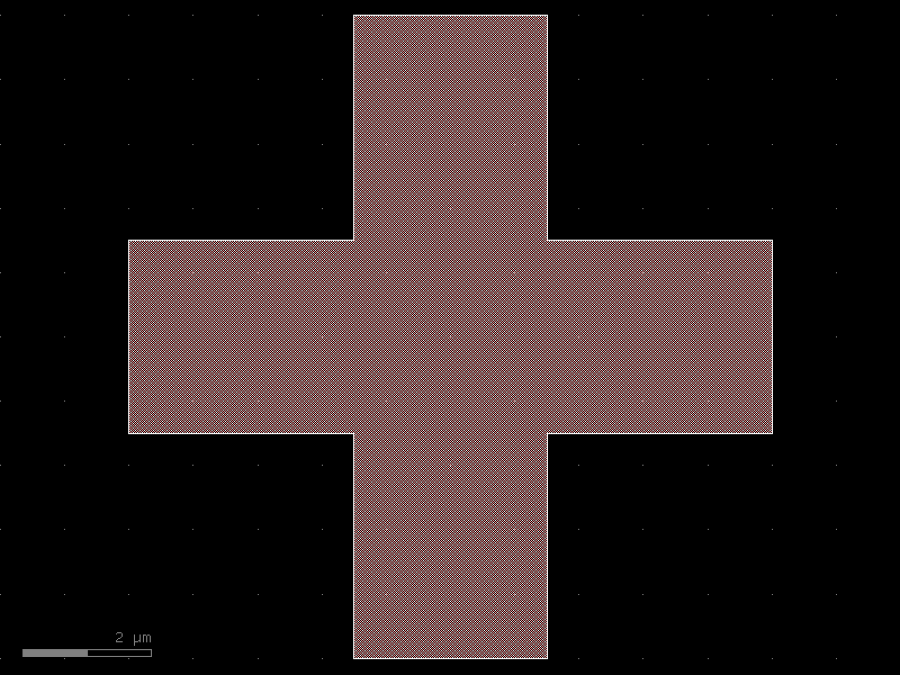
- gdsfactory.components.containers.extend_ports(component: ComponentSpec = 'mmi1x2', port_names: PortNames | None = None, length: float = 5.0, extension: ComponentSpec | None = None, port1: str | None = None, port2: str | None = None, port_type: str = 'optical', centered: bool = False, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, extension_port_names: list[str] | None = None, allow_width_mismatch: bool = False, auto_taper: bool = True, **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns a new component with some ports extended.
You can define extension Spec defaults to port cross_section of each port to extend.
- Parameters
component– component to extend ports.port_names– list of ports names to extend, if None it extends all ports.length– extension length.extension– function to extend ports (defaults to a straight).port1– extension input port name.port2– extension output port name.port_type– type of the ports to extend.centered– if True centers rectangle at (0, 0).cross_section– extension cross_section, defaults to port cross_section if port has no cross_section it creates one using width and layer.extension_port_names– extension port names add to the new component.allow_width_mismatch– allow width mismatches.auto_taper– if True adds automatic tapers.kwargs– cross_section settings.
- Keyword Arguments
layer– port GDS layer.prefix– port name prefix.orientation– in degrees.width– port width.layers_excluded– List of layers to exclude.port_type– optical, electrical, ….clockwise– if True, sort ports clockwise, False: counter-clockwise.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.extend_ports(component='mmi1x2', length=5, port_type='optical', centered=False, allow_width_mismatch=False, auto_taper=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()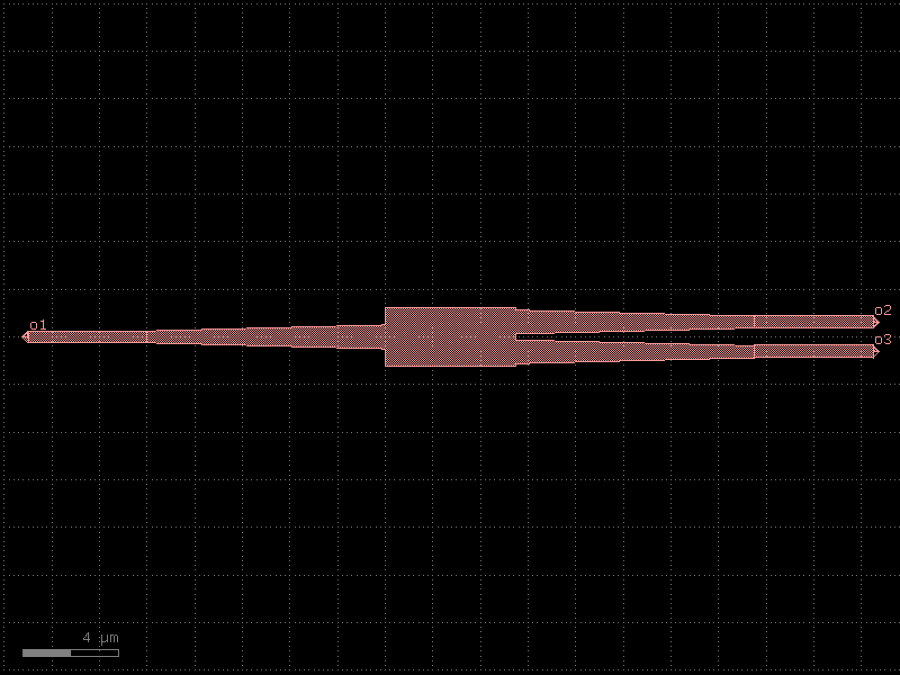
- gdsfactory.components.containers.extend_ports_list(component_spec: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell, extension: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell, extension_port_name: str | None = None, ignore_ports: Sequence[str] | None = None)Component
Returns a component with an extension attached to a list of ports.
- Parameters
component_spec– component from which to get ports.extension– function for extension.extension_port_name– to connect extension.ignore_ports– list of port names to ignore.
- gdsfactory.components.containers.splitter_chain(splitter: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'mmi1x2', columns: int = 3, bend: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'bend_s')Component
Chain of splitters.
- Parameters
splitter– splitter to chain.columns– number of splitters to chain.bend– bend to connect splitters.
__o5 __| __| |__o4 o1 _| |__o3 |__o2 __o2 o1 _| |__o3
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.splitter_chain(splitter='mmi1x2', columns=3, bend='bend_s').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()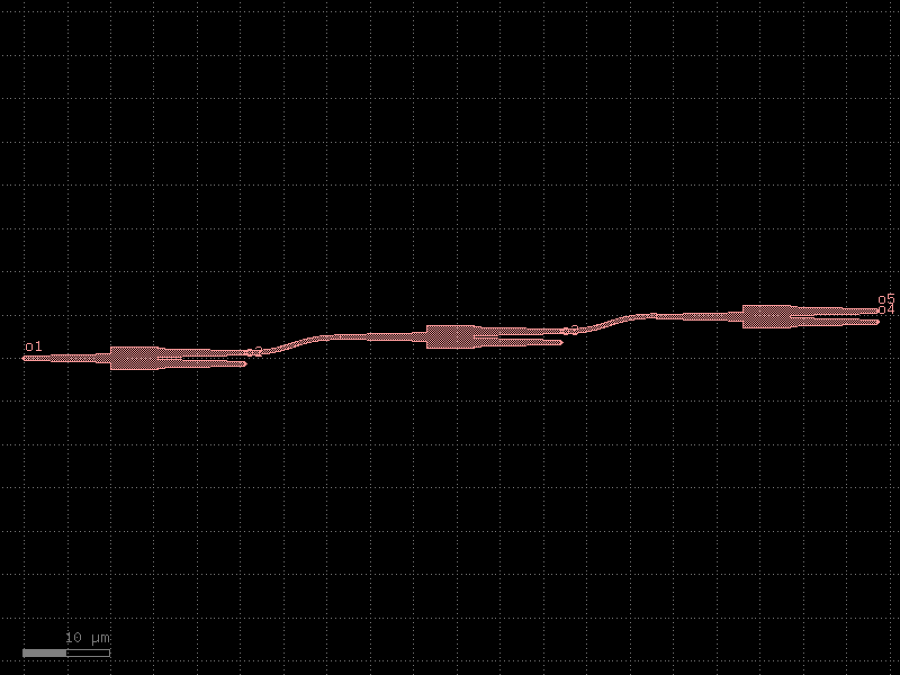
- gdsfactory.components.containers.splitter_tree(coupler: ComponentSpec = 'mmi1x2', noutputs: int = 4, spacing: Spacing = (90.0, 50.0), bend_s: ComponentSpec | None = 'bend_s', bend_s_xsize: float | None = None, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')gf.Component
Tree of power splitters.
- Parameters
coupler– coupler factory.noutputs– number of outputs.spacing– x, y spacing between couplers.bend_s– Sbend function for termination.bend_s_xsize– xsize for the sbend.cross_section– cross_section.
__| __| |__ _| |__ |__ dy dx
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.splitter_tree(coupler='mmi1x2', noutputs=4, spacing=(90, 50), bend_s='bend_s', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()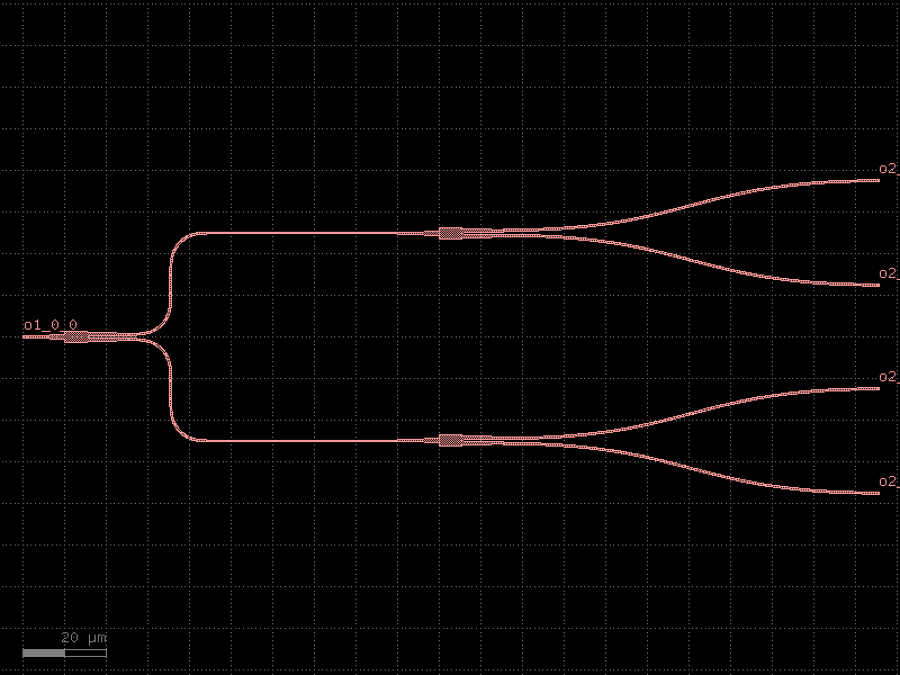
- gdsfactory.components.containers.switch_tree(*, coupler: ComponentSpec = functools.partial(<function mzi>, combiner='mmi2x2', port_e1_combiner='o3', port_e0_combiner='o4', delta_length=0, straight_x_top='straight_heater_metal', length_x=None), noutputs: int = 4, spacing: Spacing = (500, 100), bend_s: ComponentSpec | None = 'bend_s', bend_s_xsize: float | None = None, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')gf.Component
Tree of power splitters.
- Parameters
coupler– coupler factory.noutputs– number of outputs.spacing– x, y spacing between couplers.bend_s– Sbend function for termination.bend_s_xsize– xsize for the sbend.cross_section– cross_section.
__| __| |__ _| |__ |__ dy dx
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.switch_tree(noutputs=4, spacing=(500, 100), bend_s='bend_s', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()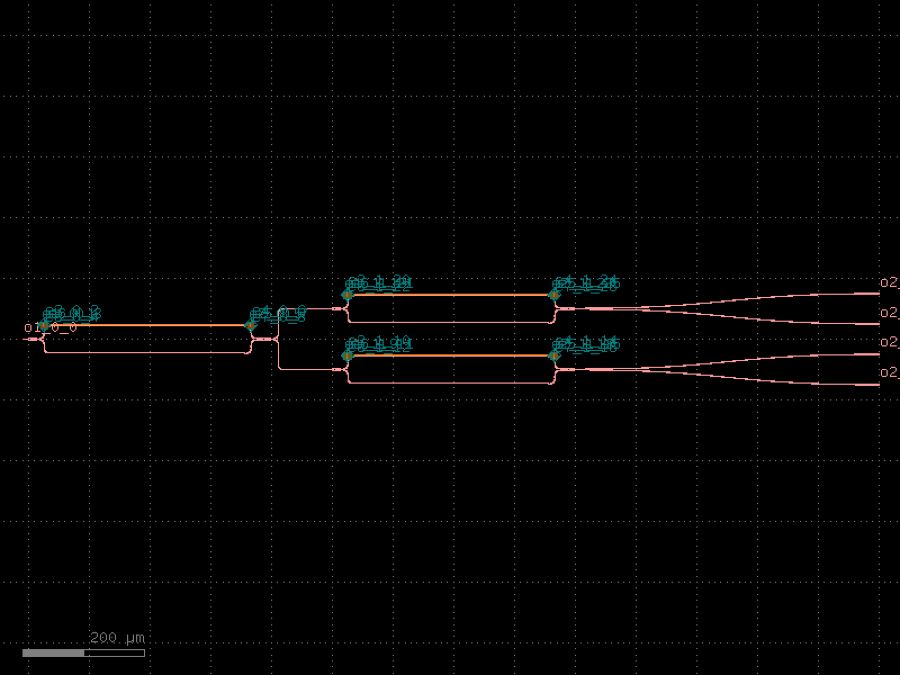
couplers¶
- gdsfactory.components.couplers.coupler(gap: float = 0.236, length: float = 20.0, dy: Delta = 4.0, dx: Delta = 10.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', allow_min_radius_violation: bool = False, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_s')Component
Symmetric coupler.
- Parameters
gap– between straights in um.length– of coupling region in um.dy– port to port vertical spacing in um.dx– length of bend in x direction in um.cross_section– spec (CrossSection, string or dict).allow_min_radius_violation– if True does not check for min bend radius.bend– input and output sbend components.
dx dx |------| |------| o2 ________ ______o3 \ / | \ length / | ======================= gap | dy / \ | ________/ \_______ | o1 o4 coupler_straight coupler_symmetric
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler(gap=0.236, length=20, dy=4, dx=10, cross_section='strip', allow_min_radius_violation=False, bend='bend_s').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()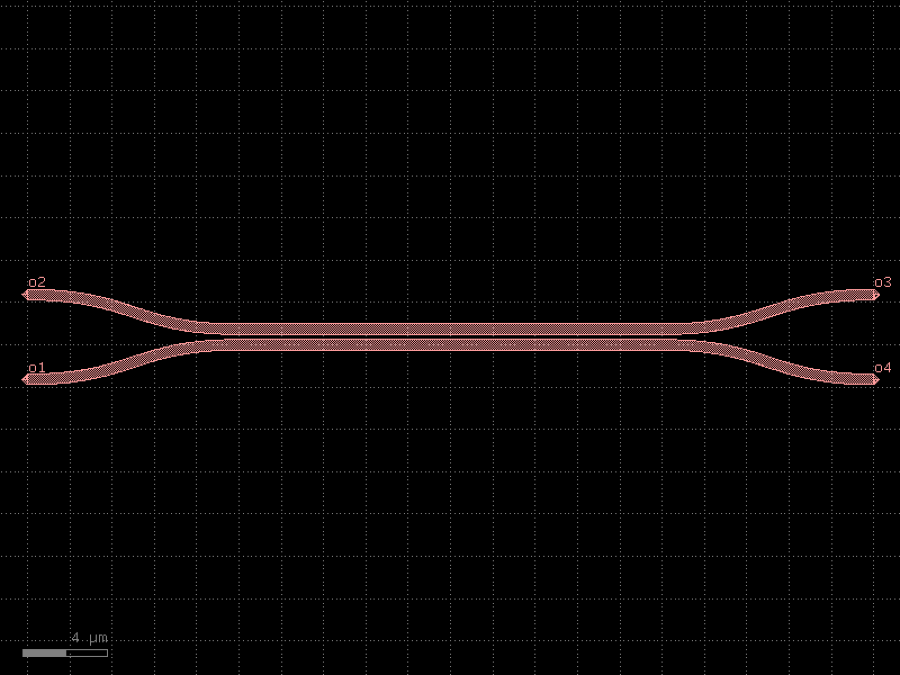
- gdsfactory.components.couplers.coupler90(gap: float = 0.2, radius: float | None = None, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_bend: CrossSectionSpec | None = None)Component
Straight coupled to a bend.
- Parameters
gap– um.radius– um.straight– for straight.bend– bend spec.cross_section– cross_section spec.cross_section_bend– optional bend cross_section spec.
o3 | / / o2_/ o1___o4
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler90(gap=0.2, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()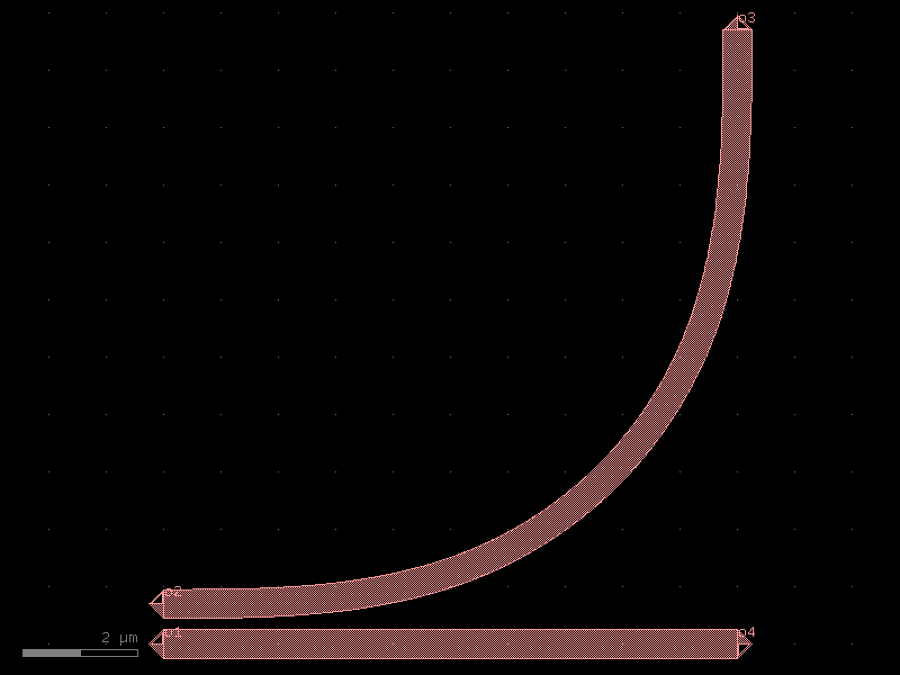
- gdsfactory.components.couplers.coupler90bend(radius: float = 10.0, gap: float = 0.2, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', cross_section_inner: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_outer: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns 2 coupled bends.
- Parameters
radius– um.gap– um.bend– for bend.cross_section_inner– spec inner bend.cross_section_outer– spec outer bend.
r 3 4 | | | | / / | / / 2____/ / 1_____/
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler90bend(radius=10, gap=0.2, bend='bend_euler', cross_section_inner='strip', cross_section_outer='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()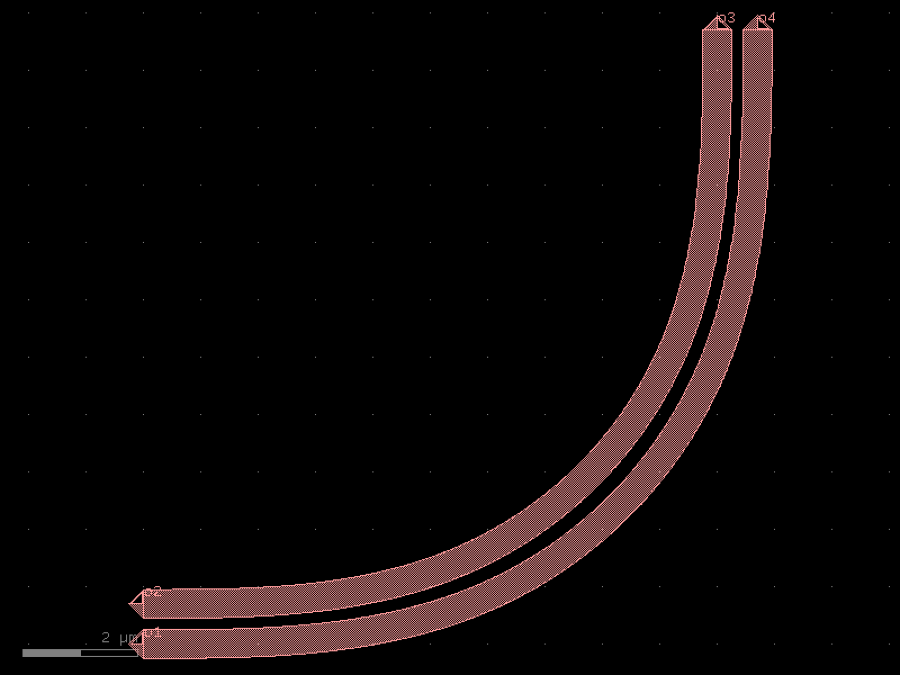
- gdsfactory.components.couplers.coupler90circular(gap: float = 0.2, radius: float | None = None, *, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_circular', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_bend: CrossSectionSpec | None = None)Component
Straight coupled to a bend.
- Parameters
gap– um.radius– um.straight– for straight.bend– bend spec.cross_section– cross_section spec.cross_section_bend– optional bend cross_section spec.
o3 | / / o2_/ o1___o4
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler90circular(gap=0.2, bend='bend_circular', straight='straight', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()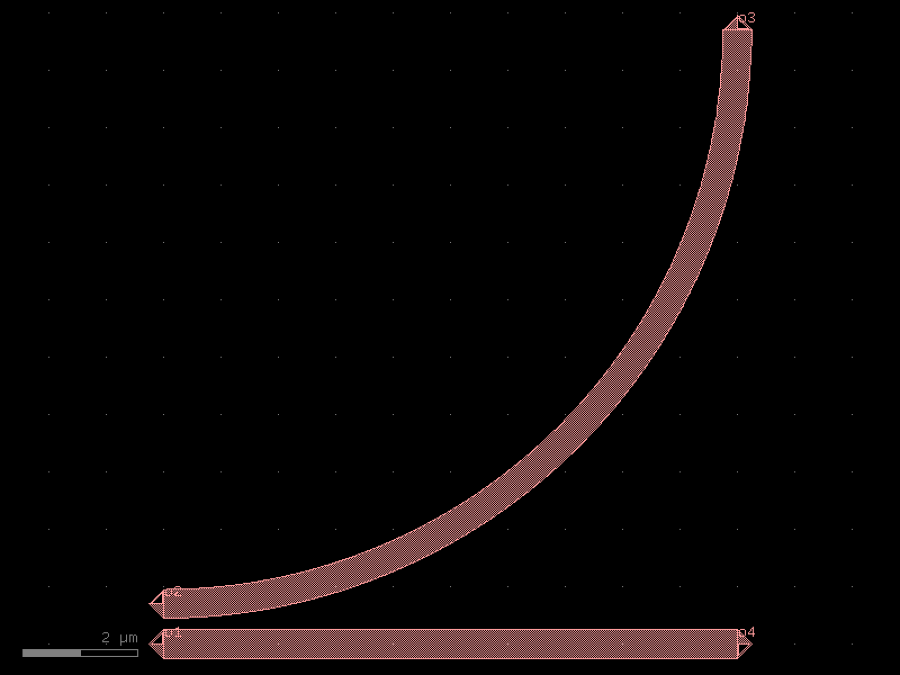
- gdsfactory.components.couplers.coupler_adiabatic(length1: float = 20.0, length2: float = 50.0, length3: float = 30.0, wg_sep: float = 1.0, input_wg_sep: float = 3.0, output_wg_sep: float = 3.0, dw: float = 0.1, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns 50/50 adiabatic coupler.
Design based on asymmetric adiabatic 3dB coupler designs, such as those. - Cao et al. (2010), - Xu et al. (2017) - Tamazin et al. (2018)
input Bezier curves, with poles set to half of the x-length of the S-bend. 1. is the first half of input S-bend where input widths taper by +dw and -dw 2. is the second half of the S-bend straight with constant, unbalanced widths 3. is the region where the two asymmetric straights gradually come together 4. straights taper back to the original width at a fixed distance from one another 5. is the output S-bend straight.
- Parameters
length1– region that gradually brings the two asymmetric straights together. In this region the straight widths gradually change to be different by dw.length2– coupling region, where asymmetric straights gradually become the same width.length3– output region where the two straights separate.wg_sep– Distance between center-to-center in the coupling region (Region 2).input_wg_sep– Separation of the two straights at the input, center-to-center.output_wg_sep– Separation of the two straights at the output, center-to-center.dw– Change in straight width. In Region 1, top arm tapers to width+dw/2.0, bottom taper to width-dw/2.0.cross_section– cross_section spec.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler_adiabatic(length1=20, length2=50, length3=30, wg_sep=1, input_wg_sep=3, output_wg_sep=3, dw=0.1, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()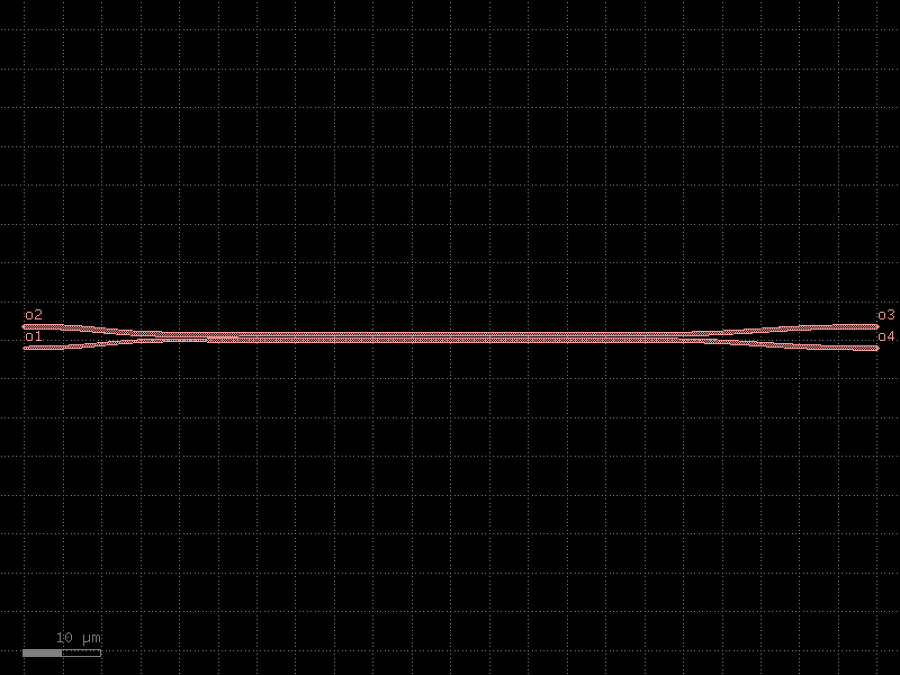
- gdsfactory.components.couplers.coupler_asymmetric(gap: float = 0.234, dy: Delta = 2.5, dx: Delta = 10.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Bend coupled to straight waveguide.
- Parameters
gap– um.dy– port to port vertical spacing.dx– bend length in x direction.cross_section– spec.
dx |-----| _____ o2 / | _____/ | gap o1____________ | dy o3
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler_asymmetric(gap=0.234, dy=2.5, dx=10, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()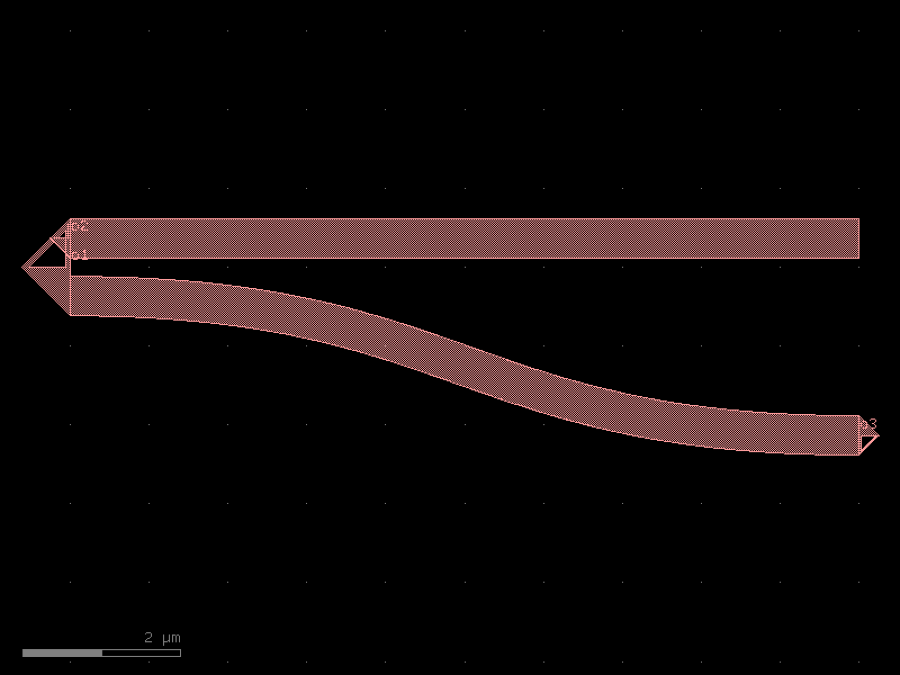
- gdsfactory.components.couplers.coupler_bent(gap: float = 0.2, radius: float = 26, length: float = 8.6, width1: float = 0.4, width2: float = 0.4, length_straight: float = 10, cross_section: str = 'strip')Component
Returns Broadband SOI curved / straight directional coupler.
based on: Chen et al. (2017).
- Parameters
gap– gap.radius– radius coupling.length– coupler_length.width1– width1.width2– width2.length_straight– input and output straight length.cross_section– cross_section.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler_bent(gap=0.2, radius=26, length=8.6, width1=0.4, width2=0.4, length_straight=10, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()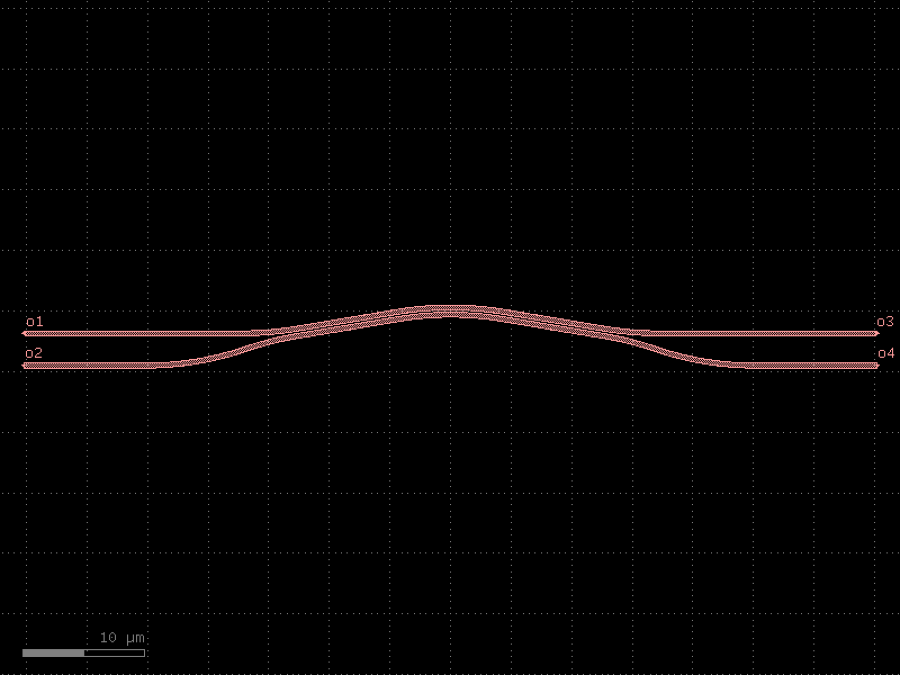
- gdsfactory.components.couplers.coupler_broadband(w_sc: float = 0.5, gap_sc: float = 0.2, w_top: float = 0.6, gap_pc: float = 0.3, legnth_taper: float = 1.0, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', coupler_straight: ComponentSpec = 'coupler_straight', length_coupler_straight: float = 12.4, lenght_coupler_big_gap: float = 4.7, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', radius: float = 10.0)Component
Returns broadband coupler component.
https://
docs .flexcompute .com /projects /tidy3d /en /latest /notebooks /BroadbandDirectionalCoupler .html proposed in Zeqin Lu, Han Yun, Yun Wang, Zhitian Chen, Fan Zhang, Nicolas A. F. Jaeger, and Lukas Chrostowski, “Broadband silicon photonic directional coupler using asymmetric-waveguide based phase control,” Opt. Express 23, 3795-3808 (2015), DOI: 10.1364/OE.23.003795. - Parameters
w_sc– width of waveguides in the symmetric coupler section.gap_sc– gap size between the waveguides in the symmetric coupler section.w_top– width of the top waveguide in the phase control section.gap_pc– gap size in the phase control section.legnth_taper– length of the tapers.bend– bend factory.coupler_straight– coupler_straight factory.length_coupler_straight– optimal L_1 from the 3d fdtd analysis.lenght_coupler_big_gap– optimal L_2 from the 3d fdtd analysis.cross_section– cross_section of the waveguides.radius– bend radius.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler_broadband(w_sc=0.5, gap_sc=0.2, w_top=0.6, gap_pc=0.3, legnth_taper=1, bend='bend_euler', coupler_straight='coupler_straight', length_coupler_straight=12.4, lenght_coupler_big_gap=4.7, cross_section='strip', radius=10).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()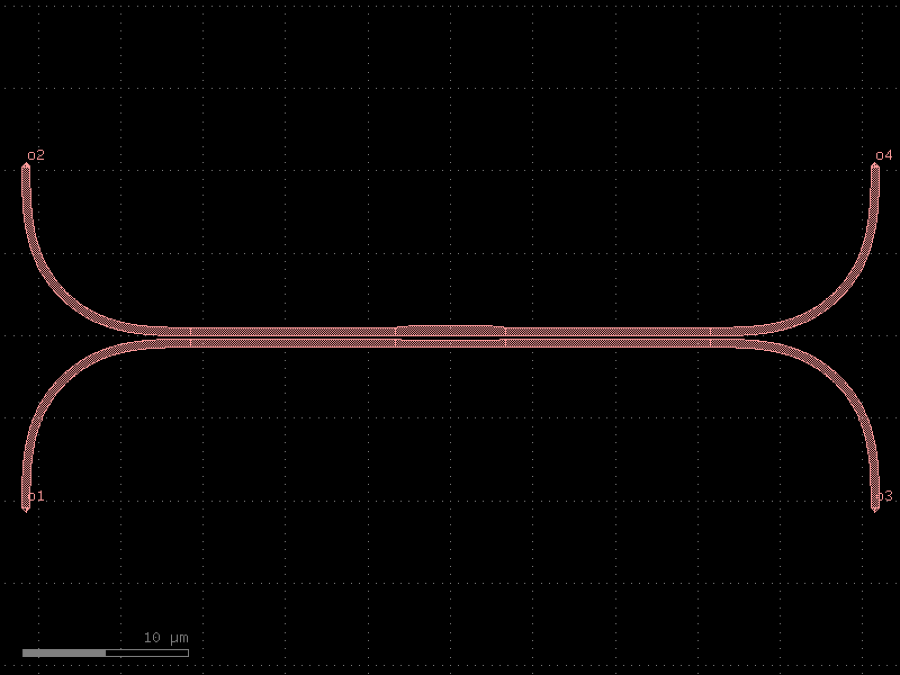
- gdsfactory.components.couplers.coupler_full(coupling_length: float = 40.0, dx: Delta = 10.0, dy: Delta = 4.8, gap: float = 0.5, dw: float = 0.1, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', width: float | None = None)Component
Adiabatic Full coupler.
Design based on asymmetric adiabatic full coupler designs, such as the one reported in ‘Integrated Optic Adiabatic Devices on Silicon’ by Y. Shani, et al (IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, Vol. 27, No. 3 March 1991).
1. is the first half of the input S-bend straight where the input straights widths taper by +dw and -dw, 2. is the second half of the S-bend straight with constant, unbalanced widths, 3. is the coupling region where the straights from unbalanced widths to balanced widths to reverse polarity unbalanced widths, 4. is the fixed width straight that curves away from the coupling region, 5.is the final curve where the straights taper back to the regular width specified in the straight template.
- Parameters
coupling_length– Length of the coupling region in um.dx– Length of the bend regions in um.dy– Port-to-port distance between the bend regions in um.gap– Distance between the two straights in um.dw– delta width. Top arm tapers to width - dw, bottom to width + dw in um.cross_section– cross-section spec.width– width of the waveguide. If None, it will use the width of the cross_section.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler_full(coupling_length=40, dx=10, dy=4.8, gap=0.5, dw=0.1, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()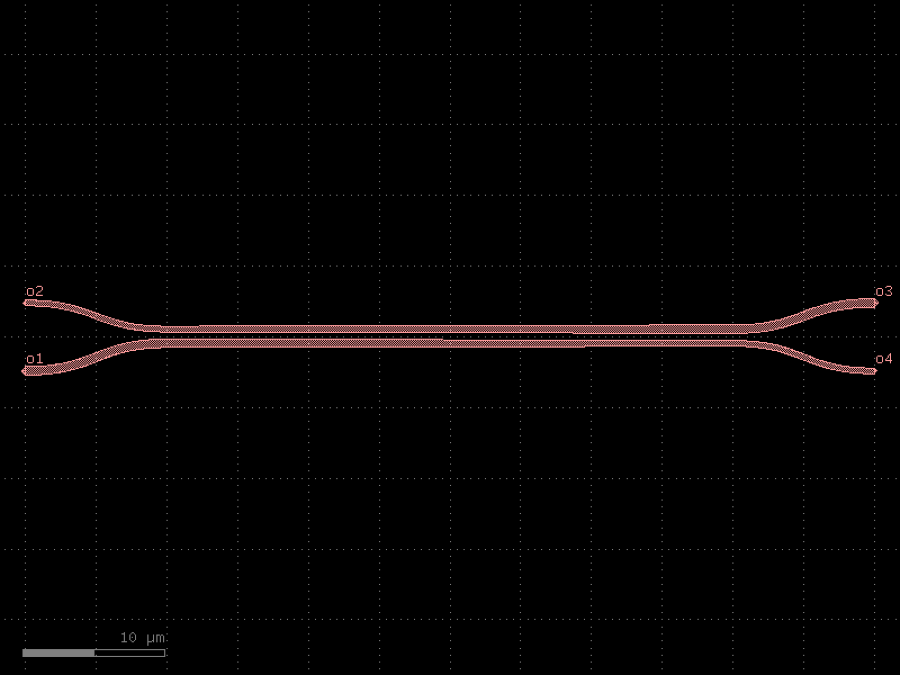
- gdsfactory.components.couplers.coupler_ring(gap: float = 0.2, radius: float = 5.0, length_x: float = 4.0, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_bend: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, length_extension: float = 3)Component
Coupler for ring.
- Parameters
gap– spacing between parallel coupled straight waveguides.radius– of the bends.length_x– length of the parallel coupled straight waveguides.bend– 90 degrees bend spec.straight– straight spec.cross_section– cross_section spec.cross_section_bend– optional bend cross_section spec.length_extension– for the ports.
o2 o3 | | \ / \ / ---=========--- o1 length_x o4
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler_ring(gap=0.2, radius=5, length_x=4, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', cross_section='strip', length_extension=3).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()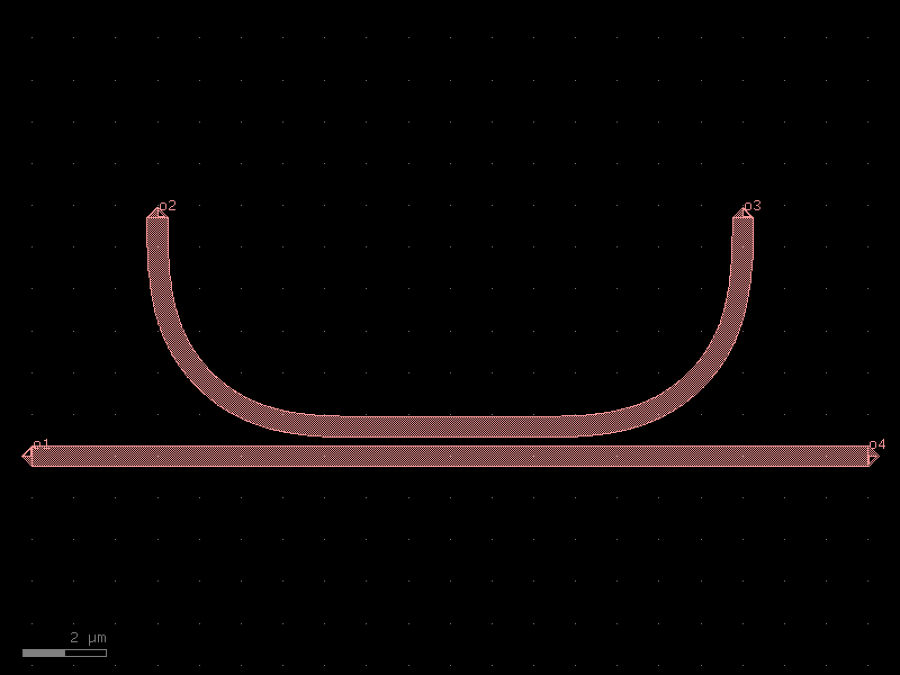
- gdsfactory.components.couplers.coupler_straight(length: float = 10.0, gap: float = 0.27, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Coupler_straight with two parallel straights.
- Parameters
length– of straight.gap– between straights.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string or dict).
o2──────▲─────────o3 │gap o1──────▼─────────o4
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler_straight(length=10, gap=0.27, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.couplers.coupler_straight_asymmetric(length: float = 10.0, gap: float = 0.27, width_top: float = 0.5, width_bot: float = 1, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Coupler with two parallel straights of different widths.
- Parameters
length– of straight.gap– between straights.width_top– of top straight.width_bot– of bottom straight.cross_section– cross_section spec.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler_straight_asymmetric(length=10, gap=0.27, width_top=0.5, width_bot=1, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.couplers.coupler_symmetric(bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_s', gap: float = 0.234, dy: Delta = 4.0, dx: Delta = 10.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Two coupled straights with bends.
- Parameters
bend– bend spec.gap– in um.dy– port to port vertical spacing.dx– bend length in x direction.cross_section– section.
dx |-----| ___ o3 / | o2 _____/ | | o1 _____ | dy \ | \___ | o4
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler_symmetric(bend='bend_s', gap=0.234, dy=4, dx=10, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()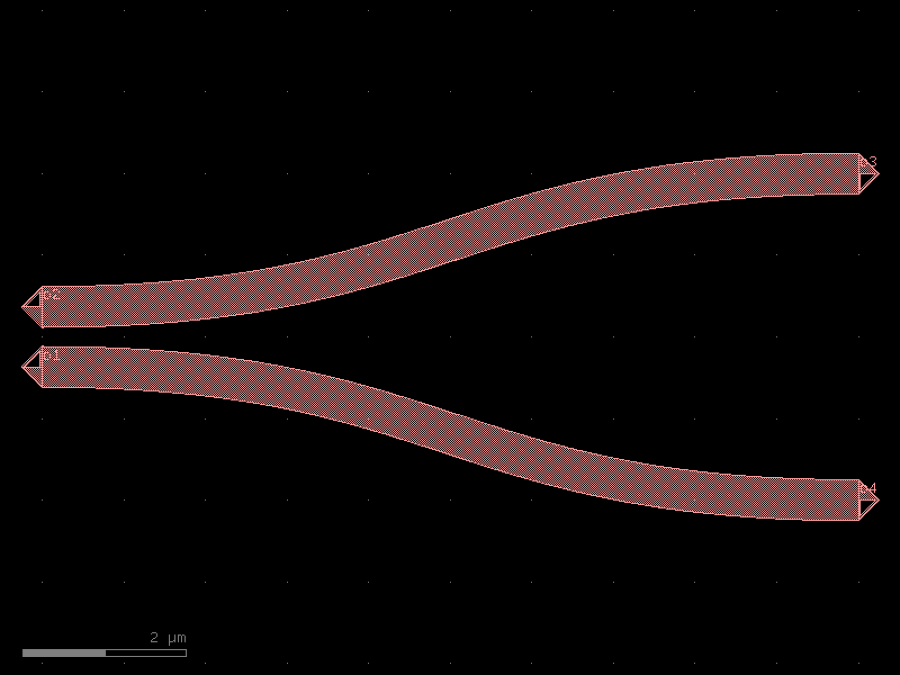
detectors¶
- gdsfactory.components.detectors.ge_detector_straight_si_contacts(length: float = 40.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'pn_ge_detector_si_contacts', via_stack: ComponentSpec = 'via_stack_slab_m3', via_stack_width: float = 10.0, via_stack_spacing: float = 5.0, via_stack_offset: float = 0.0, taper_length: float = 20.0, taper_width: float = 0.8, taper_cros_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns a straight Ge on Si detector with silicon contacts.
There are no contacts on the Ge. These detectors could have lower dark current and sensitivity compared to those with contacts in the Ge. See Chen et al., “High-Responsivity Low-Voltage 28-Gb/s Ge p-i-n Photodetector With Silicon Contacts”, Journal of Lightwave Technology 33(4), 2015.
- Parameters
length– pd length.cross_section– for the waveguide.via_stack– for the via_stacks. First elementvia_stack_width– width of the via_stack.via_stack_spacing– spacing between via_stacks.via_stack_offset– with respect to the detectortaper_length– length of the taper.taper_width– width of the taper.taper_cros_section– cross_section of the taper.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ge_detector_straight_si_contacts(length=40, cross_section='pn_ge_detector_si_contacts', via_stack='via_stack_slab_m3', via_stack_width=10, via_stack_spacing=5, via_stack_offset=0, taper_length=20, taper_width=0.8, taper_cros_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()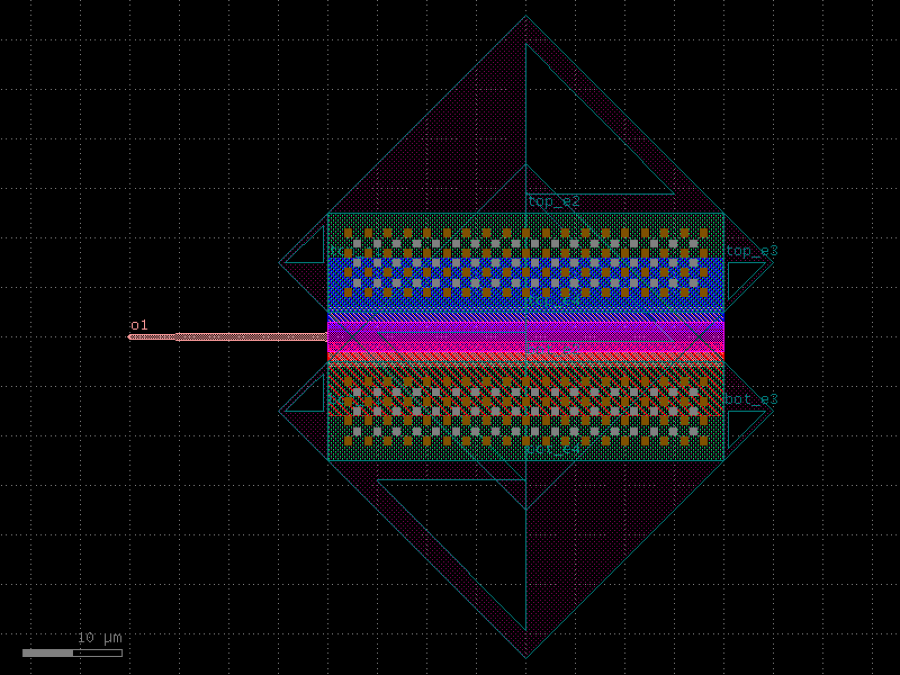
dies¶
- gdsfactory.components.dies.add_frame(component: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'rectangle', width: float = 10.0, spacing: float = 10.0, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG')Component
Returns component with a frame around it.
- Parameters
component– Component to frame.width– of the frame.spacing– of component to frame.layer– frame layer.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.add_frame(component='rectangle', width=10, spacing=10, layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()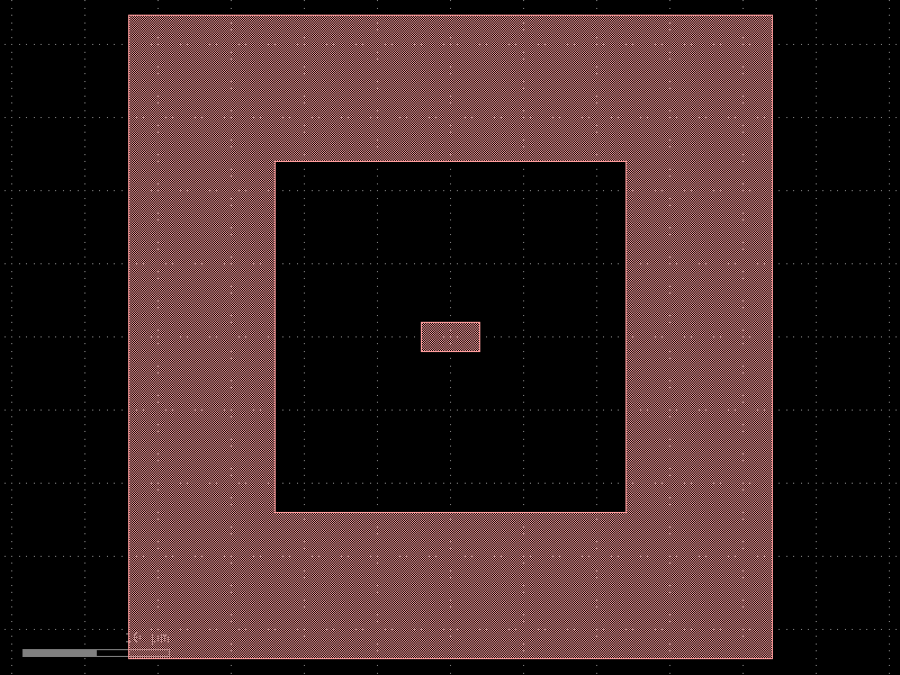
- gdsfactory.components.dies.align_wafer(width: float = 10.0, spacing: float = 10.0, cross_length: float = 80.0, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', layer_cladding: tuple[int, int] | None = None, square_corner: str = 'bottom_left')Component
Returns cross inside a frame to align wafer.
- Parameters
width– in um.spacing– in um.cross_length– for the cross.layer– for the cross.layer_cladding– optional.square_corner– bottom_left, bottom_right, top_right, top_left.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.align_wafer(width=10, spacing=10, cross_length=80, layer='WG', square_corner='bottom_left').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()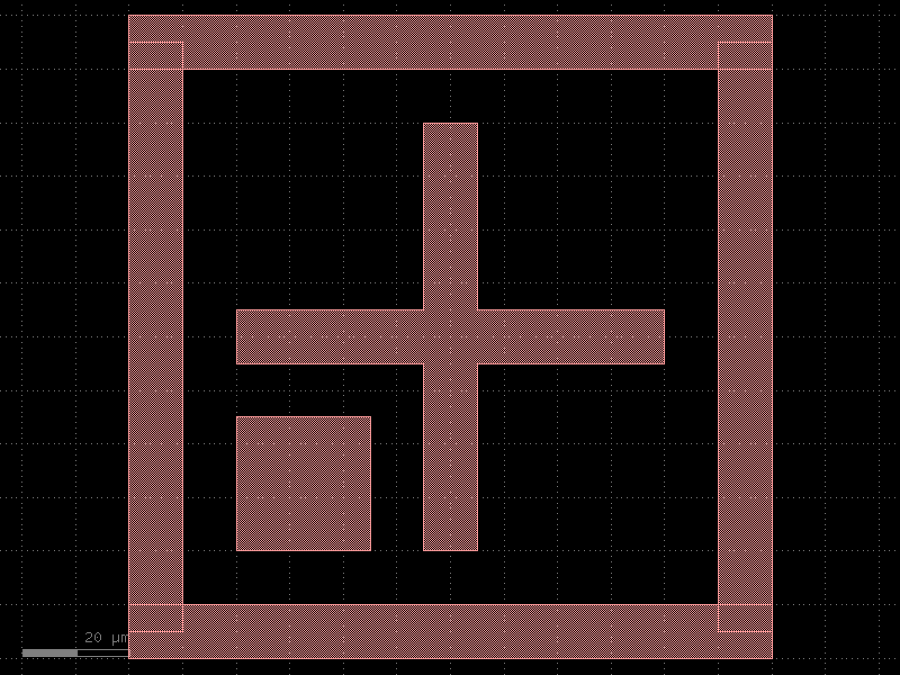
- gdsfactory.components.dies.die(size: tuple[float, float] = (10000.0, 10000.0), street_width: float = 100.0, street_length: float = 1000.0, die_name: str | None = 'chip99', text_size: float = 100.0, text_location: str | tuple[float, float] = 'SW', layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum | None = 'FLOORPLAN', bbox_layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum | None = 'FLOORPLAN', text: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'text', draw_corners: bool = False)Component
Returns die with optional markers marking the boundary of the die.
- Parameters
size– x, y dimensions of the die.street_width– Width of the corner marks for die-sawing.street_length– Length of the corner marks for die-sawing.die_name– Label text. If None, no label is added.text_size– Label text size.text_location– {‘NW’, ‘N’, ‘NE’, ‘SW’, ‘S’, ‘SE’} or (x, y) coordinate.layer– For street widths. None to not draw the street widths.bbox_layer– optional bbox layer drawn bounding box around the die.text– function use for generating text. Needs to accept text, size, layer.draw_corners– True draws only corners. False draws a square die.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.die(size=(10000, 10000), street_width=100, street_length=1000, die_name='chip99', text_size=100, text_location='SW', layer='FLOORPLAN', bbox_layer='FLOORPLAN', text='text', draw_corners=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()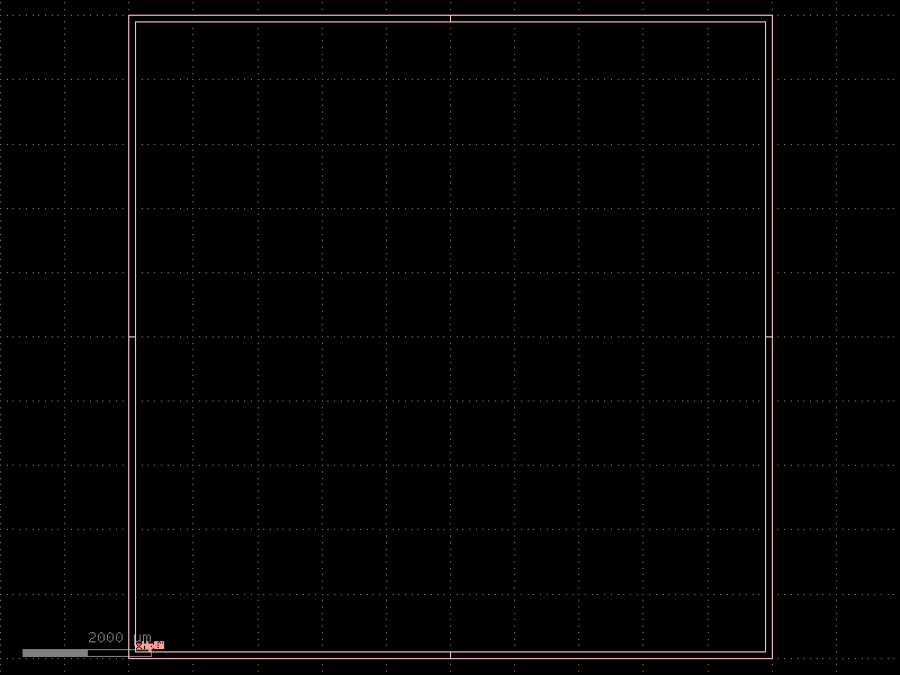
- gdsfactory.components.dies.die_with_pads(size: tuple[float, float] = (11470.0, 4900.0), ngratings: int = 14, npads: int = 31, grating_pitch: float = 250.0, pad_pitch: float = 300.0, grating_coupler: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'grating_coupler_te', cross_section: CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection = 'strip', pad: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'pad', layer_floorplan: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'FLOORPLAN', edge_to_pad_distance: float = 150.0, edge_to_grating_distance: float = 150.0, with_loopback: bool = True, loopback_radius: float | None = None)Component
A die with grating couplers and pads.
- Parameters
size– the size of the die, in um.ngratings– the number of grating couplers.npads– the number of pads.grating_pitch– the pitch of the grating couplers, in um.pad_pitch– the pitch of the pads, in um.grating_coupler– the grating coupler component.cross_section– the cross section.pad– the pad component.layer_floorplan– the layer of the floorplan.edge_to_pad_distance– the distance from the edge to the pads, in um.edge_to_grating_distance– the distance from the edge to the grating couplers, in um.with_loopback– if True, adds a loopback between edge GCs. Only works for rotation = 90 for now.loopback_radius– optional radius for loopback.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.die_with_pads(size=(11470, 4900), ngratings=14, npads=31, grating_pitch=250, pad_pitch=300, grating_coupler='grating_coupler_te', cross_section='strip', pad='pad', layer_floorplan='FLOORPLAN', edge_to_pad_distance=150, edge_to_grating_distance=150, with_loopback=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()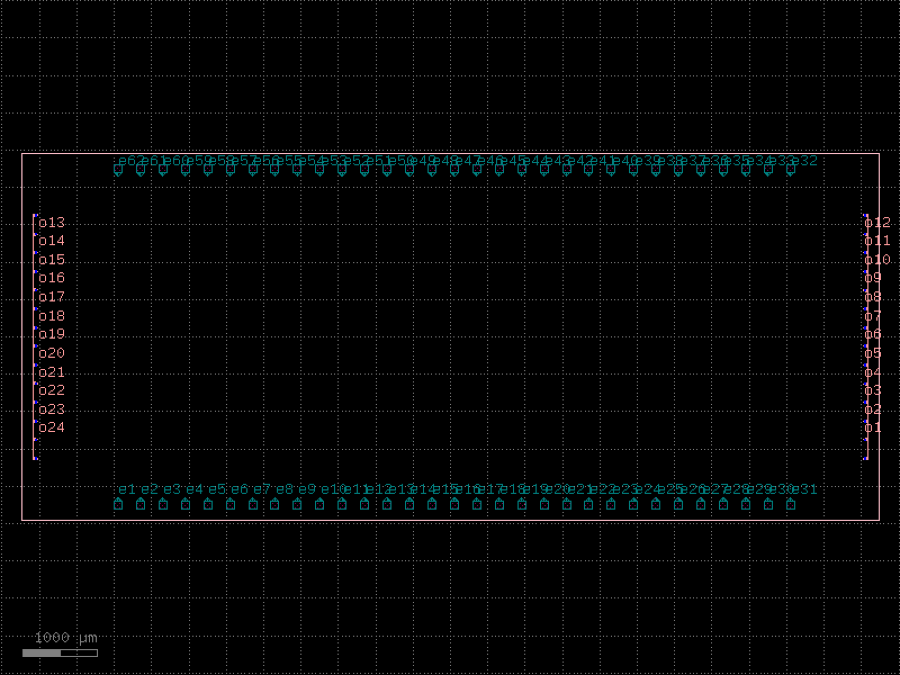
- gdsfactory.components.dies.seal_ring(size: tuple[float, float] = (500, 500), seal: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'via_stack', width: float = 10, padding: float = 10.0, with_north: bool = True, with_south: bool = True, with_east: bool = True, with_west: bool = True)Component
Returns a continuous seal ring boundary at the chip/die.
Prevents cracks from spreading and shields when connected to ground.
- Parameters
size– of the seal.seal– function for the seal.width– of the seal.padding– from component to seal.with_north– includes seal.with_south– includes seal.with_east– includes seal.with_west– includes seal.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.seal_ring(size=(500, 500), seal='via_stack', width=10, padding=10, with_north=True, with_south=True, with_east=True, with_west=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()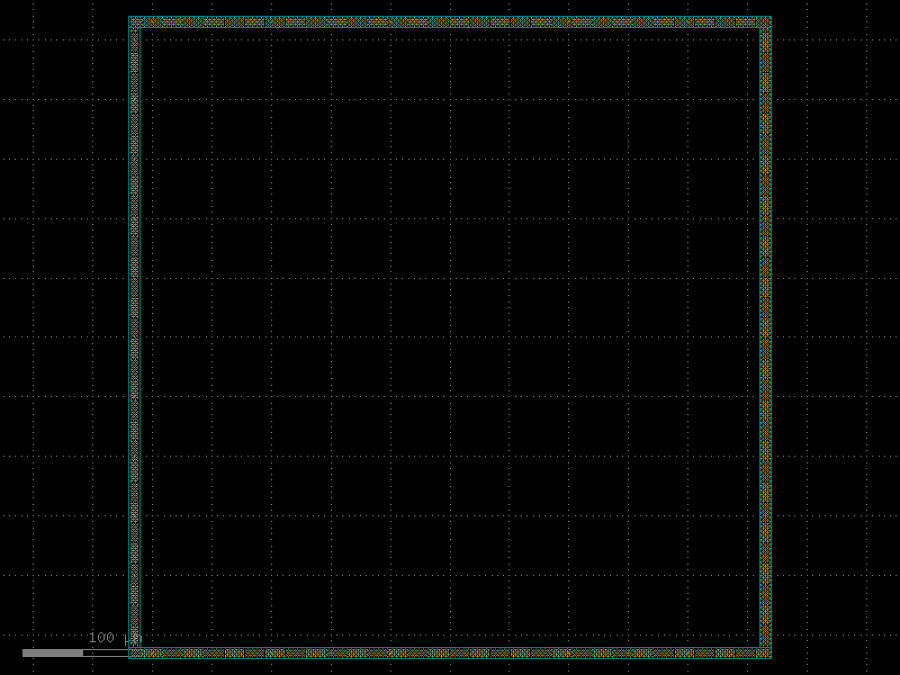
- gdsfactory.components.dies.seal_ring_segmented(size: tuple[float, float] = (500, 500), length_segment: float = 10, width_segment: float = 3, spacing_segment: float = 2, corner: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'via_stack_corner45_extended', via_stack: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'via_stack_m1_mtop', with_north: bool = True, with_south: bool = True, with_east: bool = True, with_west: bool = True)Component
Segmented Seal ring.
- Parameters
size– of the seal ring.length_segment– length of each segment.width_segment– width of each segment.spacing_segment– spacing between segments.corner– corner component.via_stack– via_stack component.with_north– includes seal.with_south– includes seal.with_east– includes seal.with_west– includes seal.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.seal_ring_segmented(size=(500, 500), length_segment=10, width_segment=3, spacing_segment=2, corner='via_stack_corner45_extended', via_stack='via_stack_m1_mtop', with_north=True, with_south=True, with_east=True, with_west=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.dies.wafer(reticle: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'die', cols: tuple[int, ...] = (2, 6, 6, 8, 8, 6, 6, 2), xspacing: float | None = None, yspacing: float | None = None, die_name_col_row: bool = False)Component
Returns complete wafer. Useful for mask aligner steps.
- Parameters
reticle– spec for each wafer reticle.cols– how many columns per row.xspacing– optional spacing, defaults to reticle.xsize.yspacing– optional spacing, defaults to reticle.ysize.die_name_col_row– if True, die name is row_col, otherwise is a number
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.wafer(reticle='die', cols=(2, 6, 6, 8, 8, 6, 6, 2), die_name_col_row=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()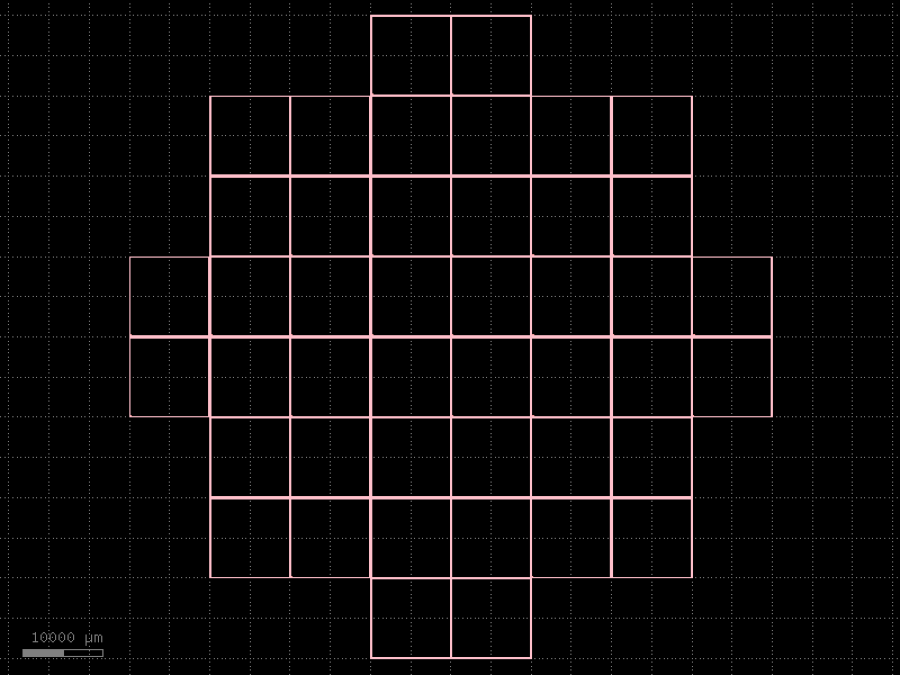
edge_couplers¶
- gdsfactory.components.edge_couplers.edge_coupler_array(edge_coupler: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'edge_coupler_silicon', n: int = 5, pitch: float = 127.0, x_reflection: bool = False, text: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | None = 'text_rectangular', text_offset: tuple[float, float] = (10, 20), text_rotation: float = 0)Component
Fiber array edge coupler based on an inverse taper.
Each edge coupler adds a ruler for polishing.
- Parameters
edge_coupler– edge coupler spec.n– number of channels.pitch– Fiber pitch.x_reflection– horizontal mirror.text– text spec.text_offset– from edge coupler.text_rotation– text rotation in degrees.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.edge_coupler_array(edge_coupler='edge_coupler_silicon', n=5, pitch=127, x_reflection=False, text='text_rectangular', text_offset=(10, 20), text_rotation=0).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()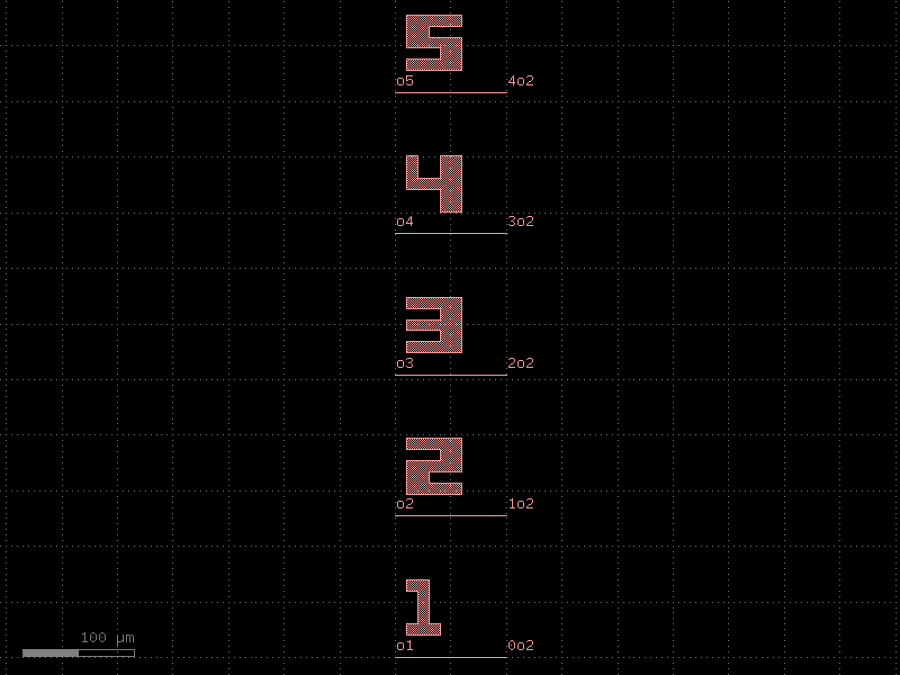
- gdsfactory.components.edge_couplers.edge_coupler_array_with_loopback(edge_coupler: ComponentSpec = 'edge_coupler_silicon', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', radius: float = 30, n: int = 8, pitch: float = 127.0, extension_length: float = 1.0, x_reflection: bool = False, text: ComponentSpec | None = 'text_rectangular', text_offset: Float2 = (0, 10), text_rotation: float = 0)Component
Fiber array edge coupler.
- Parameters
edge_coupler– edge coupler.cross_section– spec.radius– bend radius loopback (um).n– number of channels.pitch– Fiber pitch (um).extension_length– in um.x_reflection– horizontal mirror.text– Optional text spec.text_offset– x, y.text_rotation– text rotation in degrees.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.edge_coupler_array_with_loopback(edge_coupler='edge_coupler_silicon', cross_section='strip', radius=30, n=8, pitch=127, extension_length=1, x_reflection=False, text='text_rectangular', text_offset=(0, 10), text_rotation=0).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()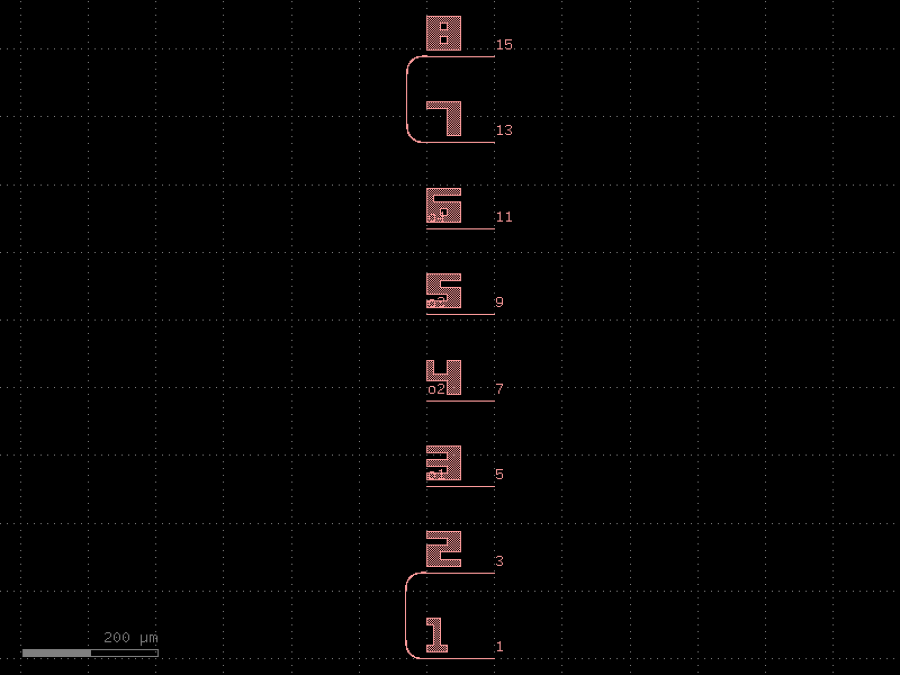
- gdsfactory.components.edge_couplers.edge_coupler_silicon(length: float = 100, width1: float = 0.5, width2: float = 0.2, with_two_ports: bool = True, port_names: tuple[str, str] = ('o1', 'o2'), port_types: tuple[str, str] = ('optical', 'edge_coupler'), cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Edge coupler for silicon photonics.
- Parameters
length– length of the taper.width1– width1 of the taper.width2– width2 of the taper.with_two_ports– add two ports.port_names– tuple with port names.port_types– tuple with port types.cross_section– cross_section spec.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.edge_coupler_silicon(length=100, width1=0.5, width2=0.2, with_two_ports=True, port_names=('o1', 'o2'), port_types=('optical', 'edge_coupler'), cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()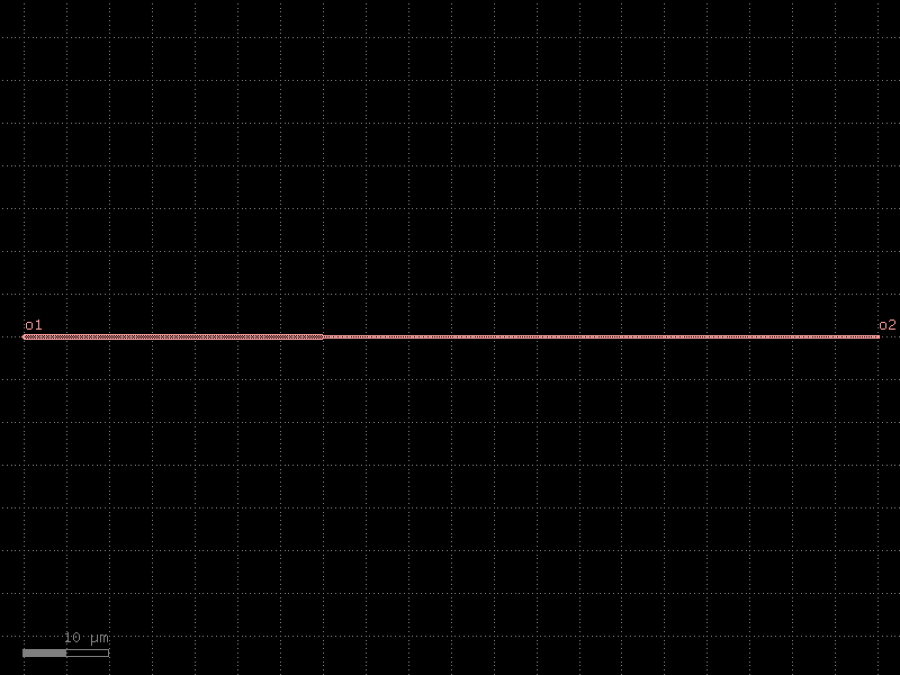
filters¶
- gdsfactory.components.filters.awg(arms: int = 10, outputs: int = 3, free_propagation_region_input_function: ComponentSpec = functools.partial(<function free_propagation_region>, inputs=1), free_propagation_region_output_function: ComponentSpec = functools.partial(<function free_propagation_region>, inputs=10, width1=10, width2=20.0), fpr_spacing: float = 50.0, arm_spacing: float = 1.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns a basic Arrayed Waveguide grating.
To simulate you can use https://
github .com /dnrobin /awg -python - Parameters
arms– number of arms.outputs– number of outputs.free_propagation_region_input_function– for input.free_propagation_region_output_function– for output.fpr_spacing– x separation between input/output free propagation region.arm_spacing– y separation between arms.cross_section– cross_section function.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.awg(arms=10, outputs=3, fpr_spacing=50, arm_spacing=1, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()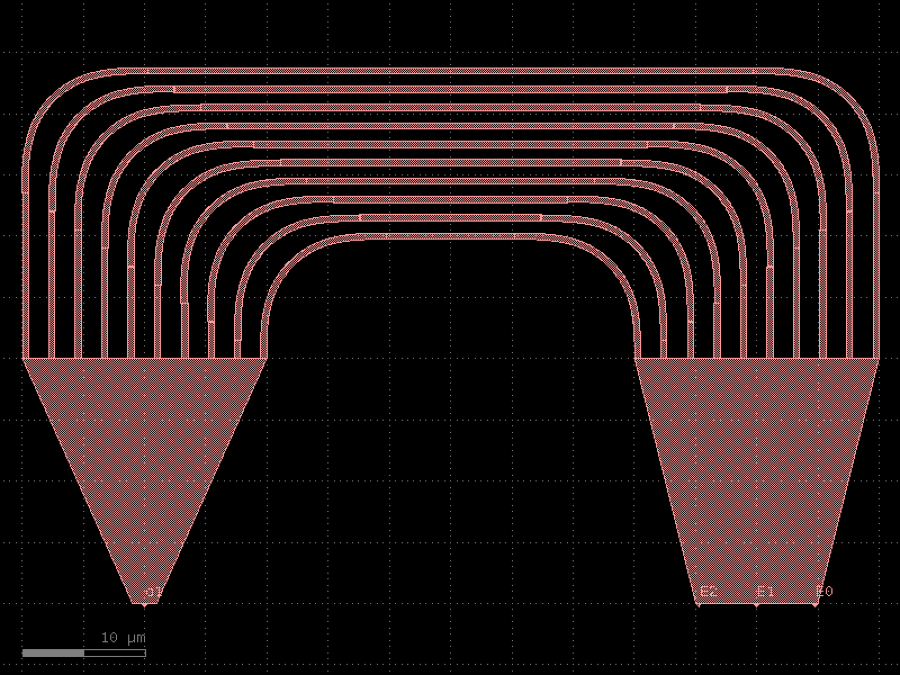
- gdsfactory.components.filters.dbr(w1: float = 0.45, w2: float = 0.55, l1: float = 0.159, l2: float = 0.159, n: int = 10, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', straight_length: float = 0.01)Component
Distributed Bragg Reflector.
- Parameters
w1– thin width in um.w2– thick width in um.l1– thin length in um.l2– thick length in um.n– number of periods.cross_section– cross_section spec.straight_length– length of the straight section between cutbacks.
l1 l2 <-----><--------> _________ _______| w1 w2 ... n times _______ |_________
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.dbr(w1=0.45, w2=0.55, l1=0.159, l2=0.159, n=10, cross_section='strip', straight_length=0.01).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()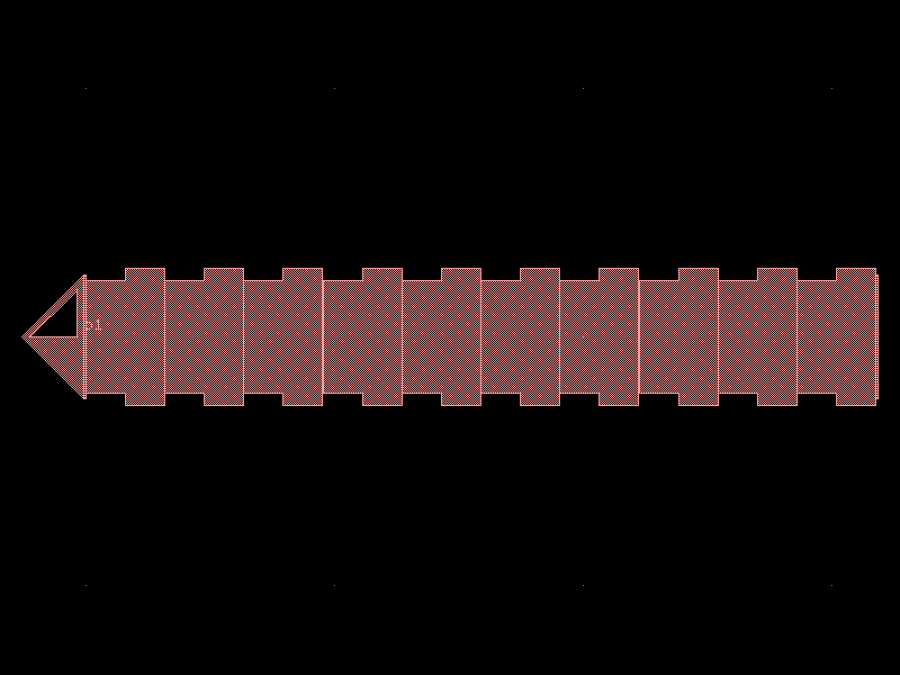
- gdsfactory.components.filters.dbr_cell(w1: float = 0.45, w2: float = 0.55, l1: float = 0.159, l2: float = 0.159, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Distributed Bragg Reflector unit cell.
- Parameters
w1– thin width in um.l1– thin length in um.w2– thick width in um.l2– thick length in um.n– number of periods.cross_section– cross_section spec.
l1 l2 <-----><--------> _________ _______| w1 w2 _______ |_________
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.dbr_cell(w1=0.45, w2=0.55, l1=0.159, l2=0.159, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()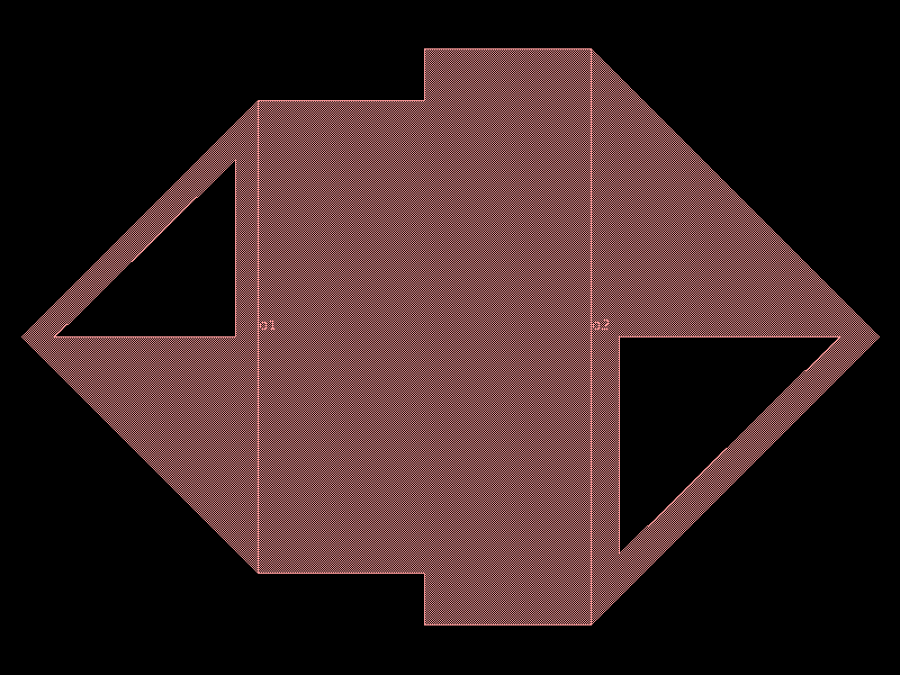
- gdsfactory.components.filters.dbr_tapered(length: float = 10.0, period: float = 0.85, dc: float = 0.5, w1: float = 0.4, w2: float = 1.0, taper_length: float = 20.0, fins: bool = False, fin_size: Size = (0.2, 0.05), cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Distributed Bragg Reflector Cell class.
Tapers the input straight to a periodic straight structure with varying width (1-D photonic crystal).
- Parameters
length– Length of the DBR region.period– Period of the repeated unit.dc– Duty cycle of the repeated unit (must be a float between 0 and 1.0).w1– thin section width. w1 = 0 corresponds to disconnected periodic blocks.w2– wide section width.taper_length– between the input/output straight and the DBR region.fins– If True, adds fins to the input/output straights.fin_size– Specifies the x- and y-size of the fins. Defaults to 200 nm x 50 nmcross_section– cross_section spec.
period <-----><--------> _________ _______| w1 w2 ... n times _______ |_________
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.dbr_tapered(length=10, period=0.85, dc=0.5, w1=0.4, w2=1, taper_length=20, fins=False, fin_size=(0.2, 0.05), cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.filters.fiber(core_diameter: float = 10, cladding_diameter: float = 125, layer_core: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', layer_cladding: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WGCLAD')Component
Returns a fiber.
- Parameters
core_diameter– in um.cladding_diameter– in um.layer_core– layer spec for fiber core.layer_cladding– layer spec for fiber cladding.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.fiber(core_diameter=10, cladding_diameter=125, layer_core='WG', layer_cladding='WGCLAD').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.filters.fiber_array(n: int = 8, pitch: float = 127.0, core_diameter: float = 10, cladding_diameter: float = 125, layer_core: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', layer_cladding: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WGCLAD')Component
Returns a fiber array.
- Parameters
n– number of fibers.pitch– spacing.core_diameter– 10um.cladding_diameter– in um.layer_core– layer spec for fiber core.layer_cladding– layer spec for fiber cladding.
pitch <-> _________ | | lid | o o o o | | | base |_________| length
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.fiber_array(n=8, pitch=127, core_diameter=10, cladding_diameter=125, layer_core='WG', layer_cladding='WGCLAD').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()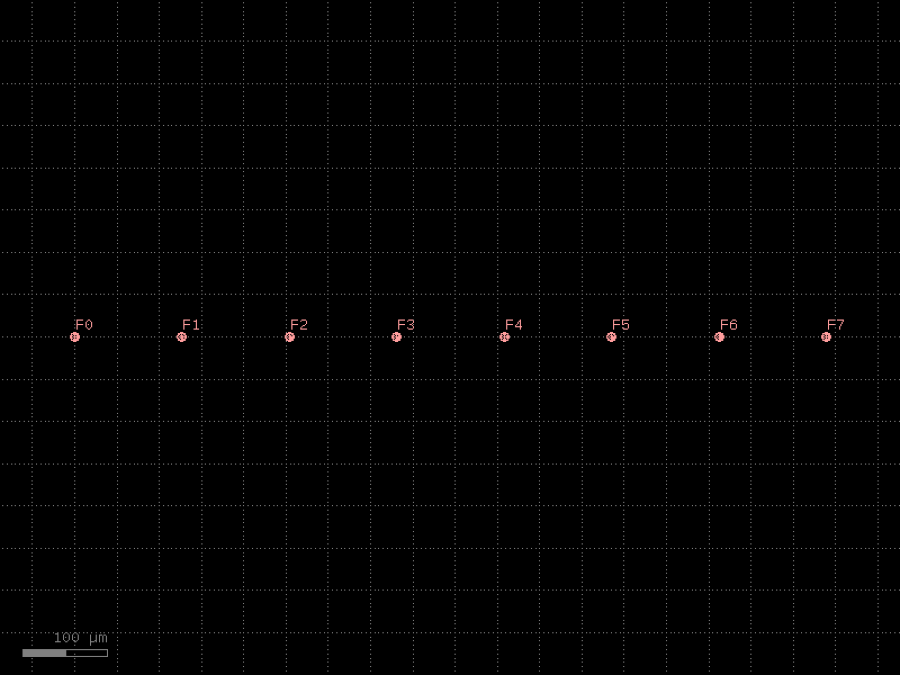
- gdsfactory.components.filters.free_propagation_region(width1: float = 2.0, width2: float = 20.0, length: float = 20.0, wg_width: float = 0.5, inputs: int = 1, outputs: int = 10, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Free propagation region.
- Parameters
width1– width of the input region.width2– width of the output region.length– length of the free propagation region.wg_width– waveguide width.inputs– number of inputs.outputs– number of outputs.cross_section– cross_section function.
length <--> /| / | width1| | width2 \ | \|
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.free_propagation_region(width1=2, width2=20, length=20, wg_width=0.5, inputs=1, outputs=10, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()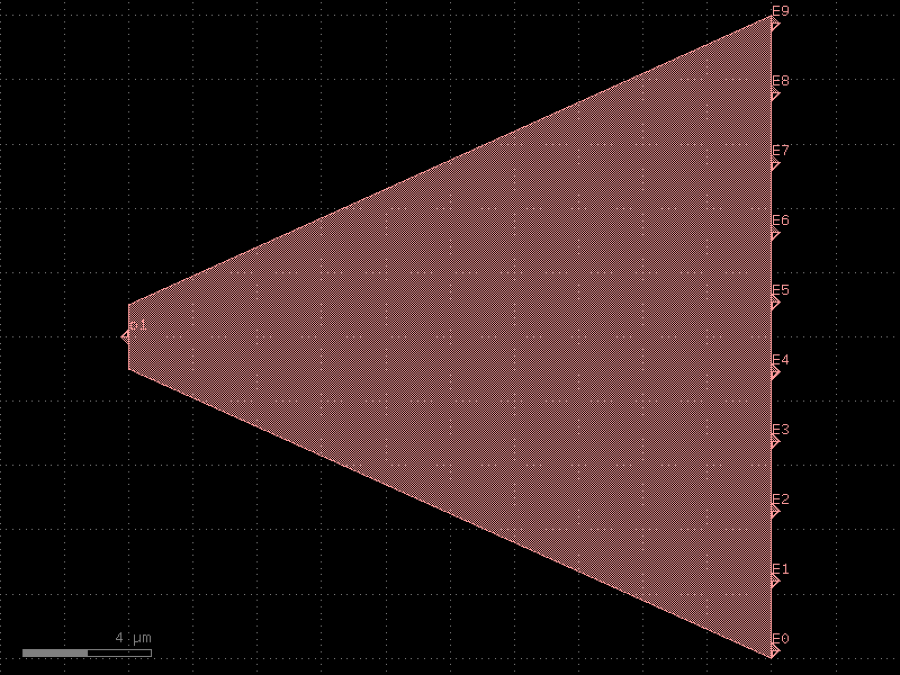
- gdsfactory.components.filters.loop_mirror(component: ComponentSpec = 'mmi1x2', bend90: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns Sagnac loop_mirror.
- Parameters
component– 1x2 splitter.bend90– 90 deg bend.cross_section– cross_section settings.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.loop_mirror(component='mmi1x2', bend90='bend_euler', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()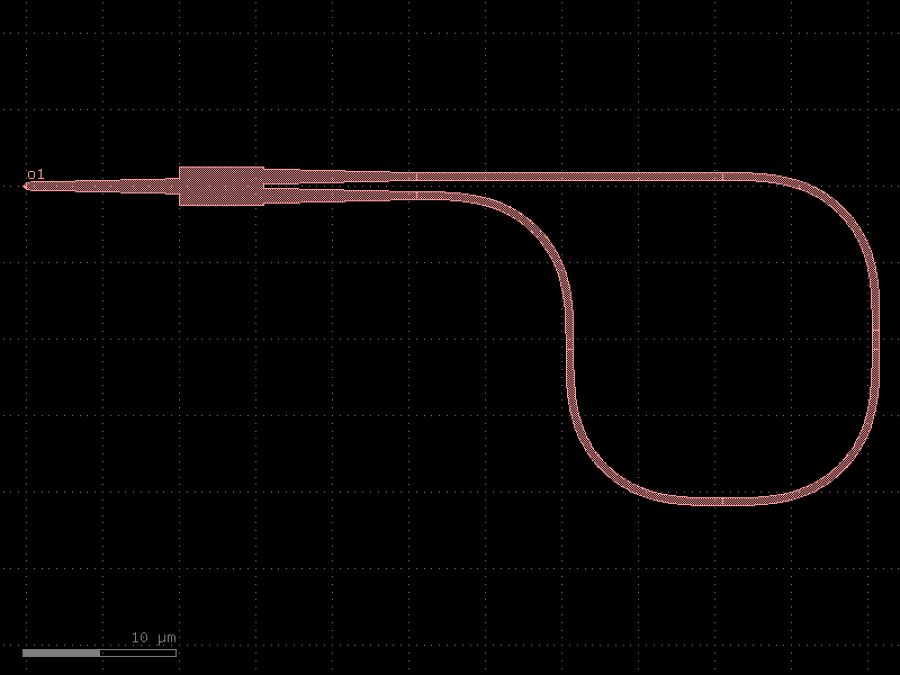
- gdsfactory.components.filters.mode_converter(gap: float = 0.3, length: float = 10, coupler_straight_asymmetric: ComponentSpec = 'coupler_straight_asymmetric', bend: ComponentSpec = functools.partial(<function bend_s>, size=(25, 3)), taper: ComponentSpec = 'taper', mm_width: float = 1.2, mc_mm_width: float = 1, sm_width: float = 0.5, taper_length: float = 25, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns Mode converter from TE0 to TE1.
By matching the effective indices of two waveguides with different widths, light can couple from different transverse modes e.g. TE0 <-> TE1. Shu et al. (2019)
- Parameters
gap– directional coupler gap.length– coupler length interaction.coupler_straight_asymmetric– spec.bend– spec.taper– spec.mm_width– input/output multimode waveguide width.mc_mm_width– mode converter multimode waveguide widthsm_width– single mode waveguide width.taper_length– taper length.cross_section– cross_section spec.
o2 --- --- o4 \ / \ / ------- o1 -----=======----- o3 |-----| length = : multimode width - : singlemode width
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mode_converter(gap=0.3, length=10, coupler_straight_asymmetric='coupler_straight_asymmetric', taper='taper', mm_width=1.2, mc_mm_width=1, sm_width=0.5, taper_length=25, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()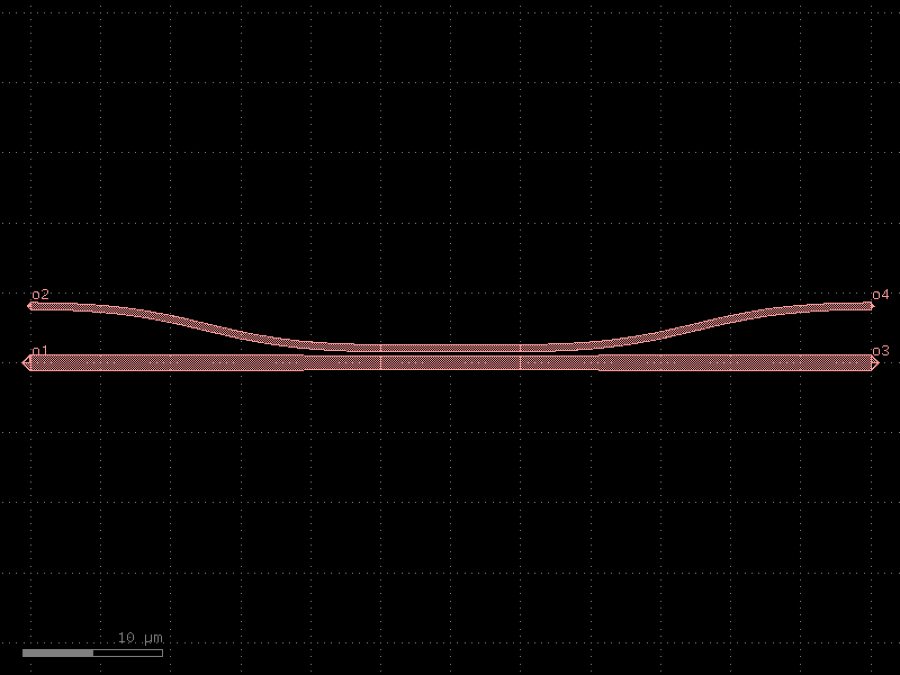
- gdsfactory.components.filters.polarization_splitter_rotator(width_taper_in: Float3 = (0.54, 0.69, 0.83), length_taper_in: Float2 | Float3 = (4.0, 44.0), width_coupler: Float2 = (0.9, 0.404), length_coupler: float = 7.0, gap: float = 0.15, width_out: float = 0.54, length_out: float = 14.33, dy: Delta = 5.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns polarization splitter rotator.
“Novel concept for ultracompact polarization splitter-rotator based on silicon nanowires.” By D. Dai, and J. E. Bowers (Optics express vol 19, no. 11 pp. 10940-10949 (2011)).
- Parameters
width_taper_in– Three west widths of the input tapers in um.length_taper_in– Two or three length of the bend regions in um.width_coupler– Top and bottom widths of the coupling region in um.length_coupler– Length of the coupling region in um.gap– Distance between the coupler in um.width_out– Width of the splitter region in um.length_out– Length of the splitter region in um.dy– Port-to-port distance between the splitter region in um.cross_section– cross-section spec.
Notes
The length of third input taper is automatically determined if only two lengths are in arguments.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.polarization_splitter_rotator(width_taper_in=(0.54, 0.69, 0.83), length_taper_in=(4, 44), width_coupler=(0.9, 0.404), length_coupler=7, gap=0.15, width_out=0.54, length_out=14.33, dy=5, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()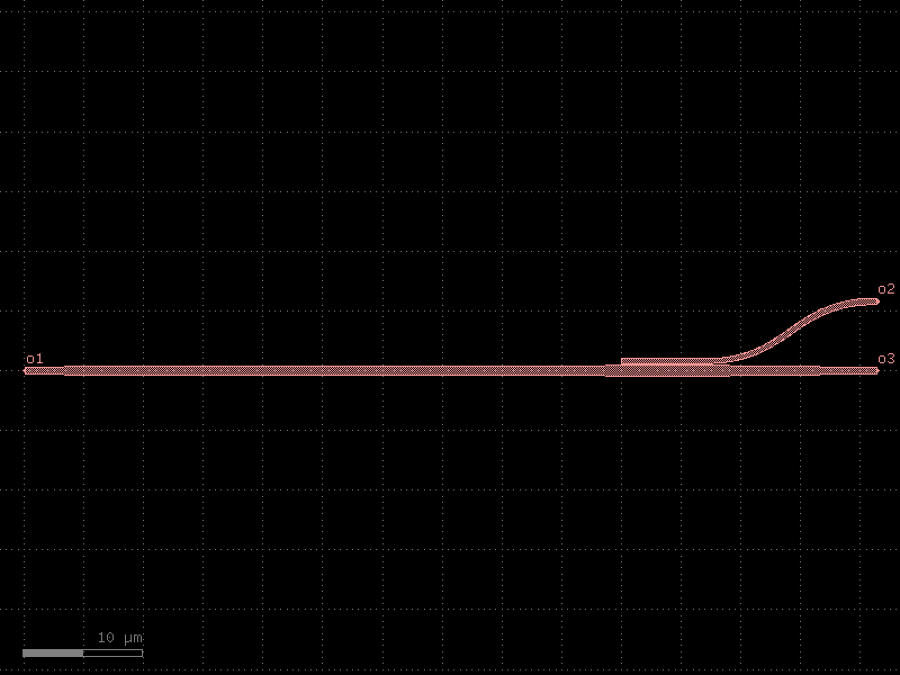
- gdsfactory.components.filters.terminator(length: float | None = 50, cross_section_input: CrossSectionSpec = <function strip>, cross_section_tip: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, tapered_width: float = 0.2, doping_layers: LayerSpecs = ('NPP', ), doping_offset: float = 1.0)gf.Component
Returns doped taper to terminate waveguides.
- Parameters
length– distance between input and narrow tapered end.cross_section_input– input cross-section.cross_section_tip– cross-section at the end of the termination.tapered_width– width of the default cross-section at the end of the termination. Only used if cross_section_tip is not None.doping_layers– doping layers to superimpose on the taper. Default N++.doping_offset– offset of the doping layer beyond the bbox
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.terminator(length=50, tapered_width=0.2, doping_layers=('NPP',), doping_offset=1).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()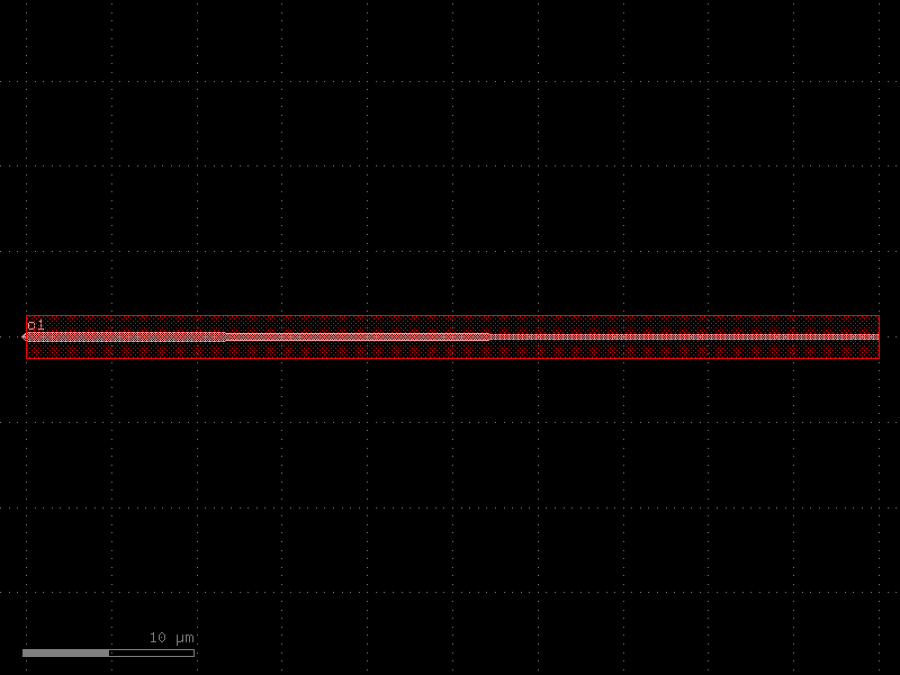
- gdsfactory.components.filters.terminator_spiral(separation: float = 3.0, width_tip: float = 0.2, number_of_loops: float = 1, npoints: int = 1000, min_bend_radius: float | None = None, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')gf.Component
Returns doped taper to terminate waveguides.
- Parameters
separation– separation between the loops.width_tip– width of the default cross-section at the end of the termination. Only used if cross_section_tip is not None.number_of_loops– number of loops in the spiral.npoints– points for the spiral.min_bend_radius– minimum bend radius for the spiral.cross_section– input cross-section.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.terminator_spiral(separation=3, width_tip=0.2, number_of_loops=1, npoints=1000, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()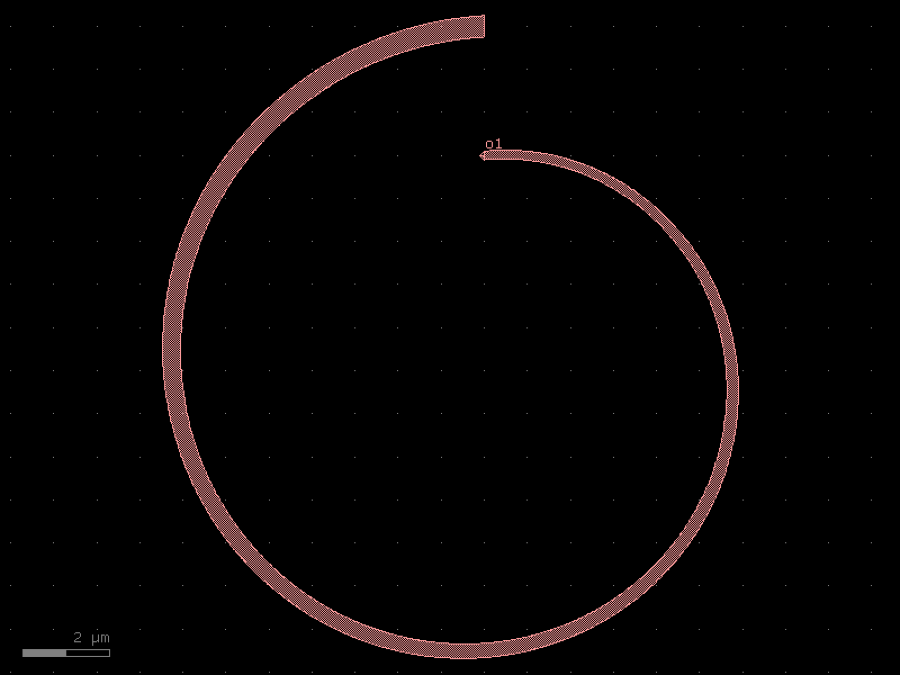
grating_couplers¶
- gdsfactory.components.grating_couplers.grating_coupler_array(grating_coupler: ComponentSpec = 'grating_coupler_elliptical', pitch: float = 127.0, n: int = 6, port_name: str = 'o1', rotation: int = -90, with_loopback: bool = False, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', straight_to_grating_spacing: float = 10.0, centered: bool = True, radius: float | None = None)Component
Array of grating couplers.
- Parameters
grating_coupler– ComponentSpec.pitch– x spacing.n– number of grating couplers.port_name– port name.rotation– rotation angle for each reference.with_loopback– if True, adds a loopback between edge GCs. Only works for rotation = 90 for now.cross_section– cross_section for the routing.straight_to_grating_spacing– spacing between the last grating coupler and the loopback.centered– if True, centers the array around the origin.radius– optional radius for routing the loopback.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.grating_coupler_array(grating_coupler='grating_coupler_elliptical', pitch=127, n=6, port_name='o1', rotation=-90, with_loopback=False, cross_section='strip', straight_to_grating_spacing=10, centered=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()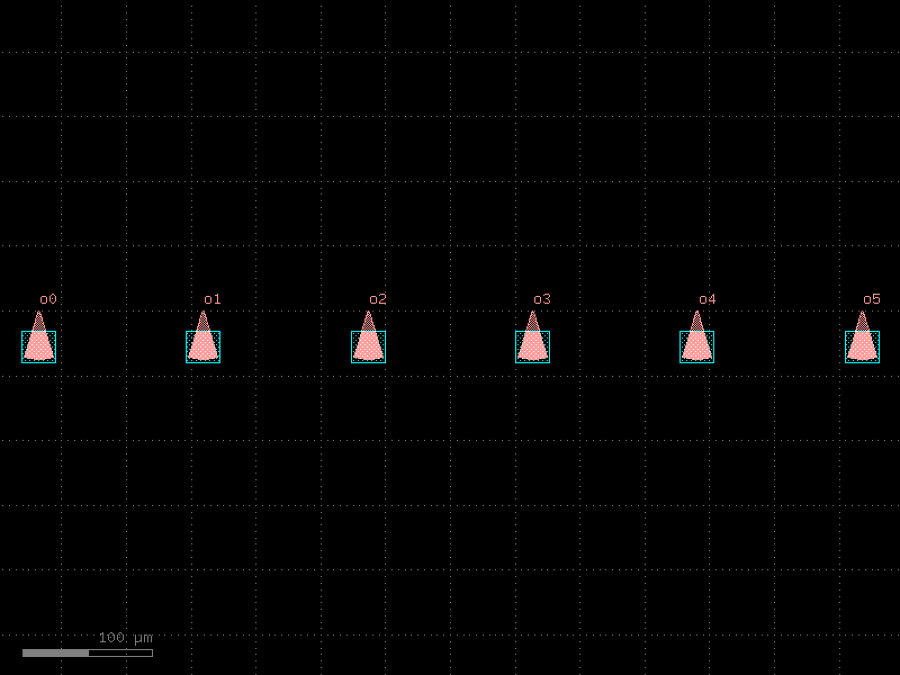
- gdsfactory.components.grating_couplers.grating_coupler_dual_pol(unit_cell: ComponentSpec = <function _unit_cell>, period_x: float = 0.58, period_y: float = 0.58, x_span: float = 11, y_span: float = 11, length_taper: float = 150.0, width_taper: float = 10.0, polarization: str = 'te', wavelength: float = 1.55, taper: ComponentSpec = 'taper', base_layer: LayerSpec = 'WG', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
2 dimensional, dual polarization grating coupler.
Based on a photonic crystal with a unit cell that is usually an ellipse, a rectangle or a circle. # The default values are loosely based on Taillaert et al, # “A Compact Two-Dimensional Grating Coupler Used as a Polarization Splitter”, IEEE Phot. Techn. Lett. 15(9), 2003
- Parameters
unit_cell– component describing the unit cell of the photonic crystal.period_x– spacing between unit cells in the x direction [um].period_y– spacing between unit cells in the y direction [um].x_span– full x span of the photonic crystal.y_span– full y span of the photonic crystal.length_taper– taper length [um].width_taper– width of the taper at the grating coupler side [um].polarization– polarization of the grating coupler.wavelength– operation wavelength [um]taper– function to generate the tapers.base_layer– layer to draw over the whole photonic crystal � (necessary if the unit cells are etched into a base layer).cross_section– for the routing waveguides.
side view fiber / / / / / / / / _|-|_|-|_|-|___ --> unit_cells base_layer | o1 ______________| top view ------------- // | o o o | o1 __ // | o o o | \\ | o o o | \\ | o o o | ------------- \\ // \\ // | o2
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.grating_coupler_dual_pol(period_x=0.58, period_y=0.58, x_span=11, y_span=11, length_taper=150, width_taper=10, polarization='te', wavelength=1.55, taper='taper', base_layer='WG', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()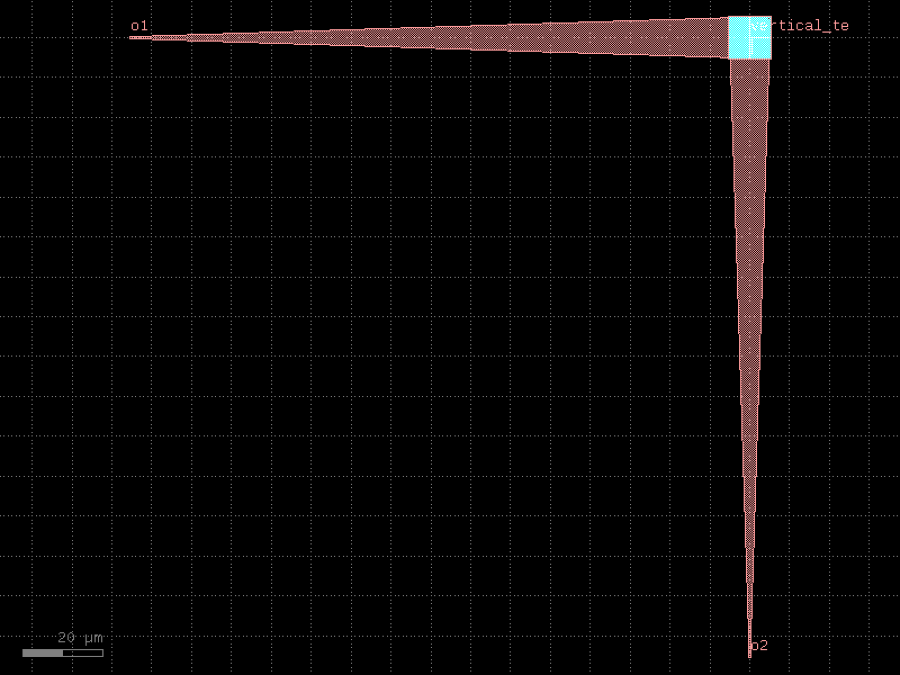
- gdsfactory.components.grating_couplers.grating_coupler_elliptical(polarization: str = 'te', taper_length: float = 16.6, taper_angle: float = 40.0, wavelength: float = 1.554, fiber_angle: float = 15.0, grating_line_width: float = 0.343, neff: float = 2.638, nclad: float = 1.443, n_periods: int = 30, big_last_tooth: bool = False, layer_slab: LayerSpec | None = 'SLAB150', slab_xmin: float = -1.0, slab_offset: float = 2.0, spiked: bool = True, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Grating coupler with parametrization based on Lumerical FDTD simulation.
- Parameters
polarization– te or tm.taper_length– taper length from input.taper_angle– grating flare angle.wavelength– grating transmission central wavelength (um).fiber_angle– fibre angle in degrees determines ellipticity.grating_line_width– in um.neff– tooth effective index.nclad– cladding effective index.n_periods– number of periods.big_last_tooth– adds a big_last_tooth.layer_slab– layer that protects the slab under the grating.slab_xmin– where 0 is at the start of the taper.slab_offset– in um.spiked– grating teeth have sharp spikes to avoid non-manhattan drc errors.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string or dict).
fiber / / / / / / / / _|-|_|-|_|-|___ layer layer_slab | o1 ______________|
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.grating_coupler_elliptical(polarization='te', taper_length=16.6, taper_angle=40, wavelength=1.554, fiber_angle=15, grating_line_width=0.343, neff=2.638, nclad=1.443, n_periods=30, big_last_tooth=False, layer_slab='SLAB150', slab_xmin=-1, slab_offset=2, spiked=True, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()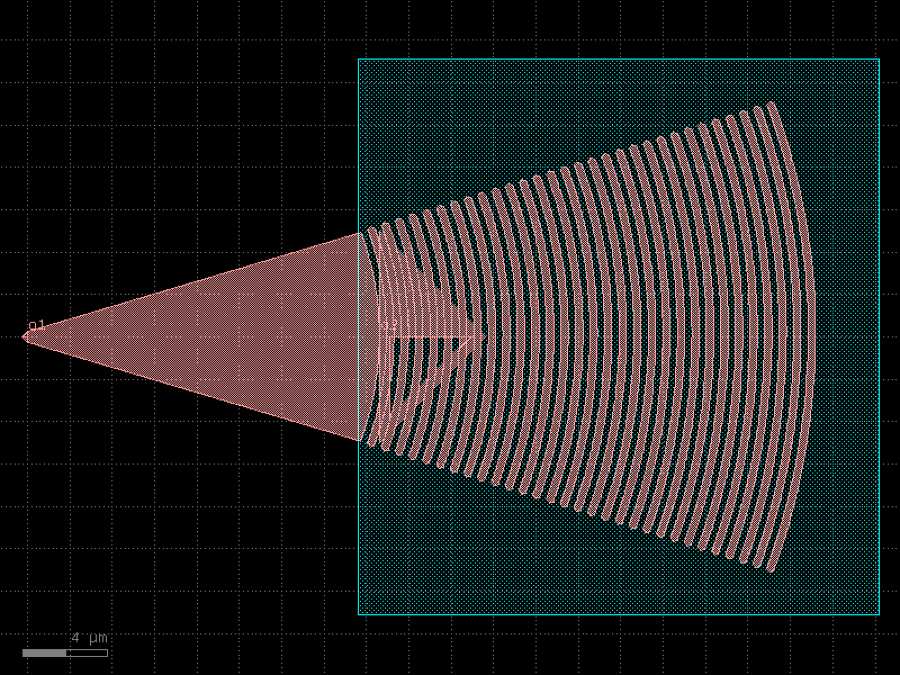
- gdsfactory.components.grating_couplers.grating_coupler_elliptical_arbitrary(gaps: Floats = (0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1), widths: Floats = (0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5), taper_length: float = 16.6, taper_angle: float = 60.0, wavelength: float = 1.554, fiber_angle: float = 15.0, nclad: float = 1.443, layer_slab: LayerSpec | None = 'SLAB150', layer_grating: LayerSpec | None = None, taper_to_slab_offset: float = -3.0, polarization: str = 'te', spiked: bool = True, bias_gap: float = 0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Grating coupler with parametrization based on Lumerical FDTD simulation.
The ellipticity is derived from Lumerical knowledge base it depends on fiber_angle (degrees), neff, and nclad
- Parameters
gaps– list of gaps.widths– list of widths.taper_length– taper length from input.taper_angle– grating flare angle.wavelength– grating transmission central wavelength (um).fiber_angle– fibre angle in degrees determines ellipticity.nclad– cladding effective index to compute ellipticity.layer_slab– Optional slab.layer_grating– Optional layer for grating. by default None uses cross_section.layer. if different from cross_section.layer expands taper.taper_to_slab_offset– 0 is where taper ends.polarization– te or tm.spiked– grating teeth have spikes to avoid drc errors.bias_gap– etch gap (um). Positive bias increases gap and reduces width to keep period constant.cross_section– cross_section spec for waveguide port.
Ellipse c = (a1 ** 2 - b1 ** 2) ** 0.5 e = (1 - (b1 / a1) ** 2) ** 0.5 print(e)
fiber / / / / / / / / _|-|_|-|_|-|___ layer layer_slab | o1 ______________|
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.grating_coupler_elliptical_arbitrary(gaps=(0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1), widths=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5), taper_length=16.6, taper_angle=60, wavelength=1.554, fiber_angle=15, nclad=1.443, layer_slab='SLAB150', taper_to_slab_offset=-3, polarization='te', spiked=True, bias_gap=0, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()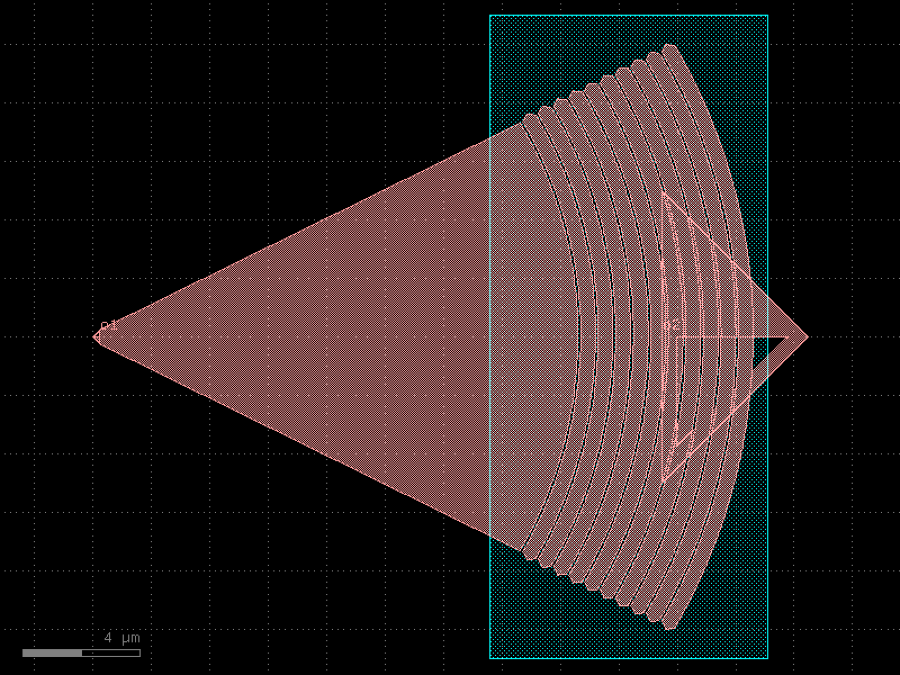
- gdsfactory.components.grating_couplers.grating_coupler_elliptical_lumerical(parameters: Floats = (-2.4298362615732447, 0.1, 0.48007023217536954, 0.1, 0.607397685752365, 0.1, 0.4498844003086115, 0.1, 0.4274116312627637, 0.1, 0.4757904248387285, 0.1, 0.5026649898504233, 0.10002922416240886, 0.5100366774007897, 0.1, 0.494399635363353, 0.1079599958465788, 0.47400592737426483, 0.14972685326277918, 0.43272750134545823, 0.1839530796530385, 0.3872023336708212, 0.2360175325711591, 0.36032212454768675, 0.24261846353500535, 0.35770350120764394, 0.2606637836858316, 0.3526104381544335, 0.24668202254540886, 0.3717488388788273, 0.22920754299702897, 0.37769616507688464, 0.2246528336925301, 0.3765437598650894, 0.22041773376471022, 0.38047596041838994, 0.21923601658169187, 0.3798873698864591, 0.21700438236445285, 0.38291698672245644, 0.21827768053295463, 0.3641322152037017, 0.23729077006065105, 0.3676834419346081, 0.24865079519725933, 0.34415050295044936, 0.2733570818755685, 0.3306230780901629, 0.27350446437732157), layer_slab: LayerSpec | None = 'SLAB150', taper_angle: float = 55, taper_length: float = 12.6, fiber_angle: float = 5, info: dict[str, Any] | None = None, bias_gap: float = 0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns a grating coupler from lumerical inverse design 3D optimization.
this is a wrapper of components.grating_coupler_elliptical_arbitrary https://
support .lumerical .com /hc /en -us /articles /1500000306621 https:// support .lumerical .com /hc /en -us /articles /360042800573 Here are the simulation settings used in lumerical
n_bg=1.44401 #Refractive index of the background material (cladding) wg=3.47668 # Refractive index of the waveguide material (core) lambda0=1550e-9 bandwidth = 0e-9 polarization = ‘TE’ wg_width=500e-9 # Waveguide width wg_height=220e-9 # Waveguide height etch_depth=80e-9 # etch depth theta_fib_mat = 5 # Angle of the fiber mode in material theta_taper=30 efficiency=0.55 # 5.2 dB
- Parameters
parameters– xinput, gap1, width1, gap2, width2 …layer– for waveguide.layer_slab– for slab.taper_angle– in deg.taper_length– in um.fiber_angle– used to compute ellipticity.info– optional simulation settings.bias_gap– gap/trenches bias (um) to compensate for etching bias.
- Keyword Arguments
taper_length– taper length from input in um.taper_angle– grating flare angle in degrees.wavelength– grating transmission central wavelength (um).fiber_angle– fibre angle in degrees determines ellipticity.neff– tooth effective index.nclad– cladding effective index.polarization– te or tm.spiked– grating teeth include sharp spikes to avoid non-manhattan drc errors.cross_section– cross_section spec for waveguide port.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.grating_coupler_elliptical_lumerical(parameters=(-2.43, 0.1, 0.48, 0.1, 0.607, 0.1, 0.45, 0.1, 0.427, 0.1, 0.476, 0.1, 0.503, 0.1, 0.51, 0.1, 0.494, 0.108, 0.474, 0.15, 0.433, 0.184, 0.387, 0.236, 0.36, 0.243, 0.358, 0.261, 0.353, 0.247, 0.372, 0.229, 0.378, 0.225, 0.377, 0.22, 0.38, 0.219, 0.38, 0.217, 0.383, 0.218, 0.364, 0.237, 0.368, 0.249, 0.344, 0.273, 0.331, 0.274), layer_slab='SLAB150', taper_angle=55, taper_length=12.6, fiber_angle=5, bias_gap=0, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()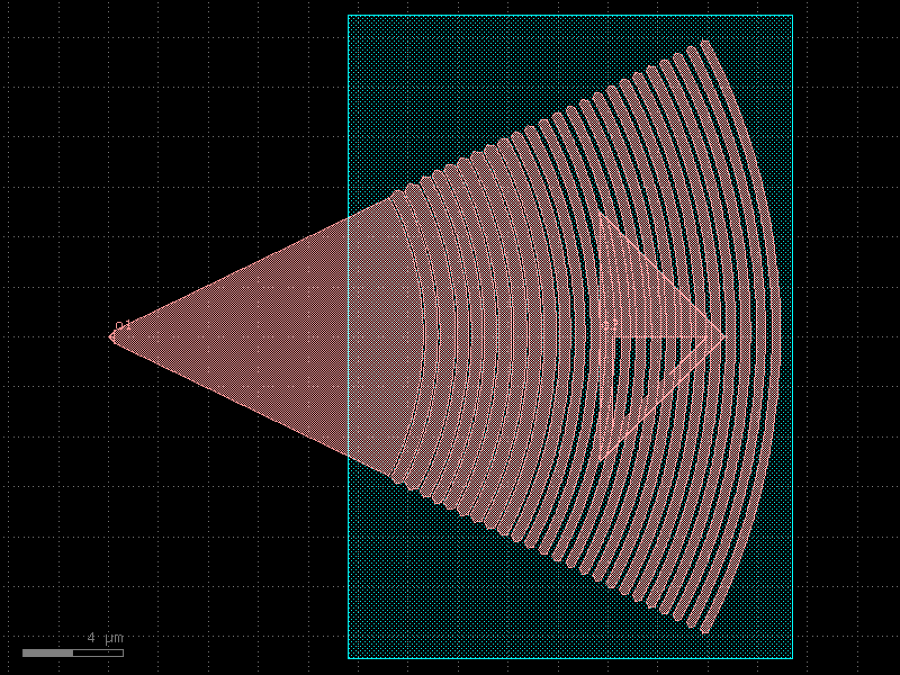
- gdsfactory.components.grating_couplers.grating_coupler_elliptical_lumerical_etch70(parameters: Floats = (-2.4298362615732447, 0.1, 0.48007023217536954, 0.1, 0.607397685752365, 0.1, 0.4498844003086115, 0.1, 0.4274116312627637, 0.1, 0.4757904248387285, 0.1, 0.5026649898504233, 0.10002922416240886, 0.5100366774007897, 0.1, 0.494399635363353, 0.1079599958465788, 0.47400592737426483, 0.14972685326277918, 0.43272750134545823, 0.1839530796530385, 0.3872023336708212, 0.2360175325711591, 0.36032212454768675, 0.24261846353500535, 0.35770350120764394, 0.2606637836858316, 0.3526104381544335, 0.24668202254540886, 0.3717488388788273, 0.22920754299702897, 0.37769616507688464, 0.2246528336925301, 0.3765437598650894, 0.22041773376471022, 0.38047596041838994, 0.21923601658169187, 0.3798873698864591, 0.21700438236445285, 0.38291698672245644, 0.21827768053295463, 0.3641322152037017, 0.23729077006065105, 0.3676834419346081, 0.24865079519725933, 0.34415050295044936, 0.2733570818755685, 0.3306230780901629, 0.27350446437732157), layer_slab: LayerSpec | None = 'SLAB150', taper_angle: float = 55, taper_length: float = 12.6, fiber_angle: float = 5, *, info: dict[str, Any] | None = {'efficiency': 0.55, 'etch_depth': 0.08, 'fiber_angle': 5, 'gap_min': 0.1, 'link': 'https://support.lumerical.com/hc/en-us/articles/1500000306621', 'width_min': 0.1}, bias_gap: float = 0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns a grating coupler from lumerical inverse design 3D optimization.
this is a wrapper of components.grating_coupler_elliptical_arbitrary https://
support .lumerical .com /hc /en -us /articles /1500000306621 https:// support .lumerical .com /hc /en -us /articles /360042800573 Here are the simulation settings used in lumerical
n_bg=1.44401 #Refractive index of the background material (cladding) wg=3.47668 # Refractive index of the waveguide material (core) lambda0=1550e-9 bandwidth = 0e-9 polarization = ‘TE’ wg_width=500e-9 # Waveguide width wg_height=220e-9 # Waveguide height etch_depth=80e-9 # etch depth theta_fib_mat = 5 # Angle of the fiber mode in material theta_taper=30 efficiency=0.55 # 5.2 dB
- Parameters
parameters– xinput, gap1, width1, gap2, width2 …layer– for waveguide.layer_slab– for slab.taper_angle– in deg.taper_length– in um.fiber_angle– used to compute ellipticity.info– optional simulation settings.bias_gap– gap/trenches bias (um) to compensate for etching bias.
- Keyword Arguments
taper_length– taper length from input in um.taper_angle– grating flare angle in degrees.wavelength– grating transmission central wavelength (um).fiber_angle– fibre angle in degrees determines ellipticity.neff– tooth effective index.nclad– cladding effective index.polarization– te or tm.spiked– grating teeth include sharp spikes to avoid non-manhattan drc errors.cross_section– cross_section spec for waveguide port.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.grating_coupler_elliptical_lumerical_etch70(parameters=(-2.43, 0.1, 0.48, 0.1, 0.607, 0.1, 0.45, 0.1, 0.427, 0.1, 0.476, 0.1, 0.503, 0.1, 0.51, 0.1, 0.494, 0.108, 0.474, 0.15, 0.433, 0.184, 0.387, 0.236, 0.36, 0.243, 0.358, 0.261, 0.353, 0.247, 0.372, 0.229, 0.378, 0.225, 0.377, 0.22, 0.38, 0.219, 0.38, 0.217, 0.383, 0.218, 0.364, 0.237, 0.368, 0.249, 0.344, 0.273, 0.331, 0.274), layer_slab='SLAB150', taper_angle=55, taper_length=12.6, fiber_angle=5, bias_gap=0, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()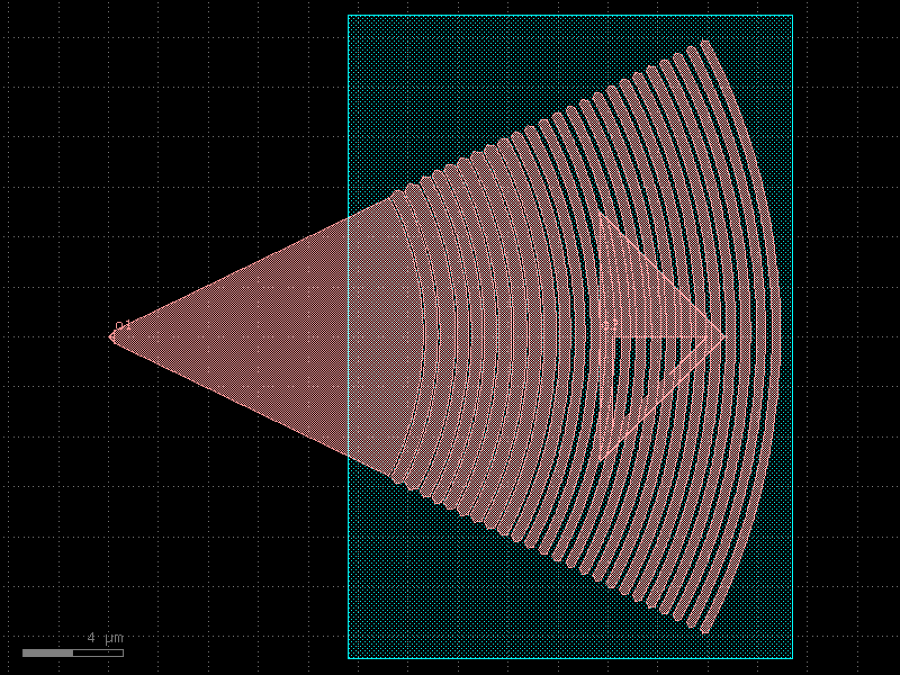
- gdsfactory.components.grating_couplers.grating_coupler_elliptical_trenches(polarization: str = 'te', taper_length: float = 16.6, taper_angle: float = 30.0, trenches_extra_angle: float = 9.0, wavelength: float = 1.53, fiber_angle: float = 15.0, grating_line_width: float = 0.343, neff: float = 2.638, ncladding: float = 1.443, layer_trench: LayerSpec = 'SHALLOW_ETCH', p_start: int = 26, n_periods: int = 30, end_straight_length: float = 0.2, taper: ComponentSpec = 'taper', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns Grating coupler with defined trenches.
Some foundries define the grating coupler by a shallow etch step (trenches) Others define the slab that they keep (see grating_coupler_elliptical)
- Parameters
polarization– ‘te’ or ‘tm’.taper_length– taper length from straight I/O.taper_angle– grating flare angle.trenches_extra_angle– extra angle for the trenches.wavelength– grating transmission central wavelength.fiber_angle– fibre polish angle in degrees.grating_line_width– of the 220 ridge.neff– tooth effective index.ncladding– cladding index.layer_trench– for the trench.p_start– first tooth.n_periods– number of grating teeth.end_straight_length– at the end of straight.taper– taper function.cross_section– cross_section spec.
fiber / / / / / / / / _|-|_|-|_|-|___ WG o1 ______________|
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.grating_coupler_elliptical_trenches(polarization='te', taper_length=16.6, taper_angle=30, trenches_extra_angle=9, wavelength=1.53, fiber_angle=15, grating_line_width=0.343, neff=2.638, ncladding=1.443, layer_trench='SHALLOW_ETCH', p_start=26, n_periods=30, end_straight_length=0.2, taper='taper', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()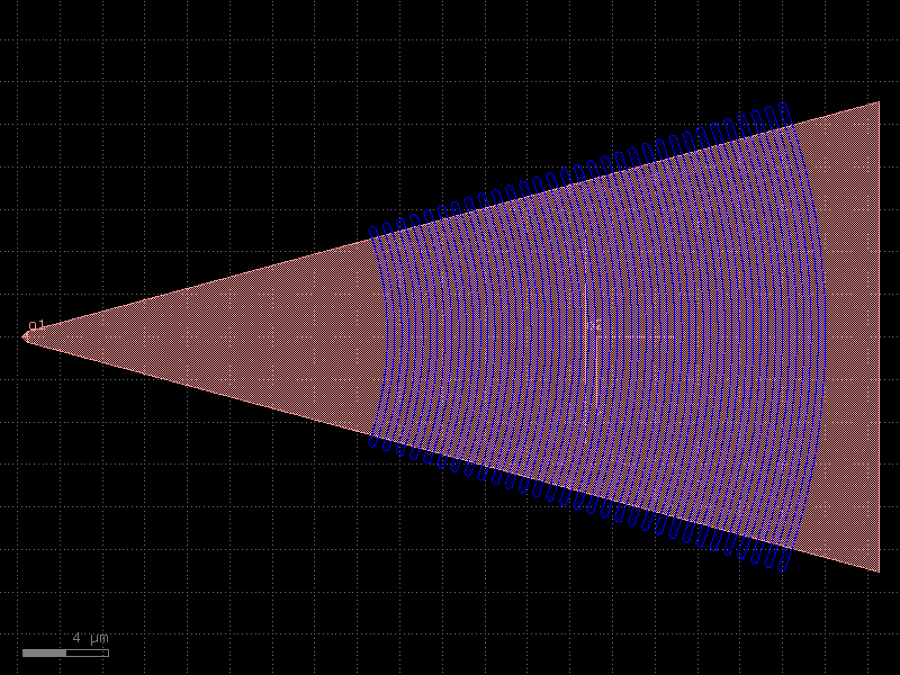
- gdsfactory.components.grating_couplers.grating_coupler_elliptical_uniform(n_periods: int = 20, period: float = 0.75, fill_factor: float = 0.5, **kwargs: Any)Component
Grating coupler with parametrization based on Lumerical FDTD simulation.
The ellipticity is derived from Lumerical knowledge base it depends on fiber_angle (degrees), neff, and nclad
- Parameters
n_periods– number of grating periods.period– grating pitch in um.fill_factor– ratio of grating width vs gap.
- Keyword Arguments
taper_length– taper length from input.taper_angle– grating flare angle.wavelength– grating transmission central wavelength (um).fiber_angle– fibre angle in degrees determines ellipticity.neff– tooth effective index to compute ellipticity.nclad– cladding effective index to compute ellipticity.layer_slab– Optional slab.taper_to_slab_offset– where 0 is at the start of the taper.polarization– te or tm.spiked– grating teeth have spikes to avoid drc errors..bias_gap– etch gap (um). Positive bias increases gap and reduces width to keep period constant.cross_section– cross_section spec for waveguide port.kwargs– cross_section settings.
fiber / / / / / / / / _|-|_|-|_|-|___ layer layer_slab | o1 ______________|
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.grating_coupler_elliptical_uniform(n_periods=20, period=0.75, fill_factor=0.5).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()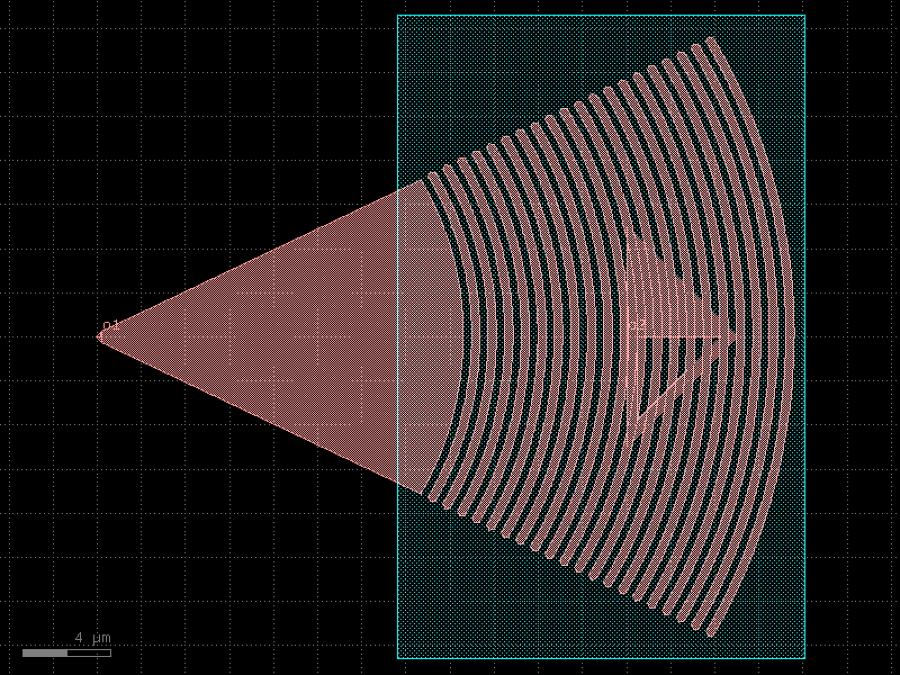
- gdsfactory.components.grating_couplers.grating_coupler_loss(pitch: float = 127.0, grating_coupler: ComponentSpec = 'grating_coupler_elliptical_trenches', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', port_name: str = 'o1', rotation: float = -90, nfibers: int = 10, grating_coupler_spacing: float = 5.0)Component
Grating coupler test structure for de-embeding fiber array.
Connects channel 1->3, 1->5 … 1->nfibers with grating couplers.
Only odd channels are connected to the grating couplers as even channels in the align_tree.
- Parameters
pitch– um.grating_coupler– spec.cross_section– spec.port_name– for the grating_coupler port.rotation– degrees.nfibers– number of fibers to connect.grating_coupler_spacing– um.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.grating_coupler_loss(pitch=127, grating_coupler='grating_coupler_elliptical_trenches', cross_section='strip', port_name='o1', rotation=-90, nfibers=10, grating_coupler_spacing=5).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()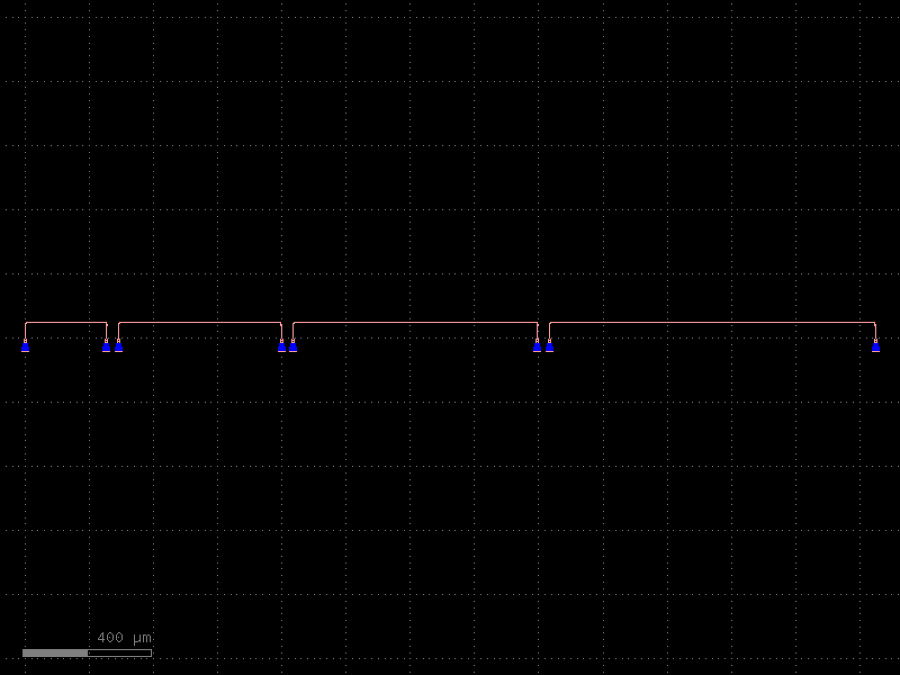
- gdsfactory.components.grating_couplers.grating_coupler_rectangular(n_periods: int = 20, period: float = 0.75, fill_factor: float = 0.5, width_grating: float = 11.0, length_taper: float = 150.0, polarization: str = 'te', wavelength: float = 1.55, taper: ComponentSpec = 'taper', layer_slab: LayerSpec | None = 'SLAB150', layer_grating: LayerSpec | None = None, fiber_angle: float = 15, slab_xmin: float = -1.0, slab_offset: float = 1.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Grating coupler with rectangular shapes (not elliptical).
Needs longer taper than elliptical. Grating teeth are straight. For a focusing grating take a look at grating_coupler_elliptical.
- Parameters
n_periods– number of grating teeth.period– grating pitch.fill_factor– ratio of grating width vs gap.width_grating–length_taper–polarization– ‘te’ or ‘tm’.wavelength– in um.taper– function.layer_slab– layer that protects the slab under the grating.layer_grating– layer for the grating.fiber_angle– in degrees.slab_xmin– where 0 is at the start of the taper.slab_offset– from edge of grating to edge of the slab.cross_section– for input waveguide port.
side view fiber / / / / / / / / _|-|_|-|_|-|___ layer layer_slab | o1 ______________| top view _________ /| | | | | / | | | | | /taper_angle /_ _| | | | | wg_width | | | | | | \ | | | | | \ | | | | | \ | | | | | \|_|_|_|_| <--> taper_length
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.grating_coupler_rectangular(n_periods=20, period=0.75, fill_factor=0.5, width_grating=11, length_taper=150, polarization='te', wavelength=1.55, taper='taper', layer_slab='SLAB150', fiber_angle=15, slab_xmin=-1, slab_offset=1, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()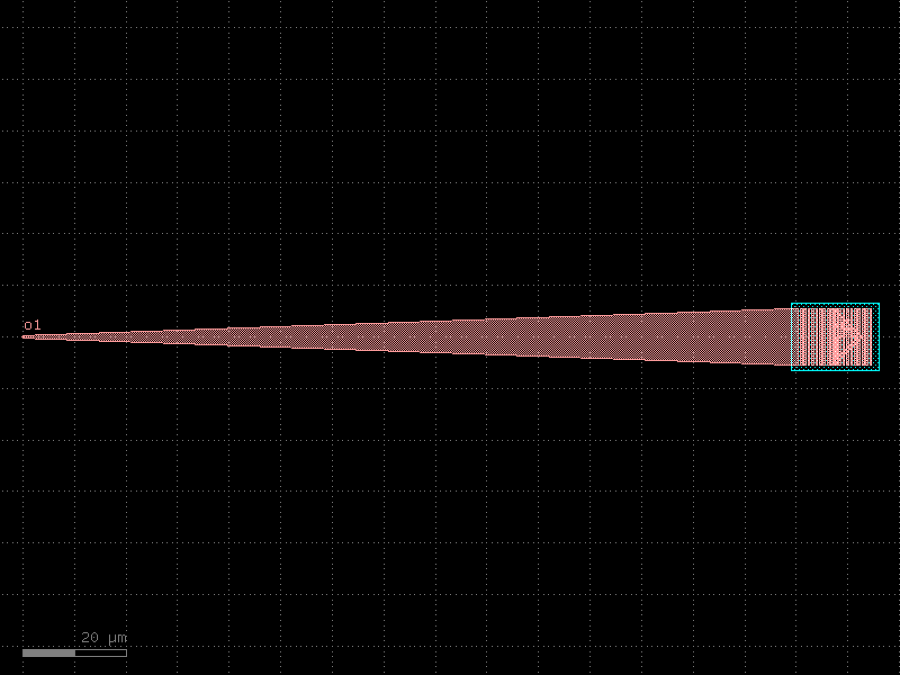
- gdsfactory.components.grating_couplers.grating_coupler_rectangular_arbitrary(gaps: Floats = (0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2), widths: Floats = (0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5), width_grating: float = 11.0, length_taper: float = 150.0, polarization: str = 'te', wavelength: float = 1.55, layer_grating: LayerSpec | None = None, layer_slab: LayerSpec | None = None, slab_xmin: float = -1.0, slab_offset: float = 1.0, fiber_angle: float = 15, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Grating coupler uniform with rectangular shape (not elliptical).
Therefore it needs a longer taper. Grating teeth are straight instead of elliptical.
- Parameters
gaps– list of gaps between grating teeth.widths– list of grating widths.width_grating– grating teeth width.length_taper– taper length (um).polarization– ‘te’ or ‘tm’.wavelength– in um.layer_grating– Optional layer for grating. � by default None uses cross_section.layer. � if different from cross_section.layer expands taper.layer_slab– layer that protects the slab under the grating.slab_xmin– where 0 is at the start of the taper.slab_offset– from edge of grating to edge of the slab.fiber_angle– in degrees.cross_section– for input waveguide port.
fiber / / / / / / / / _|-|_|-|_|-|___ layer layer_slab | o1 ______________| top view _________ /| | | | | / | | | | | /taper_angle /_ _| | | | | wg_width | | | | | | \ | | | | | \ | | | | | \ | | | | | \|_|_|_|_| <--> taper_length
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.grating_coupler_rectangular_arbitrary(gaps=(0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2), widths=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5), width_grating=11, length_taper=150, polarization='te', wavelength=1.55, slab_xmin=-1, slab_offset=1, fiber_angle=15, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()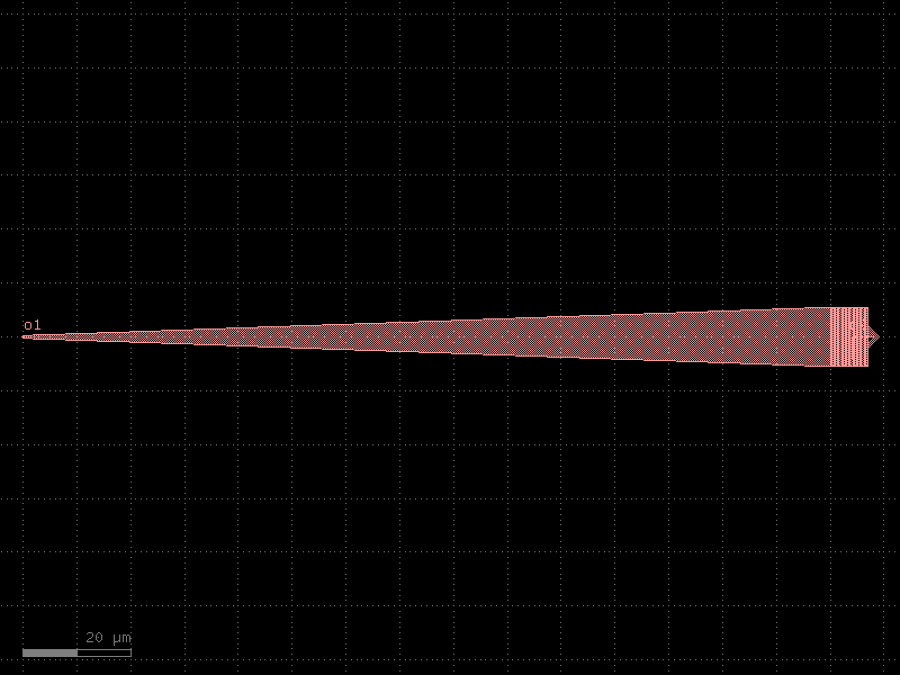
- gdsfactory.components.grating_couplers.grating_coupler_tree(n: int = 4, straight_spacing: float = 4.0, grating_coupler: ComponentSpec = 'grating_coupler_elliptical_te', with_loopback: bool = False, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', fanout_length: float = 0.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', **kwargs: Any)Component
Array of straights connected with grating couplers.
useful to align the 4 corners of the chip
- Parameters
n– number of gratings.straight_spacing– in um.grating_coupler– spec.with_loopback– adds loopback.bend– bend spec.fanout_length– in um.cross_section– cross_section function.kwargs– additional arguments.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.grating_coupler_tree(n=4, straight_spacing=4, grating_coupler='grating_coupler_elliptical_te', with_loopback=False, bend='bend_euler', fanout_length=0, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
mmis¶
- gdsfactory.components.mmis.mmi(inputs: int = 1, outputs: int = 4, width: float | None = None, width_taper: float = 1.0, length_taper: float = 10.0, length_mmi: float = 5.5, width_mmi: float = 5, gap_input_tapers: float = 0.25, gap_output_tapers: float = 0.25, taper: ComponentSpec = 'taper', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', input_positions: list[float] | None = None, output_positions: list[float] | None = None)Component
Mxn MultiMode Interferometer (MMI).
- Parameters
inputs– number of inputs.outputs– number of outputs.width– input and output straight width. Defaults to cross_section.width_taper– interface between input straights and mmi region.length_taper– into the mmi region.length_mmi– in x direction.width_mmi– in y direction.gap_input_tapers– gap between input tapers from edge to edge.gap_output_tapers– gap between output tapers from edge to edge.taper– taper function.straight– straight function.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string or dict).input_positions– optional positions of the inputs.output_positions– optional positions of the outputs.
length_mmi <------> ________ | | __/ \__ o2 __ __ o3 \ /_ _ _ _ | | _ _ _ _| gap_output_tapers __/ \__ o1 __ __ o4 \ / |________| | | <-> length_taper
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mmi(inputs=1, outputs=4, width_taper=1, length_taper=10, length_mmi=5.5, width_mmi=5, gap_input_tapers=0.25, gap_output_tapers=0.25, taper='taper', straight='straight', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.mmis.mmi1x2(width: float | None = None, width_taper: float = 1.0, length_taper: float = 10.0, length_mmi: float = 5.5, width_mmi: float = 2.5, gap_mmi: float = 0.25, taper: ComponentSpec = <function taper>, straight: ComponentSpec = <function straight>, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
1x2 MultiMode Interferometer (MMI).
- Parameters
width– input and output straight width. Defaults to cross_section width.width_taper– interface between input straights and mmi region.length_taper– into the mmi region.length_mmi– in x direction.width_mmi– in y direction.gap_mmi– gap between tapered wg.taper– taper function.straight– straight function.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string or dict).
length_mmi <------> ________ | | | \__ | __ o2 __/ /_ _ _ _ o1 __ | _ _ _ _| gap_mmi \ \__ | __ o3 | / |________| <-> length_taper
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mmi1x2(width_taper=1, length_taper=10, length_mmi=5.5, width_mmi=2.5, gap_mmi=0.25, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.mmis.mmi1x2_with_sbend(with_sbend: bool = True, s_bend: ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], ~gdsfactory.component.Component] = <function bend_s>, cross_section: ~gdsfactory.cross_section.CrossSection | str | dict[str, ~typing.Any] | ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], CrossSection] | ~kfactory.cross_section.SymmetricalCrossSection | ~kfactory.cross_section.DCrossSection = 'strip')Component
Returns 1x2 splitter for Cband.
https://
opg .optica .org /oe /fulltext .cfm ?uri = oe -21 -1 -1310 & id = 248418 - Parameters
with_sbend– add sbend.s_bend– S-bend spec.cross_section– spec.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mmi1x2_with_sbend(with_sbend=True, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()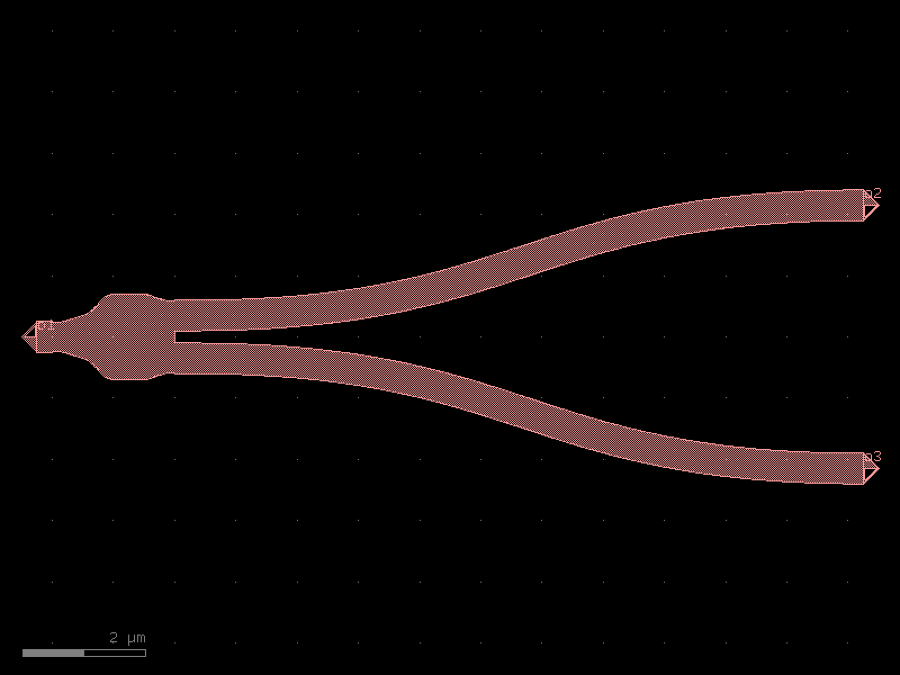
- gdsfactory.components.mmis.mmi2x2(width: float | None = None, width_taper: float = 1.0, length_taper: float = 10.0, length_mmi: float = 5.5, width_mmi: float = 2.5, gap_mmi: float = 0.25, taper: ComponentSpec = <function taper>, straight: ComponentSpec = <function straight>, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Mmi 2x2.
- Parameters
width– input and output straight width.width_taper– interface between input straights and mmi region.length_taper– into the mmi region.length_mmi– in x direction.width_mmi– in y direction.gap_mmi– (width_taper + gap between tapered wg)/2.taper– taper function.straight– straight function.cross_section– spec.
length_mmi <------> ________ | | __/ \__ o2 __ __ o3 \ /_ _ _ _ | | _ _ _ _| gap_mmi __/ \__ o1 __ __ o4 \ / |________| <-> length_taper
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mmi2x2(width_taper=1, length_taper=10, length_mmi=5.5, width_mmi=2.5, gap_mmi=0.25, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()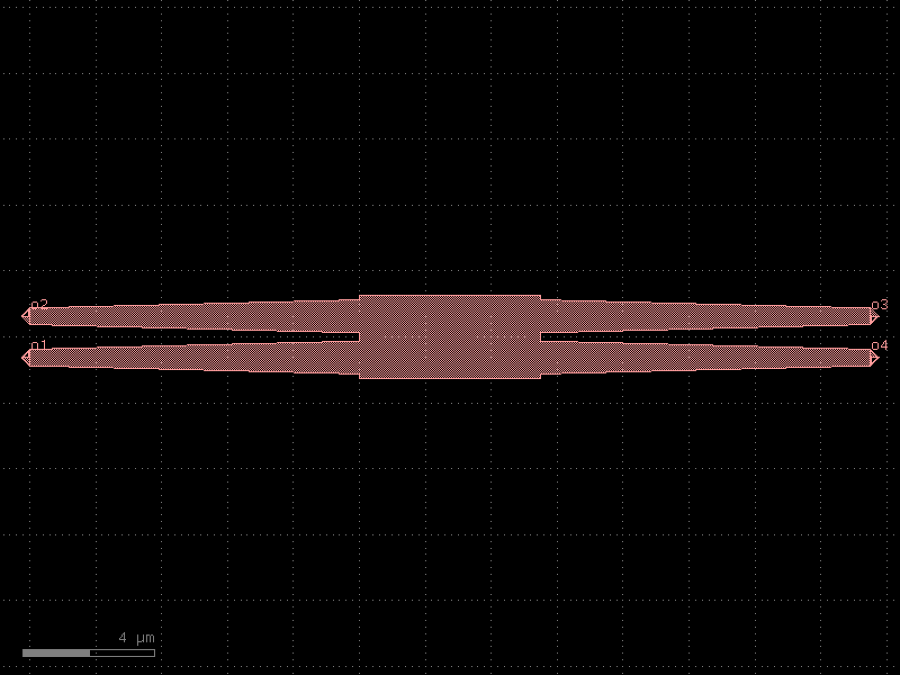
- gdsfactory.components.mmis.mmi2x2_with_sbend(with_sbend: bool = True, s_bend: ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], ~gdsfactory.component.Component] = <function bend_s>, cross_section: ~gdsfactory.cross_section.CrossSection | str | dict[str, ~typing.Any] | ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], CrossSection] | ~kfactory.cross_section.SymmetricalCrossSection | ~kfactory.cross_section.DCrossSection = 'strip')Component
Returns mmi2x2 for Cband.
C_band 2x2MMI in 220nm thick silicon https://
opg .optica .org /oe /fulltext .cfm ?uri = oe -25 -23 -28957 & id = 376719 - Parameters
with_sbend– add sbend.s_bend– S-bend function.cross_section– spec.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mmi2x2_with_sbend(with_sbend=True, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()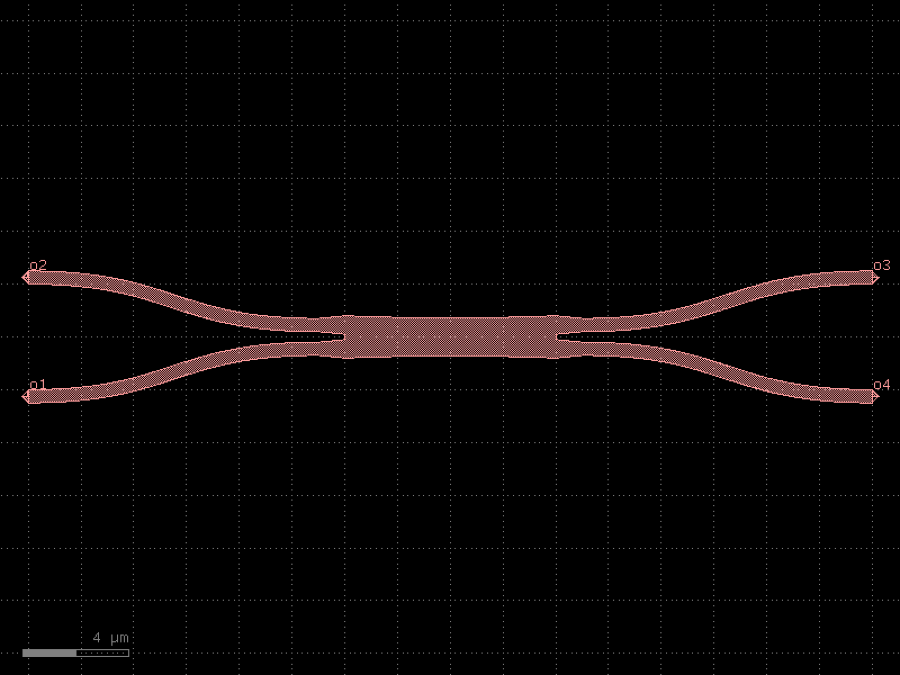
- gdsfactory.components.mmis.mmi_90degree_hybrid(width: float = 0.5, width_taper: float = 1.7, length_taper: float = 40.0, length_mmi: float = 175.0, width_mmi: float = 10.0, gap_mmi: float = 0.8, straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
90 degree hybrid based on a 4x4 MMI.
Default values from Watanabe et al., “Coherent few mode demultiplexer realized as a 2D grating coupler array in silicon”, Optics Express 28(24), 2020
It could be interesting to consider the design in Guan et al., “Compact and low loss 90° optical hybrid on a silicon-on-insulator platform”, Optics Express 25(23), 2017
- Parameters
width– input and output straight width.width_taper– interface between input straights and mmi region.length_taper– into the mmi region.length_mmi– in x direction.width_mmi– in y direction.gap_mmi– (width_taper + gap between tapered wg)/2.straight– straight function.with_bbox– box in bbox_layers and bbox_offsets avoid DRC sharp edges.cross_section– spec.
length_mmi <------> ________ | | __/ \__ signal_in __ __ I_out1 \ /_ _ _ _ | | _ _ _ _| gap_mmi | \__ | __ Q_out1 | / | | | __/ \__ LO_in __ __ Q_out2 \ /_ _ _ _ | | _ _ _ _| gap_mmi | \__ | __ I_out2 | / | ________| <-> length_taper
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mmi_90degree_hybrid(width=0.5, width_taper=1.7, length_taper=40, length_mmi=175, width_mmi=10, gap_mmi=0.8, straight='straight', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.mmis.mmi_tapered(inputs: int = 1, outputs: int = 2, width: float | None = None, width_taper_in: float = 2.0, length_taper_in: float = 1.0, width_taper_out: float | None = None, length_taper_out: float | None = None, width_taper: float = 1.0, length_taper: float = 10.0, length_taper_start: float | None = None, length_taper_end: float | None = None, length_mmi: float = 5.5, width_mmi: float = 5, width_mmi_inner: float | None = None, gap_input_tapers: float = 0.25, gap_output_tapers: float = 0.25, taper: ComponentFactory = <function taper>, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', input_positions: list[float] | None = None, output_positions: list[float] | None = None)Component
Mxn MultiMode Interferometer (MMI).
This is jut a more general version of the mmi component. Make sure you simulate and optimize the component before using it.
- Parameters
inputs– number of inputs.outputs– number of outputs.width– input and output straight width. Defaults to cross_section.width_taper_in– interface between input straights and mmi region.length_taper_in– into the mmi region.width_taper_out– interface between mmi region and output straights.length_taper_out– into the mmi region.width_taper– interface between mmi region and output straights.length_taper– into the mmi region.length_taper_start– length of the taper at the start. Defaults to length_taper.length_taper_end– length of the taper at the end. Defaults to length_taper.length_mmi– in x direction.width_mmi– in y direction.width_mmi_inner– allows adding a different width for the inner mmi region.gap_input_tapers– gap between input tapers from edge to edge.gap_output_tapers– gap between output tapers from edge to edge.taper– taper function.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string or dict).input_positions– optional positions of the inputs.output_positions– optional positions of the outputs.
┌───────────┐ │ ├───────────────┐ │ │ ├────────────┐ width_taper │ │ │ │ ▲ ┌────────────────┤ │ ├────────────┘ │ │ │ ├───────────────┘ ┌───────────┼─┤ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ ◄───────────┼─► │ ├───────────────┐ └───────────┼─┐ │ │ ├─────────────┐ ▼ └────────────────┤ │ │ │ ◄───────────────►│ │ ├─────────────┘ length_taper length_taper_in│ ├───────────────┘ length_taper ◄────────────► └───────────┘◄────────────► ◄────────────► start length_taper_out end ◄───────────► length_mmi
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mmi_tapered(inputs=1, outputs=2, width_taper_in=2, length_taper_in=1, width_taper=1, length_taper=10, length_mmi=5.5, width_mmi=5, gap_input_tapers=0.25, gap_output_tapers=0.25, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()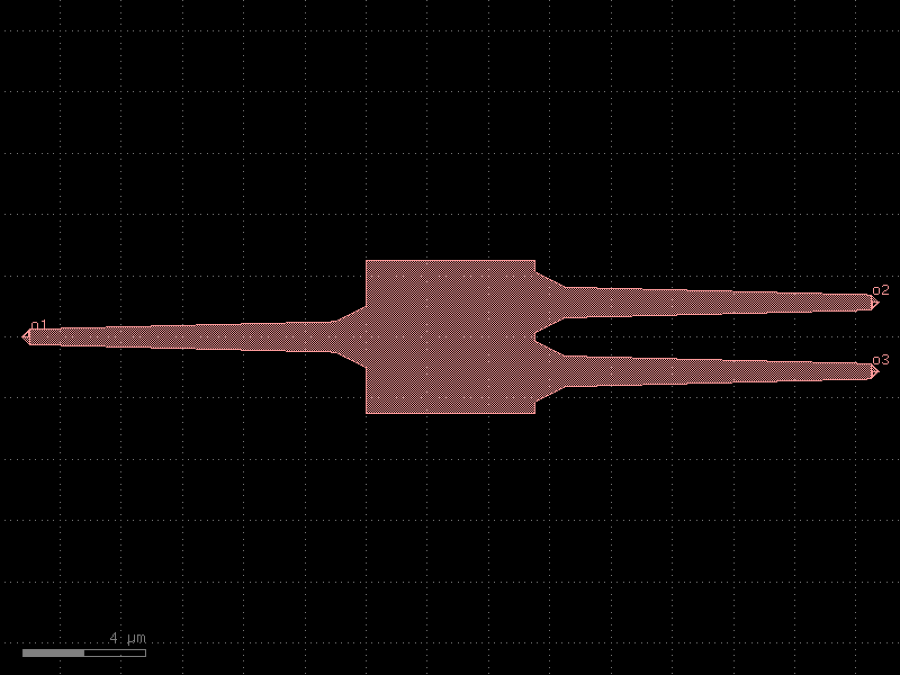
mzis¶
- gdsfactory.components.mzis.mzi(delta_length: float = 10.0, length_y: float = 2.0, length_x: float | None = 0.1, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', straight_y: ComponentSpec | None = None, straight_x_top: ComponentSpec | None = None, straight_x_bot: ComponentSpec | None = None, splitter: ComponentSpec = 'mmi1x2', combiner: ComponentSpec | None = None, with_splitter: bool = True, port_e1_splitter: str = 'o2', port_e0_splitter: str = 'o3', port_e1_combiner: str = 'o2', port_e0_combiner: str = 'o3', port1: str = 'o1', port2: str = 'o2', nbends: int = 2, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_x_top: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, cross_section_x_bot: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, mirror_bot: bool = False, add_optical_ports_arms: bool = False, min_length: float = 0.01, auto_rename_ports: bool = True)Component
Mzi.
- Parameters
delta_length– bottom arm vertical extra length.length_y– vertical length for both and top arms.length_x– horizontal length. None uses to the straight_x_bot/top defaults.bend– 90 degrees bend library.straight– straight function.straight_y– straight for length_y and delta_length.straight_x_top– top straight for length_x.straight_x_bot– bottom straight for length_x.splitter– splitter function.combiner– combiner function.with_splitter– if False removes splitter.port_e1_splitter– east top splitter port.port_e0_splitter– east bot splitter port.port_e1_combiner– east top combiner port.port_e0_combiner– east bot combiner port.port1– input port name.port2– output port name.nbends– from straight top/bot to combiner (at least 2).cross_section– for routing (sxtop/sxbot to combiner).cross_section_x_top– optional top cross_section (defaults to cross_section).cross_section_x_bot– optional bottom cross_section (defaults to cross_section).mirror_bot– if true, mirrors the bottom arm.add_optical_ports_arms– add all other optical ports in the arms with top_ and bot_ prefix.min_length– minimum length for the straight.auto_rename_ports– if True, renames ports.
b2______b3 | sxtop | straight_y | | | b1 b4 splitter==| |==combiner b5 b8 | | straight_y | | | delta_length/2 | | | b6__sxbot__b7 Lx
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mzi(delta_length=10, length_y=2, length_x=0.1, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', splitter='mmi1x2', with_splitter=True, port_e1_splitter='o2', port_e0_splitter='o3', port_e1_combiner='o2', port_e0_combiner='o3', port1='o1', port2='o2', nbends=2, cross_section='strip', mirror_bot=False, add_optical_ports_arms=False, min_length=0.01, auto_rename_ports=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.mzis.mzi1x2_2x2(delta_length: float = 10.0, length_y: float = 2.0, length_x: float | None = 0.1, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', straight_y: ComponentSpec | None = None, straight_x_top: ComponentSpec | None = None, straight_x_bot: ComponentSpec | None = None, splitter: ComponentSpec = 'mmi1x2', *, combiner: ComponentSpec | None = 'mmi2x2', with_splitter: bool = True, port_e1_splitter: str = 'o2', port_e0_splitter: str = 'o3', port_e1_combiner: str = 'o3', port_e0_combiner: str = 'o4', port1: str = 'o1', port2: str = 'o2', nbends: int = 2, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_x_top: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, cross_section_x_bot: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, mirror_bot: bool = False, add_optical_ports_arms: bool = False, min_length: float = 0.01, auto_rename_ports: bool = True)Component
Mzi.
- Parameters
delta_length– bottom arm vertical extra length.length_y– vertical length for both and top arms.length_x– horizontal length. None uses to the straight_x_bot/top defaults.bend– 90 degrees bend library.straight– straight function.straight_y– straight for length_y and delta_length.straight_x_top– top straight for length_x.straight_x_bot– bottom straight for length_x.splitter– splitter function.combiner– combiner function.with_splitter– if False removes splitter.port_e1_splitter– east top splitter port.port_e0_splitter– east bot splitter port.port_e1_combiner– east top combiner port.port_e0_combiner– east bot combiner port.port1– input port name.port2– output port name.nbends– from straight top/bot to combiner (at least 2).cross_section– for routing (sxtop/sxbot to combiner).cross_section_x_top– optional top cross_section (defaults to cross_section).cross_section_x_bot– optional bottom cross_section (defaults to cross_section).mirror_bot– if true, mirrors the bottom arm.add_optical_ports_arms– add all other optical ports in the arms with top_ and bot_ prefix.min_length– minimum length for the straight.auto_rename_ports– if True, renames ports.
b2______b3 | sxtop | straight_y | | | b1 b4 splitter==| |==combiner b5 b8 | | straight_y | | | delta_length/2 | | | b6__sxbot__b7 Lx
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mzi1x2_2x2(delta_length=10, length_y=2, length_x=0.1, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', splitter='mmi1x2', combiner='mmi2x2', with_splitter=True, port_e1_splitter='o2', port_e0_splitter='o3', port_e1_combiner='o3', port_e0_combiner='o4', port1='o1', port2='o2', nbends=2, cross_section='strip', mirror_bot=False, add_optical_ports_arms=False, min_length=0.01, auto_rename_ports=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.mzis.mzi2x2_2x2_phase_shifter(delta_length: float = 10.0, length_y: float = 2.0, *, length_x: float | None = 200, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', straight_y: ComponentSpec | None = None, straight_x_top: ComponentSpec | None = 'straight_heater_metal', straight_x_bot: ComponentSpec | None = None, splitter: ComponentSpec = 'mmi2x2', combiner: ComponentSpec | None = 'mmi2x2', with_splitter: bool = True, port_e1_splitter: str = 'o3', port_e0_splitter: str = 'o4', port_e1_combiner: str = 'o3', port_e0_combiner: str = 'o4', port1: str = 'o1', port2: str = 'o2', nbends: int = 2, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_x_top: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, cross_section_x_bot: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, mirror_bot: bool = False, add_optical_ports_arms: bool = False, min_length: float = 0.01, auto_rename_ports: bool = True)Component
Mzi.
- Parameters
delta_length– bottom arm vertical extra length.length_y– vertical length for both and top arms.length_x– horizontal length. None uses to the straight_x_bot/top defaults.bend– 90 degrees bend library.straight– straight function.straight_y– straight for length_y and delta_length.straight_x_top– top straight for length_x.straight_x_bot– bottom straight for length_x.splitter– splitter function.combiner– combiner function.with_splitter– if False removes splitter.port_e1_splitter– east top splitter port.port_e0_splitter– east bot splitter port.port_e1_combiner– east top combiner port.port_e0_combiner– east bot combiner port.port1– input port name.port2– output port name.nbends– from straight top/bot to combiner (at least 2).cross_section– for routing (sxtop/sxbot to combiner).cross_section_x_top– optional top cross_section (defaults to cross_section).cross_section_x_bot– optional bottom cross_section (defaults to cross_section).mirror_bot– if true, mirrors the bottom arm.add_optical_ports_arms– add all other optical ports in the arms with top_ and bot_ prefix.min_length– minimum length for the straight.auto_rename_ports– if True, renames ports.
b2______b3 | sxtop | straight_y | | | b1 b4 splitter==| |==combiner b5 b8 | | straight_y | | | delta_length/2 | | | b6__sxbot__b7 Lx
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mzi2x2_2x2_phase_shifter(delta_length=10, length_y=2, length_x=200, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', straight_x_top='straight_heater_metal', splitter='mmi2x2', combiner='mmi2x2', with_splitter=True, port_e1_splitter='o3', port_e0_splitter='o4', port_e1_combiner='o3', port_e0_combiner='o4', port1='o1', port2='o2', nbends=2, cross_section='strip', mirror_bot=False, add_optical_ports_arms=False, min_length=0.01, auto_rename_ports=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.mzis.mzi_lattice(coupler_lengths: Sequence[float] = (10.0, 20.0), coupler_gaps: Sequence[float] = (0.2, 0.3), delta_lengths: Sequence[float] = (10.0,), mzi: str = 'mzi_coupler', splitter: str = 'coupler', **kwargs: Any)Component
Mzi lattice filter.
- Parameters
coupler_lengths– list of length for each coupler.coupler_gaps– list of coupler gaps.delta_lengths– list of length differences.mzi– function for the mzi.splitter– splitter function.kwargs– additional settings.
- Keyword Arguments
length_y– vertical length for both and top arms.length_x– horizontal length.bend– 90 degrees bend library.straight– straight function.straight_y– straight for length_y and delta_length.straight_x_top– top straight for length_x.straight_x_bot– bottom straight for length_x.cross_section– for routing (sxtop/sxbot to combiner).
______ ______ | | | | | | | | cp1==| |===cp2=====| |=== .... ===cp_last=== | | | | | | | | DL1 | DL2 | | | | | |______| | | |______|
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mzi_lattice(coupler_lengths=(10, 20), coupler_gaps=(0.2, 0.3), delta_lengths=(10,), mzi='mzi_coupler', splitter='coupler').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()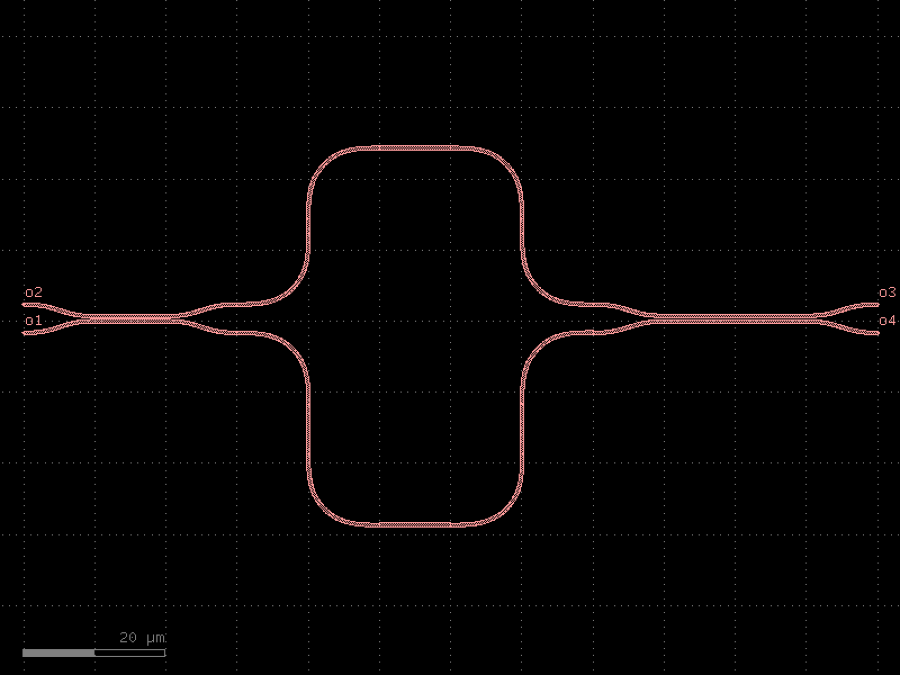
- gdsfactory.components.mzis.mzi_lattice_mmi(coupler_widths: tuple[float | None, float | None] = (None, None), coupler_widths_tapers: tuple[float, ...] = (1.0, 1.0), coupler_lengths_tapers: tuple[float, ...] = (10.0, 10.0), coupler_lengths_mmis: tuple[float, ...] = (5.5, 5.5), coupler_widths_mmis: tuple[float, ...] = (2.5, 2.5), coupler_gaps_mmis: tuple[float, ...] = (0.25, 0.25), taper_functions_mmis: tuple[str, ...] = ('taper', 'taper'), straight_functions_mmis: tuple[str, ...] = ('straight', 'straight'), cross_sections_mmis: tuple[str, ...] = ('strip', 'strip'), delta_lengths: tuple[float, ...] = (10.0,), mzi: str = 'mzi2x2_2x2', splitter: str = 'mmi2x2', **kwargs: Any)Component
Mzi lattice filter, with MMI couplers.
- Parameters
coupler_widths– (for each MMI coupler, list of) input and output straight width.coupler_widths_tapers– (for each MMI coupler, list of) interface between input straights and mmi region.coupler_lengths_tapers– (for each MMI coupler, list of) into the mmi region.coupler_lengths_mmis– (for each MMI coupler, list of) in x direction.coupler_widths_mmis– (for each MMI coupler, list of) in y direction.coupler_gaps_mmis– (for each MMI coupler, list of) (width_taper + gap between tapered wg)/2.taper_functions_mmis– (for each MMI coupler, list of) taper function.straight_functions_mmis– (for each MMI coupler, list of) straight function.cross_sections_mmis– (for each MMI coupler, list of) spec.delta_lengths– list of length differences.mzi– function for the mzi.splitter– splitter function.kwargs– additional settings.
- Keyword Arguments
length_y– vertical length for both and top arms.length_x– horizontal length.bend– 90 degrees bend library.straight– straight function.straight_y– straight for length_y and delta_length.straight_x_top– top straight for length_x.straight_x_bot– bottom straight for length_x.cross_section– for routing (sxtop/sxbot to combiner).
______ ______ | | | | | | | | cp1==| |===cp2=====| |=== .... ===cp_last=== | | | | | | | | DL1 | DL2 | | | | | |______| | | |______|
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mzi_lattice_mmi(coupler_widths=(None, None), coupler_widths_tapers=(1, 1), coupler_lengths_tapers=(10, 10), coupler_lengths_mmis=(5.5, 5.5), coupler_widths_mmis=(2.5, 2.5), coupler_gaps_mmis=(0.25, 0.25), taper_functions_mmis=('taper', 'taper'), straight_functions_mmis=('straight', 'straight'), cross_sections_mmis=('strip', 'strip'), delta_lengths=(10,), mzi='mzi2x2_2x2', splitter='mmi2x2').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()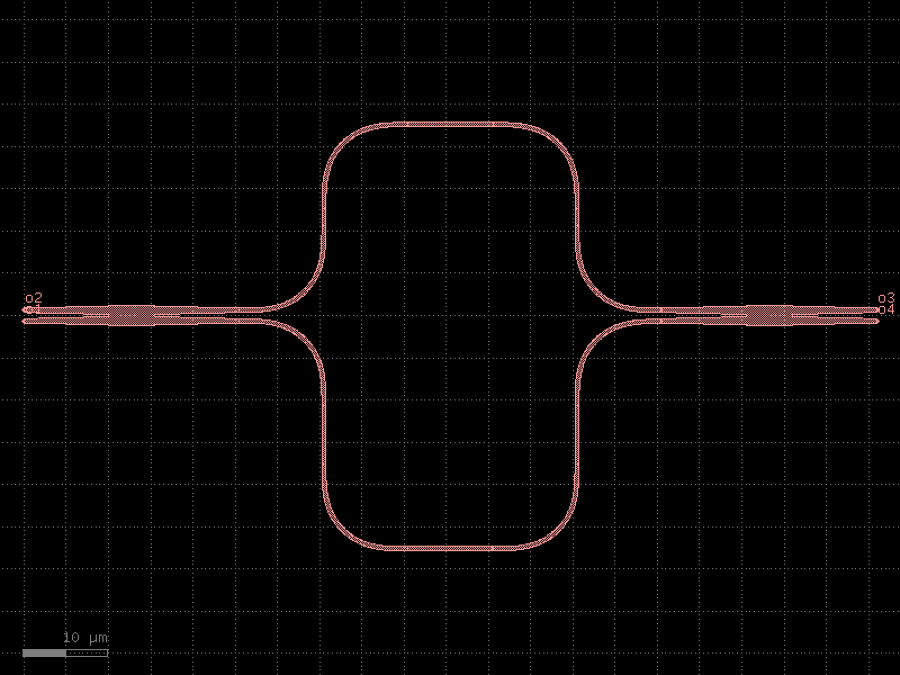
- gdsfactory.components.mzis.mzi_pads_center(ps_top: ComponentSpec = 'straight_heater_metal', ps_bot: ComponentSpec = 'straight_heater_metal', mzi: ComponentSpec = 'mzi', pad: ComponentSpec = 'pad_small', length_x: float = 500, length_y: float = 40, mzi_sig_top: str | None = 'top_r_e2', mzi_gnd_top: str | None = 'top_l_e2', mzi_sig_bot: str | None = 'bot_l_e2', mzi_gnd_bot: str | None = 'bot_r_e2', pad_sig_bot: str = 'e1_1_1', pad_sig_top: str = 'e3_1_3', pad_gnd_bot: str = 'e4_1_2', pad_gnd_top: str = 'e2_1_2', delta_length: float = 40.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_metal: CrossSectionSpec = 'metal_routing', pad_pitch: float | str = 'pad_pitch', **kwargs: Any)gf.Component
Return Mzi phase shifter with pads in the middle.
GND is the middle pad and is shared between top and bottom phase shifters.
- Parameters
ps_top– phase shifter top.ps_bot– phase shifter bottom.mzi– interferometer.pad– pad function.length_x– horizontal length.length_y– vertical length.mzi_sig_top– port name for top phase shifter signal. None if no connection.mzi_gnd_top– port name for top phase shifter GND. None if no connection.mzi_sig_bot– port name for top phase shifter signal. None if no connection.mzi_gnd_bot– port name for top phase shifter GND. None if no connection.pad_sig_bot– port name for top pad.pad_sig_top– port name for top pad.pad_gnd_bot– port name for top pad.pad_gnd_top– port name for top pad.delta_length– mzi length imbalance.cross_section– for the mzi.cross_section_metal– for routing metal.pad_pitch– pad pitch in um.kwargs– routing settings.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mzi_pads_center(ps_top='straight_heater_metal', ps_bot='straight_heater_metal', mzi='mzi', pad='pad_small', length_x=500, length_y=40, mzi_sig_top='top_r_e2', mzi_gnd_top='top_l_e2', mzi_sig_bot='bot_l_e2', mzi_gnd_bot='bot_r_e2', pad_sig_bot='e1_1_1', pad_sig_top='e3_1_3', pad_gnd_bot='e4_1_2', pad_gnd_top='e2_1_2', delta_length=40, cross_section='strip', cross_section_metal='metal_routing', pad_pitch='pad_pitch').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.mzis.mzi_phase_shifter(delta_length: float = 10.0, length_y: float = 2.0, *, length_x: float | None = 200, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', straight_y: ComponentSpec | None = None, straight_x_top: ComponentSpec | None = 'straight_heater_metal', straight_x_bot: ComponentSpec | None = None, splitter: ComponentSpec = 'mmi1x2', combiner: ComponentSpec | None = None, with_splitter: bool = True, port_e1_splitter: str = 'o2', port_e0_splitter: str = 'o3', port_e1_combiner: str = 'o2', port_e0_combiner: str = 'o3', port1: str = 'o1', port2: str = 'o2', nbends: int = 2, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_x_top: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, cross_section_x_bot: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, mirror_bot: bool = False, add_optical_ports_arms: bool = False, min_length: float = 0.01, auto_rename_ports: bool = True)Component
Mzi.
- Parameters
delta_length– bottom arm vertical extra length.length_y– vertical length for both and top arms.length_x– horizontal length. None uses to the straight_x_bot/top defaults.bend– 90 degrees bend library.straight– straight function.straight_y– straight for length_y and delta_length.straight_x_top– top straight for length_x.straight_x_bot– bottom straight for length_x.splitter– splitter function.combiner– combiner function.with_splitter– if False removes splitter.port_e1_splitter– east top splitter port.port_e0_splitter– east bot splitter port.port_e1_combiner– east top combiner port.port_e0_combiner– east bot combiner port.port1– input port name.port2– output port name.nbends– from straight top/bot to combiner (at least 2).cross_section– for routing (sxtop/sxbot to combiner).cross_section_x_top– optional top cross_section (defaults to cross_section).cross_section_x_bot– optional bottom cross_section (defaults to cross_section).mirror_bot– if true, mirrors the bottom arm.add_optical_ports_arms– add all other optical ports in the arms with top_ and bot_ prefix.min_length– minimum length for the straight.auto_rename_ports– if True, renames ports.
b2______b3 | sxtop | straight_y | | | b1 b4 splitter==| |==combiner b5 b8 | | straight_y | | | delta_length/2 | | | b6__sxbot__b7 Lx
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mzi_phase_shifter(delta_length=10, length_y=2, length_x=200, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', straight_x_top='straight_heater_metal', splitter='mmi1x2', with_splitter=True, port_e1_splitter='o2', port_e0_splitter='o3', port_e1_combiner='o2', port_e0_combiner='o3', port1='o1', port2='o2', nbends=2, cross_section='strip', mirror_bot=False, add_optical_ports_arms=False, min_length=0.01, auto_rename_ports=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.mzis.mzi_phase_shifter_top_heater_metal(delta_length: float = 10.0, length_y: float = 2.0, *, length_x: float | None = 200, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', straight_y: ComponentSpec | None = None, straight_x_top: ComponentSpec | None = 'straight_heater_metal', straight_x_bot: ComponentSpec | None = None, splitter: ComponentSpec = 'mmi1x2', combiner: ComponentSpec | None = None, with_splitter: bool = True, port_e1_splitter: str = 'o2', port_e0_splitter: str = 'o3', port_e1_combiner: str = 'o2', port_e0_combiner: str = 'o3', port1: str = 'o1', port2: str = 'o2', nbends: int = 2, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_x_top: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, cross_section_x_bot: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, mirror_bot: bool = False, add_optical_ports_arms: bool = False, min_length: float = 0.01, auto_rename_ports: bool = True)Component
Mzi.
- Parameters
delta_length– bottom arm vertical extra length.length_y– vertical length for both and top arms.length_x– horizontal length. None uses to the straight_x_bot/top defaults.bend– 90 degrees bend library.straight– straight function.straight_y– straight for length_y and delta_length.straight_x_top– top straight for length_x.straight_x_bot– bottom straight for length_x.splitter– splitter function.combiner– combiner function.with_splitter– if False removes splitter.port_e1_splitter– east top splitter port.port_e0_splitter– east bot splitter port.port_e1_combiner– east top combiner port.port_e0_combiner– east bot combiner port.port1– input port name.port2– output port name.nbends– from straight top/bot to combiner (at least 2).cross_section– for routing (sxtop/sxbot to combiner).cross_section_x_top– optional top cross_section (defaults to cross_section).cross_section_x_bot– optional bottom cross_section (defaults to cross_section).mirror_bot– if true, mirrors the bottom arm.add_optical_ports_arms– add all other optical ports in the arms with top_ and bot_ prefix.min_length– minimum length for the straight.auto_rename_ports– if True, renames ports.
b2______b3 | sxtop | straight_y | | | b1 b4 splitter==| |==combiner b5 b8 | | straight_y | | | delta_length/2 | | | b6__sxbot__b7 Lx
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mzi_phase_shifter_top_heater_metal(delta_length=10, length_y=2, length_x=200, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', straight_x_top='straight_heater_metal', splitter='mmi1x2', with_splitter=True, port_e1_splitter='o2', port_e0_splitter='o3', port_e1_combiner='o2', port_e0_combiner='o3', port1='o1', port2='o2', nbends=2, cross_section='strip', mirror_bot=False, add_optical_ports_arms=False, min_length=0.01, auto_rename_ports=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()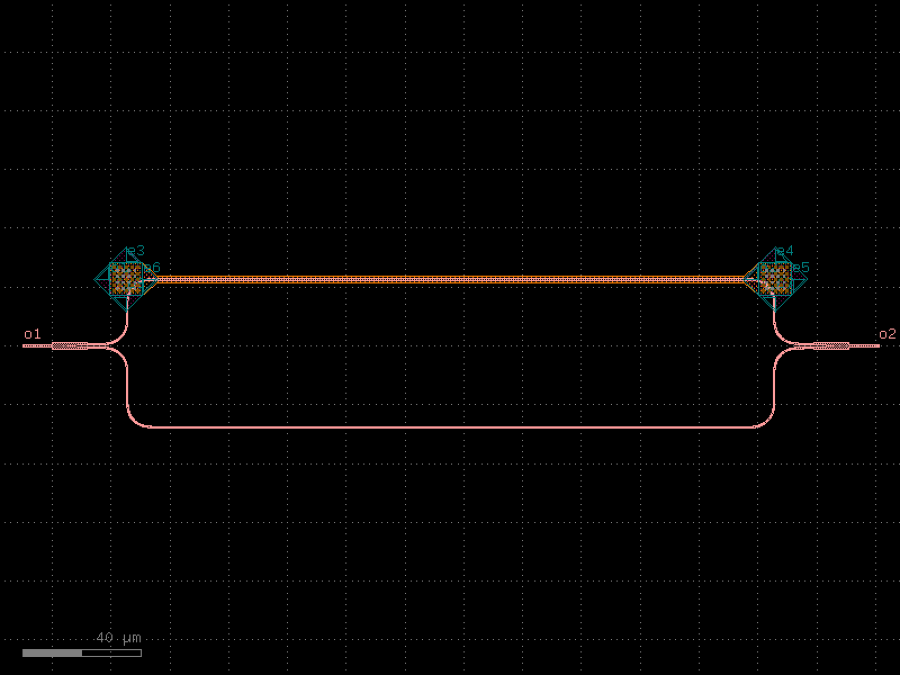
- gdsfactory.components.mzis.mzi_pin(*, delta_length: float = 0.0, length_y: float = 2.0, length_x: float | None = 100, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', straight_y: ComponentSpec | None = None, straight_x_top: ComponentSpec | None = 'straight_pin', straight_x_bot: ComponentSpec | None = None, splitter: ComponentSpec = 'mmi1x2', combiner: ComponentSpec | None = None, with_splitter: bool = True, port_e1_splitter: str = 'o2', port_e0_splitter: str = 'o3', port_e1_combiner: str = 'o2', port_e0_combiner: str = 'o3', port1: str = 'o1', port2: str = 'o2', nbends: int = 2, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_x_top: CrossSectionSpec | None = 'pin', cross_section_x_bot: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, mirror_bot: bool = False, add_optical_ports_arms: bool = False, min_length: float = 0.01, auto_rename_ports: bool = True)Component
Mzi.
- Parameters
delta_length– bottom arm vertical extra length.length_y– vertical length for both and top arms.length_x– horizontal length. None uses to the straight_x_bot/top defaults.bend– 90 degrees bend library.straight– straight function.straight_y– straight for length_y and delta_length.straight_x_top– top straight for length_x.straight_x_bot– bottom straight for length_x.splitter– splitter function.combiner– combiner function.with_splitter– if False removes splitter.port_e1_splitter– east top splitter port.port_e0_splitter– east bot splitter port.port_e1_combiner– east top combiner port.port_e0_combiner– east bot combiner port.port1– input port name.port2– output port name.nbends– from straight top/bot to combiner (at least 2).cross_section– for routing (sxtop/sxbot to combiner).cross_section_x_top– optional top cross_section (defaults to cross_section).cross_section_x_bot– optional bottom cross_section (defaults to cross_section).mirror_bot– if true, mirrors the bottom arm.add_optical_ports_arms– add all other optical ports in the arms with top_ and bot_ prefix.min_length– minimum length for the straight.auto_rename_ports– if True, renames ports.
b2______b3 | sxtop | straight_y | | | b1 b4 splitter==| |==combiner b5 b8 | | straight_y | | | delta_length/2 | | | b6__sxbot__b7 Lx
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mzi_pin(delta_length=0, length_y=2, length_x=100, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', straight_x_top='straight_pin', splitter='mmi1x2', with_splitter=True, port_e1_splitter='o2', port_e0_splitter='o3', port_e1_combiner='o2', port_e0_combiner='o3', port1='o1', port2='o2', nbends=2, cross_section='strip', cross_section_x_top='pin', mirror_bot=False, add_optical_ports_arms=False, min_length=0.01, auto_rename_ports=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()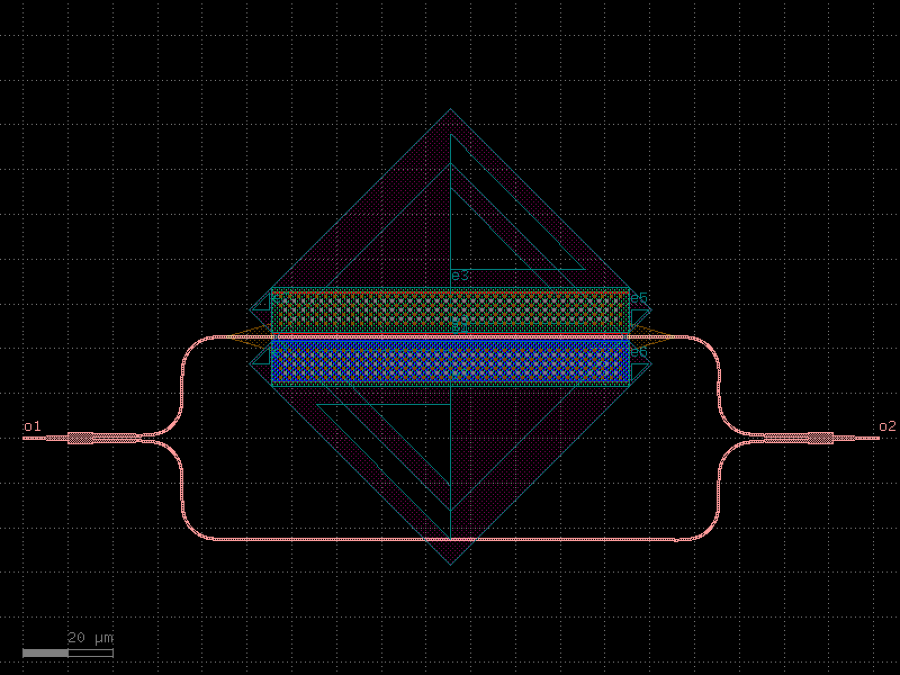
- gdsfactory.components.mzis.mzit(w0: float = 0.5, w1: float = 0.45, w2: float = 0.55, dy: float = 2.0, delta_length: float = 10.0, length: float = 1.0, coupler_length1: float = 5.0, coupler_length2: float = 10.0, coupler_gap1: float = 0.2, coupler_gap2: float = 0.3, taper: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'taper', taper_length: float = 5.0, bend90: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'bend_euler', straight: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'straight', coupler1: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | None = 'coupler', coupler2: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'coupler', cross_section: str = 'strip')Component
Mzi tolerant to fabrication variations.
based on Yufei Xing thesis http://
photonics .intec .ugent .be /publications /PhD .asp ?ID = 250 - Parameters
w0– input waveguide width (um).w1– narrow waveguide width (um).w2– wide waveguide width (um).dy– port to port vertical spacing.delta_length– length difference between arms (um).length– shared length for w1 and w2.coupler_length1– length of coupler1.coupler_length2– length of coupler2.coupler_gap1– coupler1.coupler_gap2– coupler2.taper– taper spec.taper_length– from w0 to w1.bend90– bend spec.straight– spec.coupler1– coupler1 spec (optional).coupler2– coupler2 spec.cross_section– cross_section spec.
cp1 4 2 __ __ 3___w0_t2 _w2___ \ / \ \ length1 / | ============== gap1 | / \ | __/ \_____w0___t1 _w1 | 3 1 4 \ | | | 2 2 | | __ __w0____t1____w1___/ | \ / | \ length2 / | ============== gap2 | / \ | | __/ \ E0_w0__t2 __w1______/ 1 1 cp2
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mzit(w0=0.5, w1=0.45, w2=0.55, dy=2, delta_length=10, length=1, coupler_length1=5, coupler_length2=10, coupler_gap1=0.2, coupler_gap2=0.3, taper='taper', taper_length=5, bend90='bend_euler', straight='straight', coupler1='coupler', coupler2='coupler', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.mzis.mzit_lattice(coupler_lengths: ~collections.abc.Sequence[float] = (10.0, 20.0), coupler_gaps: ~collections.abc.Sequence[float] = (0.2, 0.3), delta_lengths: ~collections.abc.Sequence[float] = (10.0,), mzi: str | ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], ~gdsfactory.component.Component] | dict[str, ~typing.Any] | ~kfactory.kcell.DKCell = <function mzit>)Component
Mzi fab tolerant lattice filter.
cp1 o4 o2 __ __ o3___w0_t2 _w2___ \ / \ \ length1 / | ============== gap1 | / \ | __/ \_____w0___t1 _w1 | o3 o1 o4 \ | . ... | | . o2 o2 o3 | | . __ _____w0___t1___w1__/ | \ / | \ lengthN / | ============== gapN | / \ | __/ \_ | o1 o1 \___w0___t2___w1_____/ cpN o4
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mzit_lattice(coupler_lengths=(10, 20), coupler_gaps=(0.2, 0.3), delta_lengths=(10,)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()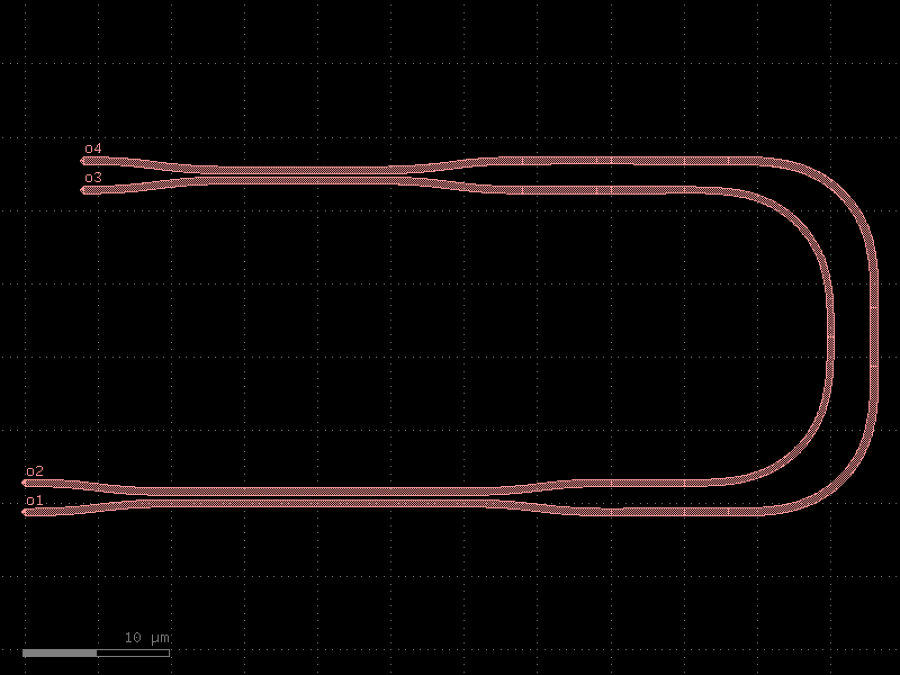
- gdsfactory.components.mzis.mzm(delta_length: float = 10.0, length_y: float = 2.0, *, length_x: float | None = 200, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', straight_y: ComponentSpec | None = None, straight_x_top: ComponentSpec | None = 'straight_pin', straight_x_bot: ComponentSpec | None = 'straight_pin', splitter: ComponentSpec = 'mmi1x2', combiner: ComponentSpec | None = None, with_splitter: bool = True, port_e1_splitter: str = 'o2', port_e0_splitter: str = 'o3', port_e1_combiner: str = 'o2', port_e0_combiner: str = 'o3', port1: str = 'o1', port2: str = 'o2', nbends: int = 2, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_x_top: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, cross_section_x_bot: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, mirror_bot: bool = False, add_optical_ports_arms: bool = False, min_length: float = 0.01, auto_rename_ports: bool = True)Component
Mzi.
- Parameters
delta_length– bottom arm vertical extra length.length_y– vertical length for both and top arms.length_x– horizontal length. None uses to the straight_x_bot/top defaults.bend– 90 degrees bend library.straight– straight function.straight_y– straight for length_y and delta_length.straight_x_top– top straight for length_x.straight_x_bot– bottom straight for length_x.splitter– splitter function.combiner– combiner function.with_splitter– if False removes splitter.port_e1_splitter– east top splitter port.port_e0_splitter– east bot splitter port.port_e1_combiner– east top combiner port.port_e0_combiner– east bot combiner port.port1– input port name.port2– output port name.nbends– from straight top/bot to combiner (at least 2).cross_section– for routing (sxtop/sxbot to combiner).cross_section_x_top– optional top cross_section (defaults to cross_section).cross_section_x_bot– optional bottom cross_section (defaults to cross_section).mirror_bot– if true, mirrors the bottom arm.add_optical_ports_arms– add all other optical ports in the arms with top_ and bot_ prefix.min_length– minimum length for the straight.auto_rename_ports– if True, renames ports.
b2______b3 | sxtop | straight_y | | | b1 b4 splitter==| |==combiner b5 b8 | | straight_y | | | delta_length/2 | | | b6__sxbot__b7 Lx
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mzm(delta_length=10, length_y=2, length_x=200, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', straight_x_top='straight_pin', straight_x_bot='straight_pin', splitter='mmi1x2', with_splitter=True, port_e1_splitter='o2', port_e0_splitter='o3', port_e1_combiner='o2', port_e0_combiner='o3', port1='o1', port2='o2', nbends=2, cross_section='strip', mirror_bot=False, add_optical_ports_arms=False, min_length=0.01, auto_rename_ports=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()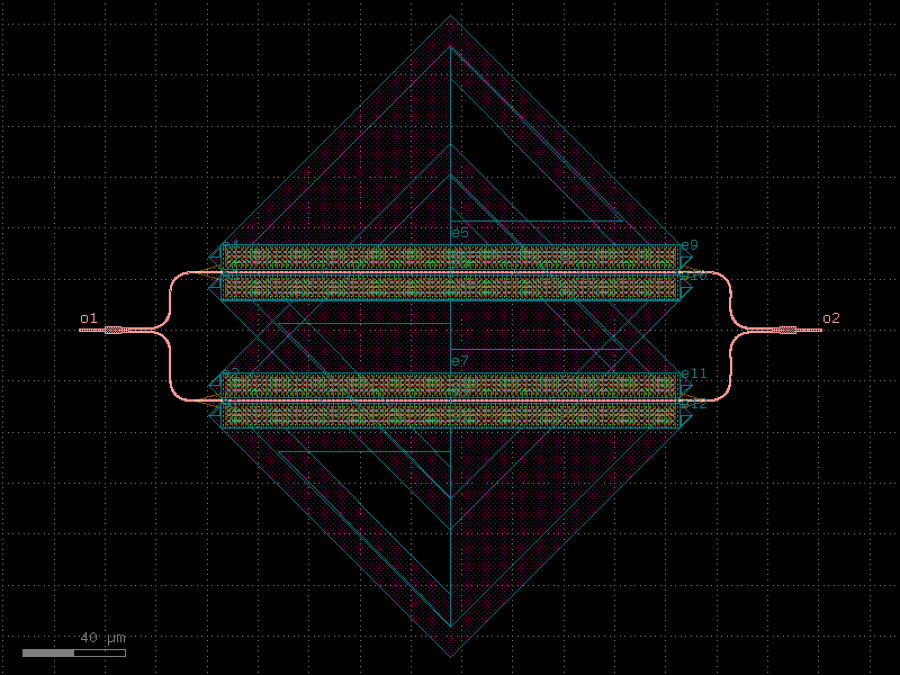
pads¶
- gdsfactory.components.pads.pad(size: tuple[float, float] | str = (100.0, 100.0), layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'MTOP', bbox_layers: tuple[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum, ...] | None = None, bbox_offsets: tuple[float, ...] | None = None, port_inclusion: float = 0, port_orientation: float | None = 0, port_orientations: tuple[int, ...] | list[int] | None = (180, 90, 0, -90), port_type: str = 'pad')Component
Returns rectangular pad with ports.
- Parameters
size– x, y size.layer– pad layer.bbox_layers– list of layers.bbox_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size.port_inclusion– from edge.port_orientation– in degrees for the center port.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.port_type– port type for pad port.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.pad(size=(100, 100), layer='MTOP', port_inclusion=0, port_orientation=0, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90), port_type='pad').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()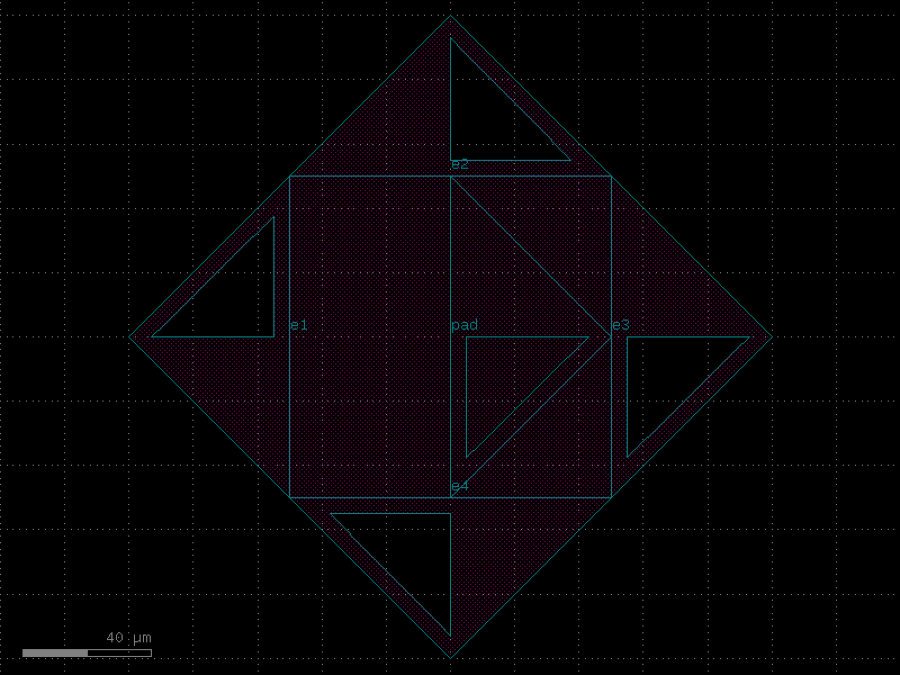
- gdsfactory.components.pads.pad_array(pad: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'pad', columns: int = 6, rows: int = 1, column_pitch: float = 150.0, row_pitch: float = 150.0, port_orientation: float = 0, size: tuple[float, float] | None = None, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum | None = 'MTOP', centered_ports: bool = False, auto_rename_ports: bool = False)Component
Returns 2D array of pads.
- Parameters
pad– pad element.columns– number of columns.rows– number of rows.column_pitch– x pitch.row_pitch– y pitch.port_orientation– port orientation in deg. None for low speed DC ports.size– pad size.layer– pad layer.centered_ports– True add ports to center. False add ports to the edge.auto_rename_ports– True to auto rename ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.pad_array(pad='pad', columns=6, rows=1, column_pitch=150, row_pitch=150, port_orientation=0, layer='MTOP', centered_ports=False, auto_rename_ports=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pads.pad_array0(pad: ComponentSpec = 'pad', *, columns: int = 1, rows: int = 3, column_pitch: float = 150.0, row_pitch: float = 150.0, port_orientation: AngleInDegrees = 0, size: Float2 | None = None, layer: LayerSpec | None = 'MTOP', centered_ports: bool = False, auto_rename_ports: bool = False)Component
Returns 2D array of pads.
- Parameters
pad– pad element.columns– number of columns.rows– number of rows.column_pitch– x pitch.row_pitch– y pitch.port_orientation– port orientation in deg. None for low speed DC ports.size– pad size.layer– pad layer.centered_ports– True add ports to center. False add ports to the edge.auto_rename_ports– True to auto rename ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.pad_array0(pad='pad', columns=1, rows=3, column_pitch=150, row_pitch=150, port_orientation=0, layer='MTOP', centered_ports=False, auto_rename_ports=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pads.pad_array180(pad: ComponentSpec = 'pad', *, columns: int = 1, rows: int = 3, column_pitch: float = 150.0, row_pitch: float = 150.0, port_orientation: AngleInDegrees = 180, size: Float2 | None = None, layer: LayerSpec | None = 'MTOP', centered_ports: bool = False, auto_rename_ports: bool = False)Component
Returns 2D array of pads.
- Parameters
pad– pad element.columns– number of columns.rows– number of rows.column_pitch– x pitch.row_pitch– y pitch.port_orientation– port orientation in deg. None for low speed DC ports.size– pad size.layer– pad layer.centered_ports– True add ports to center. False add ports to the edge.auto_rename_ports– True to auto rename ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.pad_array180(pad='pad', columns=1, rows=3, column_pitch=150, row_pitch=150, port_orientation=180, layer='MTOP', centered_ports=False, auto_rename_ports=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pads.pad_array270(pad: ComponentSpec = 'pad', columns: int = 6, rows: int = 1, column_pitch: float = 150.0, row_pitch: float = 150.0, *, port_orientation: AngleInDegrees = 270, size: Float2 | None = None, layer: LayerSpec | None = 'MTOP', centered_ports: bool = False, auto_rename_ports: bool = False)Component
Returns 2D array of pads.
- Parameters
pad– pad element.columns– number of columns.rows– number of rows.column_pitch– x pitch.row_pitch– y pitch.port_orientation– port orientation in deg. None for low speed DC ports.size– pad size.layer– pad layer.centered_ports– True add ports to center. False add ports to the edge.auto_rename_ports– True to auto rename ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.pad_array270(pad='pad', columns=6, rows=1, column_pitch=150, row_pitch=150, port_orientation=270, layer='MTOP', centered_ports=False, auto_rename_ports=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pads.pad_array90(pad: ComponentSpec = 'pad', columns: int = 6, rows: int = 1, column_pitch: float = 150.0, row_pitch: float = 150.0, *, port_orientation: AngleInDegrees = 90, size: Float2 | None = None, layer: LayerSpec | None = 'MTOP', centered_ports: bool = False, auto_rename_ports: bool = False)Component
Returns 2D array of pads.
- Parameters
pad– pad element.columns– number of columns.rows– number of rows.column_pitch– x pitch.row_pitch– y pitch.port_orientation– port orientation in deg. None for low speed DC ports.size– pad size.layer– pad layer.centered_ports– True add ports to center. False add ports to the edge.auto_rename_ports– True to auto rename ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.pad_array90(pad='pad', columns=6, rows=1, column_pitch=150, row_pitch=150, port_orientation=90, layer='MTOP', centered_ports=False, auto_rename_ports=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pads.pad_gsg_open(size: Float2 = (22, 7), layer_metal: LayerSpec = 'MTOP', metal_spacing: float = 5.0, *, short: bool = False, pad: ComponentSpec = 'pad', pad_pitch: float = 150, route_xsize: float = 50)gf.Component
Returns high speed GSG pads for calibrating the RF probes.
- Parameters
size– for the short.layer_metal– for the short.metal_spacing– in um.short– if False returns an open.pad– function for pad.pad_pitch– in um.route_xsize– in um.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.pad_gsg_open(size=(22, 7), layer_metal='MTOP', metal_spacing=5, short=False, pad='pad', pad_pitch=150, route_xsize=50).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()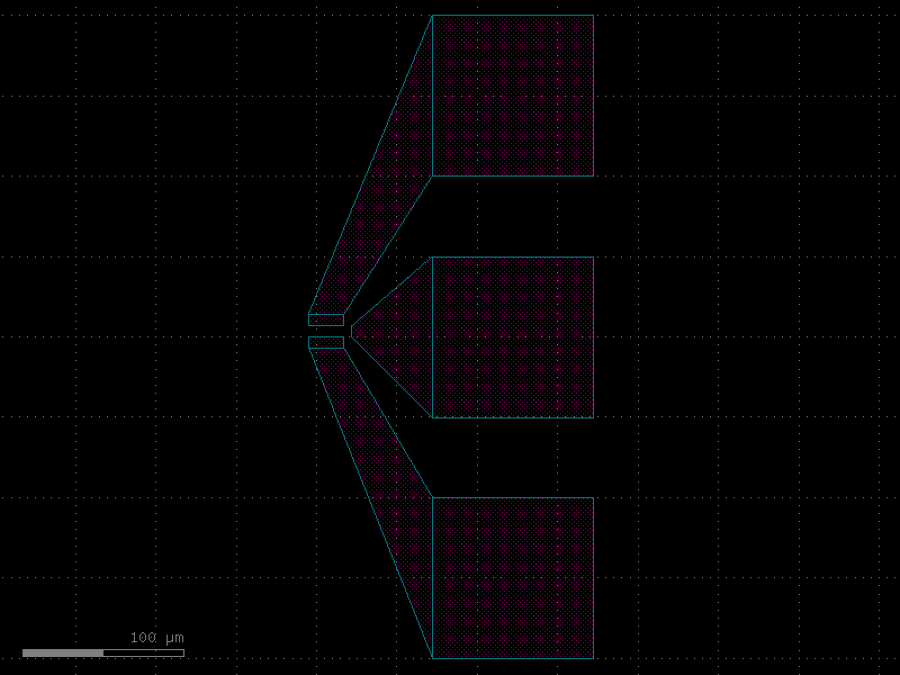
- gdsfactory.components.pads.pad_gsg_short(size: tuple[float, float] = (22, 7), layer_metal: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'MTOP', metal_spacing: float = 5.0, short: bool = True, pad: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'pad', pad_pitch: float = 150, route_xsize: float = 50)Component
Returns high speed GSG pads for calibrating the RF probes.
- Parameters
size– for the short.layer_metal– for the short.metal_spacing– in um.short– if False returns an open.pad– function for pad.pad_pitch– in um.route_xsize– in um.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.pad_gsg_short(size=(22, 7), layer_metal='MTOP', metal_spacing=5, short=True, pad='pad', pad_pitch=150, route_xsize=50).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()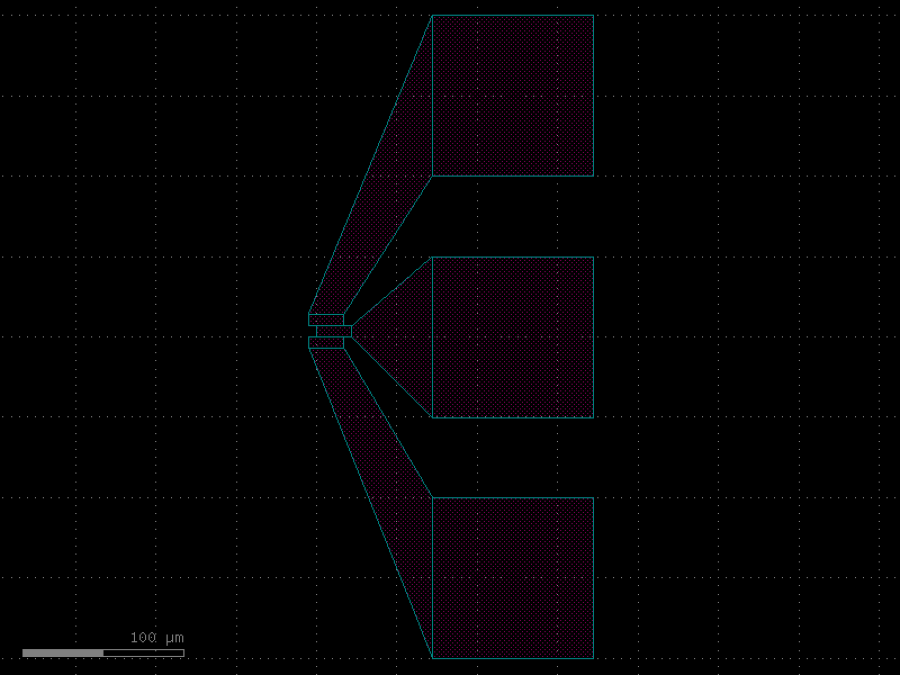
- gdsfactory.components.pads.pad_rectangular(*, size: Size | str = 'pad_size', layer: LayerSpec = 'MTOP', bbox_layers: tuple[LayerSpec, ...] | None = None, bbox_offsets: tuple[float, ...] | None = None, port_inclusion: float = 0, port_orientation: AngleInDegrees | None = 0, port_orientations: Ints | None = (180, 90, 0, -90), port_type: str = 'pad')Component
Returns rectangular pad with ports.
- Parameters
size– x, y size.layer– pad layer.bbox_layers– list of layers.bbox_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size.port_inclusion– from edge.port_orientation– in degrees for the center port.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.port_type– port type for pad port.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.pad_rectangular(size='pad_size', layer='MTOP', port_inclusion=0, port_orientation=0, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90), port_type='pad').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()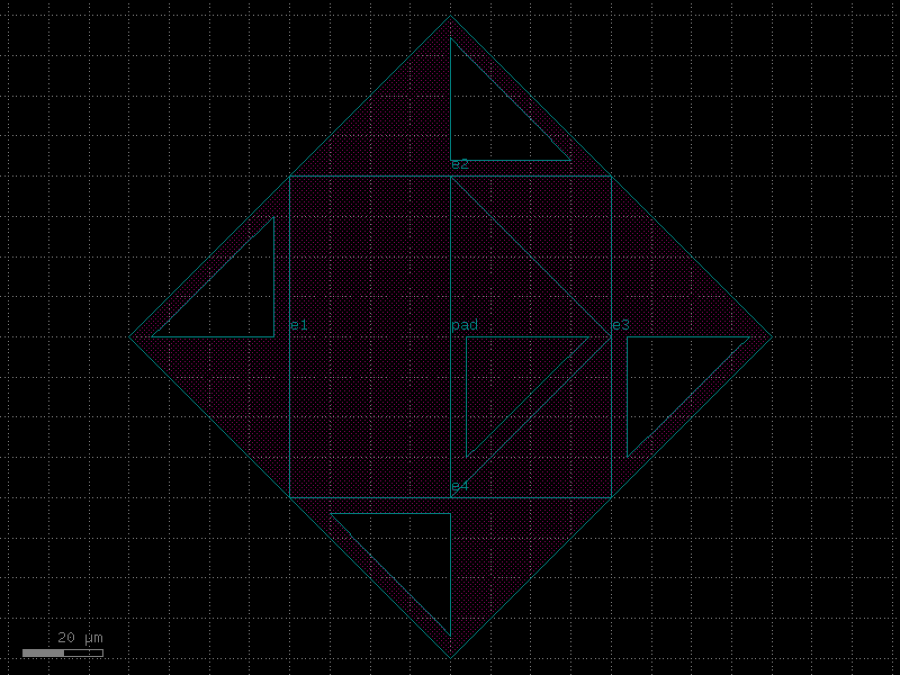
- gdsfactory.components.pads.pad_small(*, size: Size | str = (80, 80), layer: LayerSpec = 'MTOP', bbox_layers: tuple[LayerSpec, ...] | None = None, bbox_offsets: tuple[float, ...] | None = None, port_inclusion: float = 0, port_orientation: AngleInDegrees | None = 0, port_orientations: Ints | None = (180, 90, 0, -90), port_type: str = 'pad')Component
Returns rectangular pad with ports.
- Parameters
size– x, y size.layer– pad layer.bbox_layers– list of layers.bbox_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size.port_inclusion– from edge.port_orientation– in degrees for the center port.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.port_type– port type for pad port.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.pad_small(size=(80, 80), layer='MTOP', port_inclusion=0, port_orientation=0, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90), port_type='pad').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()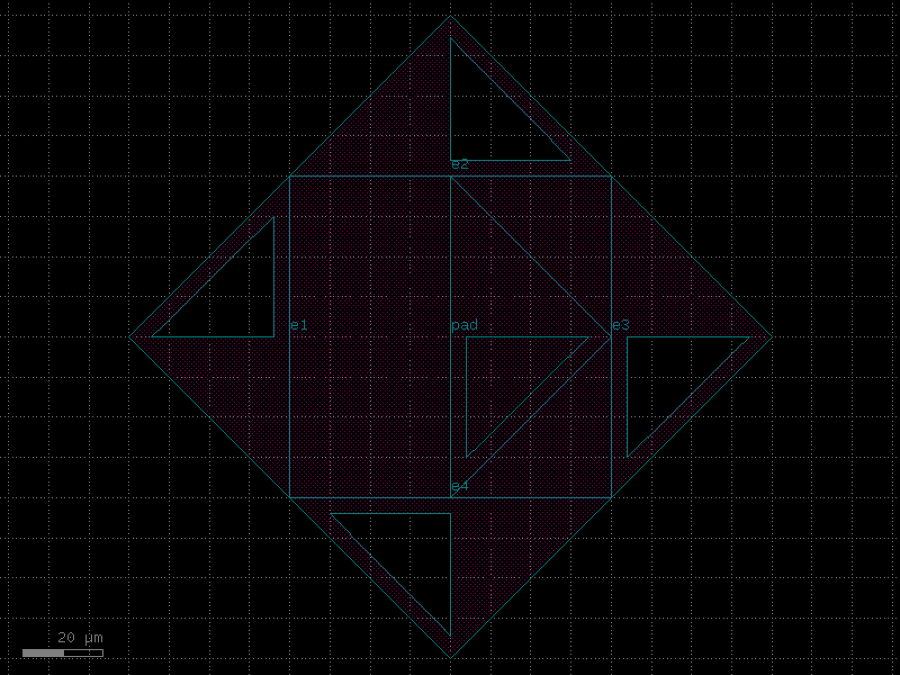
- gdsfactory.components.pads.pads_shorted(pad: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'pad', columns: int = 8, pad_pitch: float = 150.0, layer_metal: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'MTOP', metal_width: float = 10)Component
Returns a 1D array of shorted_pads.
- Parameters
pad– pad spec.columns– number of columns.pad_pitch– in umlayer_metal– for the short.metal_width– for the short.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.pads_shorted(pad='pad', columns=8, pad_pitch=150, layer_metal='MTOP', metal_width=10).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()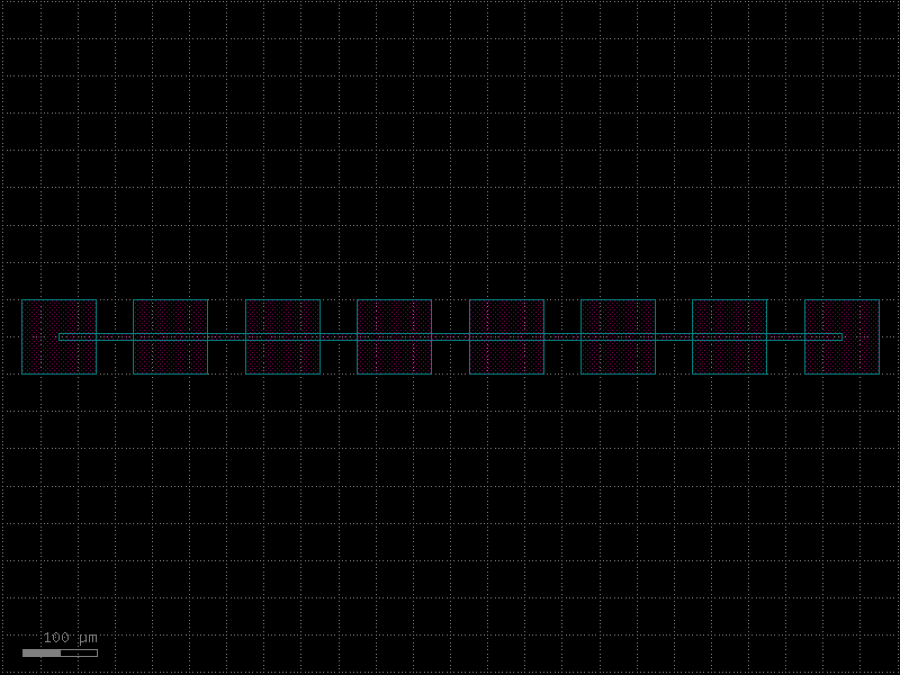
- gdsfactory.components.pads.rectangle_with_slits(size: tuple[float, float] = (100.0, 200.0), layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', layer_slit: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'SLAB150', centered: bool = False, port_type: str | None = None, slit_size: tuple[float, float] = (1.0, 1.0), slit_column_pitch: float = 20, slit_row_pitch: float = 20, slit_enclosure: float = 10)Component
Returns a rectangle with slits.
Metal slits reduce stress.
- Parameters
size– (tuple) Width and height of rectangle.layer– Specific layer to put polygon geometry on.layer_slit– does a boolean NOT when None.centered– True sets center to (0, 0), False sets south-west to (0, 0)port_type– for the rectangle.slit_size– x, y slit size.slit_column_pitch– pitch for columns of slits.slit_row_pitch– pitch for rows of slits.slit_enclosure– from slit to rectangle edge.
slit_enclosure _____________________________________ |<---> | | | | ______________________ | | | | | | | | slit_size[1] | _ |______________________| | | | | | | slit_row_pitch | | | | size[1] | | ______________________ | | | | | | | | | | | | _ |______________________| | | <---------------------> | | slit_size[0] | |___________________________________| size[0]
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.rectangle_with_slits(size=(100, 200), layer='WG', layer_slit='SLAB150', centered=False, slit_size=(1, 1), slit_column_pitch=20, slit_row_pitch=20, slit_enclosure=10).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
pcms¶
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cavity(component: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'dbr', coupler: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'coupler', length: float = 0.1, gap: float = 0.2, **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns cavity from a coupler and a mirror.
connects the W0 port of the mirror to E1 and W1 coupler ports creating a resonant cavity
- Parameters
component– mirror.coupler– coupler library.length– coupler length.gap– coupler gap.kwargs– coupler_settings.
ml (mirror left) mr (mirror right) | | |o1 - o2__ __o3 - o1| | \ / | \ / ---=========--- o1 o1 length o4 o2
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cavity(component='dbr', coupler='coupler', length=0.1, gap=0.2).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()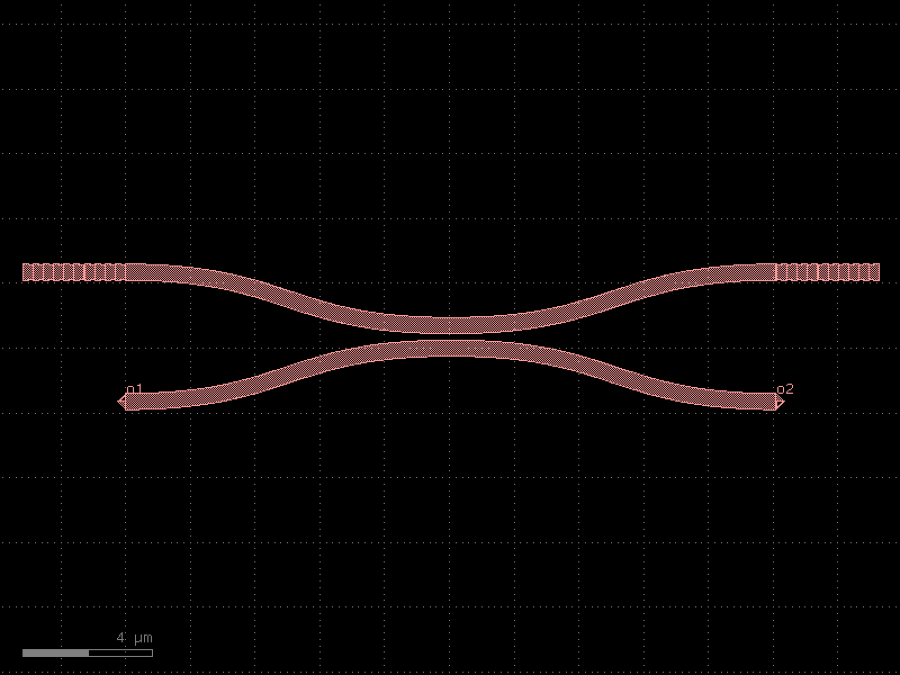
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cdsem_all(widths: tuple[float, ...] = (0.4, 0.45, 0.5, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0), dense_lines_width: float | None = 0.3, dense_lines_width_difference: float = 0.02, dense_lines_gap: float = 0.3, dense_lines_labels: tuple[str, ...] = ('DL', 'DM', 'DH'), straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', bend90: ComponentSpec | None = 'bend_circular', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', text: ComponentSpec = 'text_rectangular', spacing: float = 5, cdsem_bend180: ComponentSpec = 'cdsem_bend180', text_size: float = 1)Component
Column with all optical PCMs.
- Parameters
widths– for straight lines.dense_lines_width– in um.dense_lines_width_difference– in um.dense_lines_gap– in um.dense_lines_labels– strings.straight– spec.bend90– spec.cross_section– spec.text– spec.spacing– from group to group.cdsem_bend180– spec.text_size– in um.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cdsem_all(widths=(0.4, 0.45, 0.5, 0.6, 0.8, 1), dense_lines_width=0.3, dense_lines_width_difference=0.02, dense_lines_gap=0.3, dense_lines_labels=('DL', 'DM', 'DH'), straight='straight', bend90='bend_circular', cross_section='strip', text='text_rectangular', spacing=5, cdsem_bend180='cdsem_bend180', text_size=1).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cdsem_bend180(width: float = 0.5, radius: float = 10.0, wg_length: float | None = 420.0, straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', bend90: ComponentSpec = 'bend_circular', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', text: ComponentSpec = 'text_rectangular', text_size: float = 1.0)Component
Returns CDSEM structures.
- Parameters
width– of the line.radius– um.wg_length– in um.straight– spec.bend90– spec.cross_section– spec.text– spec.text_size– um.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cdsem_bend180(width=0.5, radius=10, wg_length=420, straight='straight', bend90='bend_circular', cross_section='strip', text='text_rectangular', text_size=1).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()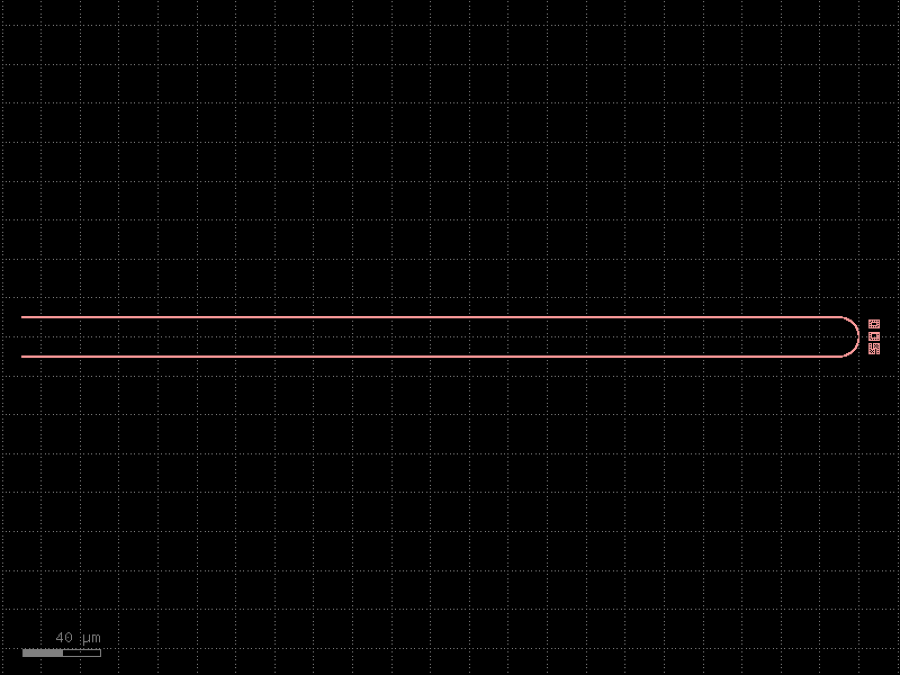
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cdsem_coupler(length: float = 420.0, gaps: Sequence[float] = (0.15, 0.2, 0.25), cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_no_ports', text: ComponentSpec | None = 'text_rectangular', spacing: float = 7.0, positions: Sequence[float | None] | None = None, width: float | None = None, text_size: float = 1.0)Component
Returns 2 coupled waveguides gap sweep.
- Parameters
length– for the line.gaps– list of gaps for the sweep.cross_section– for the lines.text– optional text for labels.spacing– Optional center to center spacing.positions– Optional positions for the text labels.width– width of the waveguide. If None, it will use the width of the cross_section.text_size– size of the text.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cdsem_coupler(length=420, gaps=(0.15, 0.2, 0.25), cross_section='strip_no_ports', text='text_rectangular', spacing=7, text_size=1).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cdsem_straight(widths: Sequence[float] = (0.4, 0.45, 0.5, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0), length: float = 420.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_no_ports', text: ComponentSpec | None = 'text_rectangular', spacing: float = 7.0, positions: Sequence[float | None] | None = None, text_size: float = 1)Component
Returns straight waveguide lines width sweep.
- Parameters
widths– for the sweep.length– for the line.cross_section– for the lines.text– optional text for labels.spacing– Optional center to center spacing.positions– Optional positions for the text labels.text_size– in um.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cdsem_straight(widths=(0.4, 0.45, 0.5, 0.6, 0.8, 1), length=420, cross_section='strip_no_ports', text='text_rectangular', spacing=7, text_size=1).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cdsem_straight_density(widths: Floats = (0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3), gaps: Floats = (0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3), length: float = 420.0, label: str = '', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_no_ports', text: ComponentSpec | None = 'text_rectangular', text_size: float = 1.0)Component
Returns sweep of dense straight lines.
- Parameters
widths– list of widths.gaps– list of gaps.length– of the lines.label– defaults to widths[0] gaps[0].cross_section– spec.text– optional function for text.text_size– size of the text.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cdsem_straight_density(widths=(0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3), gaps=(0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3), length=420, label='', cross_section='strip_no_ports', text='text_rectangular', text_size=1).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cutback_2x2(component: ComponentSpec = 'mmi2x2', cols: int = 4, rows: int = 5, port1: str = 'o1', port2: str = 'o2', port3: str = 'o3', port4: str = 'o4', bend180: ComponentSpec = 'bend_circular180', mirror: bool = False, straight_length: float | None = None, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight')Component
Returns a daisy chain of splitters for measuring their loss.
- Parameters
component– for cutback.cols– number of columns.rows– number of rows.port1– name of first optical port.port2– name of second optical port.port3– name of third optical port.port4– name of fourth optical port.bend180– ubend.mirror– Flips component. Useful when ‘o2’ is the port that you want to route to.straight_length– length of the straight section between cutbacks.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string or dict).straight– straight spec.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cutback_2x2(component='mmi2x2', cols=4, rows=5, port1='o1', port2='o2', port3='o3', port4='o4', bend180='bend_circular180', mirror=False, cross_section='strip', straight='straight').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()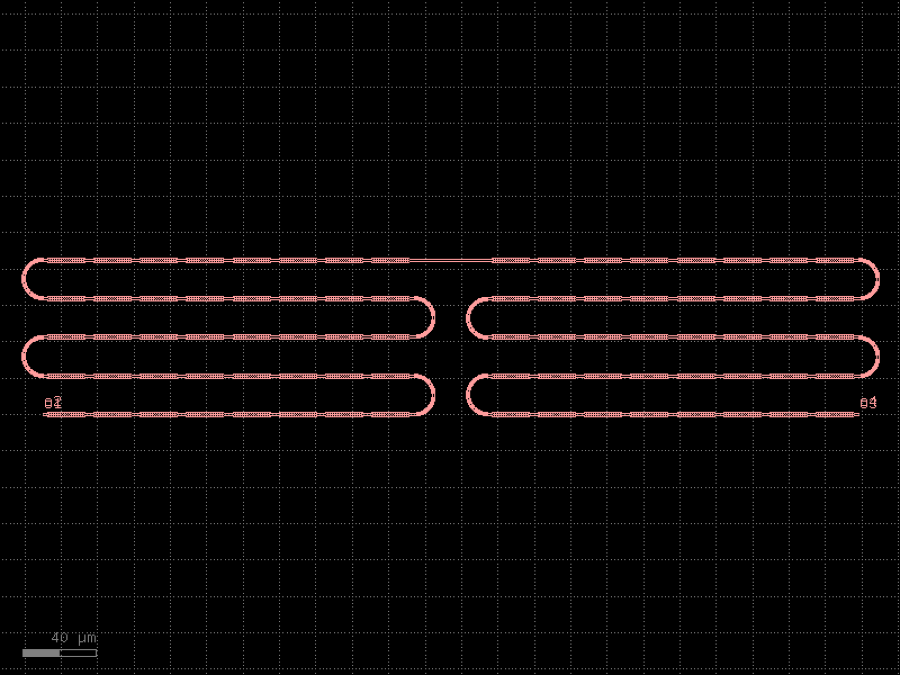
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cutback_bend(component: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'bend_euler', straight: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'straight', straight_length: float = 5.0, rows: int = 6, cols: int = 5, **kwargs: Any)Component
We recommend using cutback_bend90 instead for a smaller footprint.
- Parameters
component– bend spec.straight– straight spec.straight_length– in um.rows– number of rows.cols– number of cols.kwargs– cross_section settings.
this is a column _ _| _| _ this is a row
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cutback_bend(component='bend_euler', straight='straight', straight_length=5, rows=6, cols=5).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()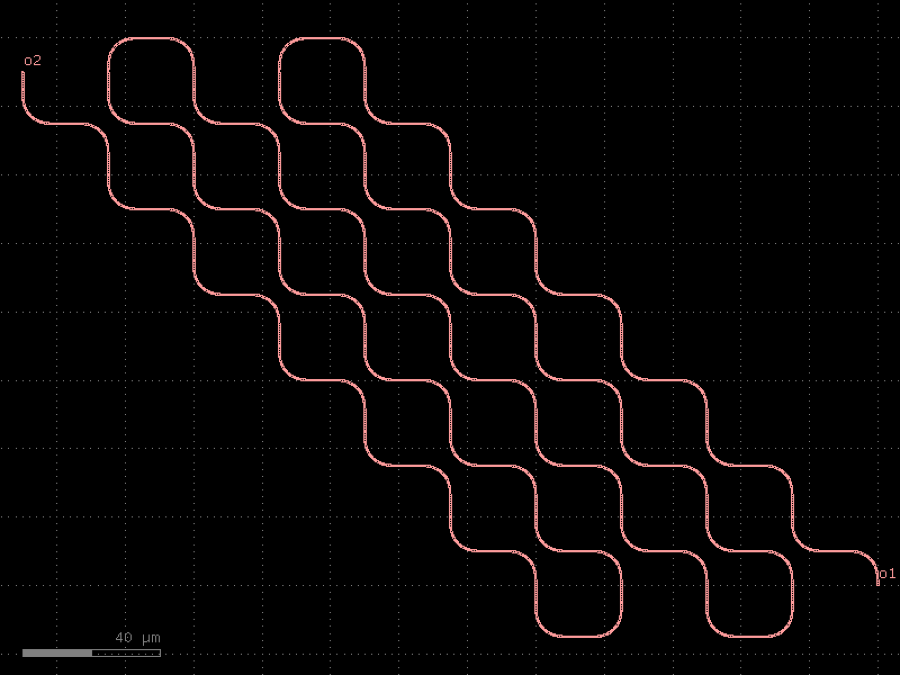
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cutback_bend180(component: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'bend_euler180', straight: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'straight', straight_length: float = 5.0, rows: int = 6, cols: int = 6, spacing: float = 3.0, **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns cutback to measure u bend loss.
- Parameters
component– bend spec.straight– straight spec.straight_length– in um.rows– number of rows.cols– number of cols.spacing– in um.kwargs– cross_section settings.
_ _| |_ this is a row _ this is a column
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cutback_bend180(component='bend_euler180', straight='straight', straight_length=5, rows=6, cols=6, spacing=3).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()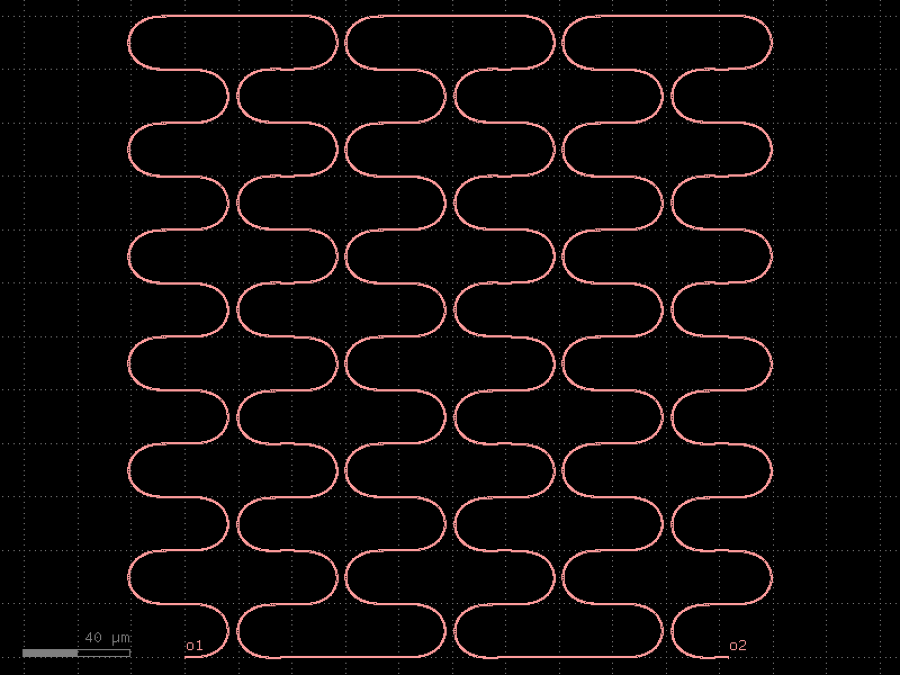
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cutback_bend180circular(*, component: ComponentSpec = 'bend_circular180', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', straight_length: float = 5.0, rows: int = 6, cols: int = 6, spacing: float = 3.0, **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns cutback to measure u bend loss.
- Parameters
component– bend spec.straight– straight spec.straight_length– in um.rows– number of rows.cols– number of cols.spacing– in um.kwargs– cross_section settings.
_ _| |_ this is a row _ this is a column
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cutback_bend180circular(component='bend_circular180', straight='straight', straight_length=5, rows=6, cols=6, spacing=3).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()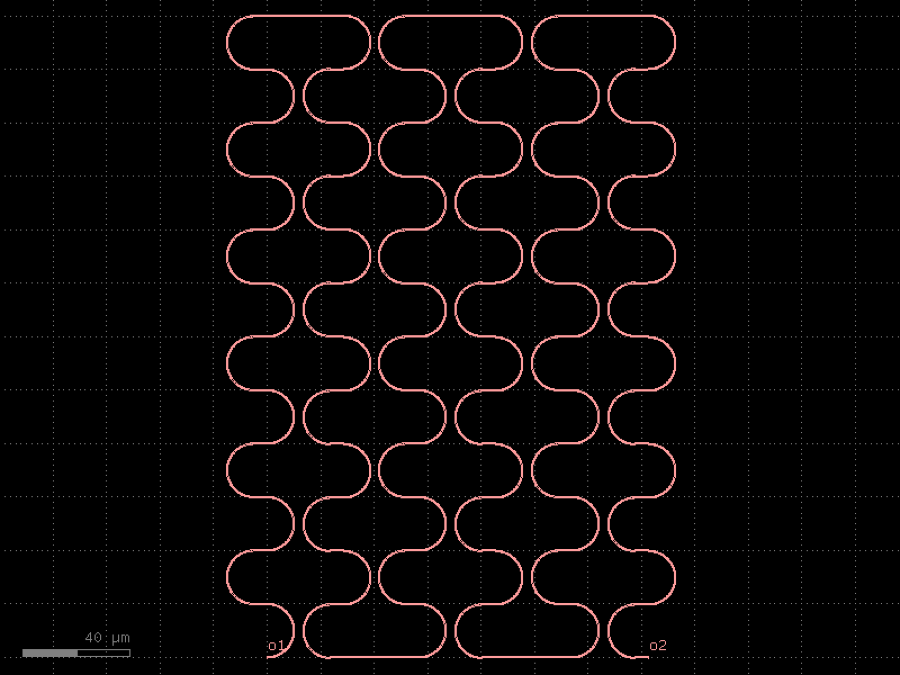
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cutback_bend90(component: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'bend_euler', straight: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'straight', straight_length: float = 5.0, rows: int = 6, cols: int = 6, spacing: int = 5, **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns bend90 cutback.
- Parameters
component– bend spec.straight– straight spec.straight_length– in um.rows– number of rows.cols– number of cols.spacing– in um.kwargs– cross_section settings.
_ |_| |
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cutback_bend90(component='bend_euler', straight='straight', straight_length=5, rows=6, cols=6, spacing=5).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()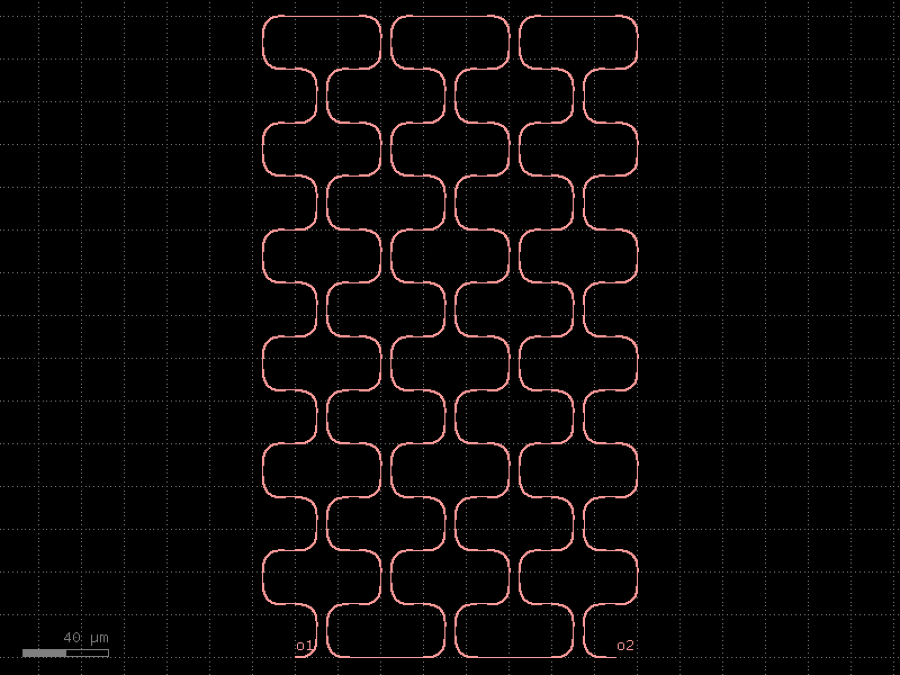
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cutback_bend90circular(*, component: ComponentSpec = 'bend_circular', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', straight_length: float = 5.0, rows: int = 6, cols: int = 6, spacing: int = 5, **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns bend90 cutback.
- Parameters
component– bend spec.straight– straight spec.straight_length– in um.rows– number of rows.cols– number of cols.spacing– in um.kwargs– cross_section settings.
_ |_| |
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cutback_bend90circular(component='bend_circular', straight='straight', straight_length=5, rows=6, cols=6, spacing=5).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()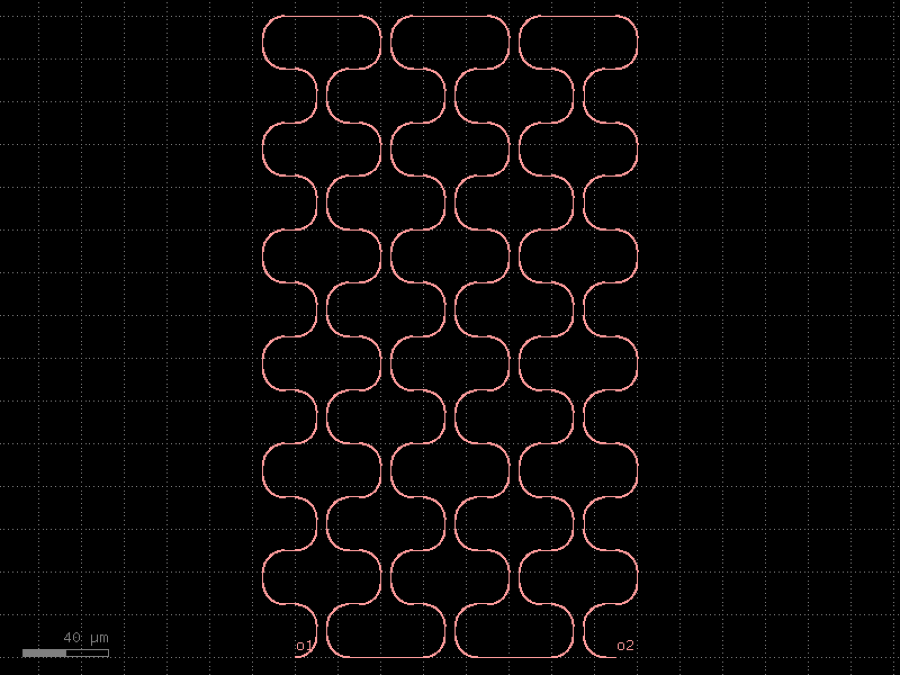
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cutback_component(component: ComponentSpec = 'taper_0p5_to_3_l36', cols: int = 4, rows: int = 5, port1: str = 'o1', port2: str = 'o2', bend180: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler180', mirror: bool = False, mirror1: bool = False, mirror2: bool = False, straight_length: float | None = None, straight_length_pair: float | None = None, straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns a daisy chain of components for measuring their loss.
Works only for components with 2 ports (input, output).
- Parameters
component– for cutback.cols– number of columns.rows– number of rows.port1– name of first optical port.port2– name of second optical port.bend180– ubend.mirror– Flips component. Useful when ‘o2’ is the port that you want to route to.mirror1– mirrors first component.mirror2– mirrors second component.straight_length– length of the straight section between cutbacks.straight_length_pair– length of the straight section between each component pair.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string or dict).straight– straight spec.kwargs– component settings.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cutback_component(component='taper_0p5_to_3_l36', cols=4, rows=5, port1='o1', port2='o2', bend180='bend_euler180', mirror=False, mirror1=False, mirror2=False, straight='straight', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()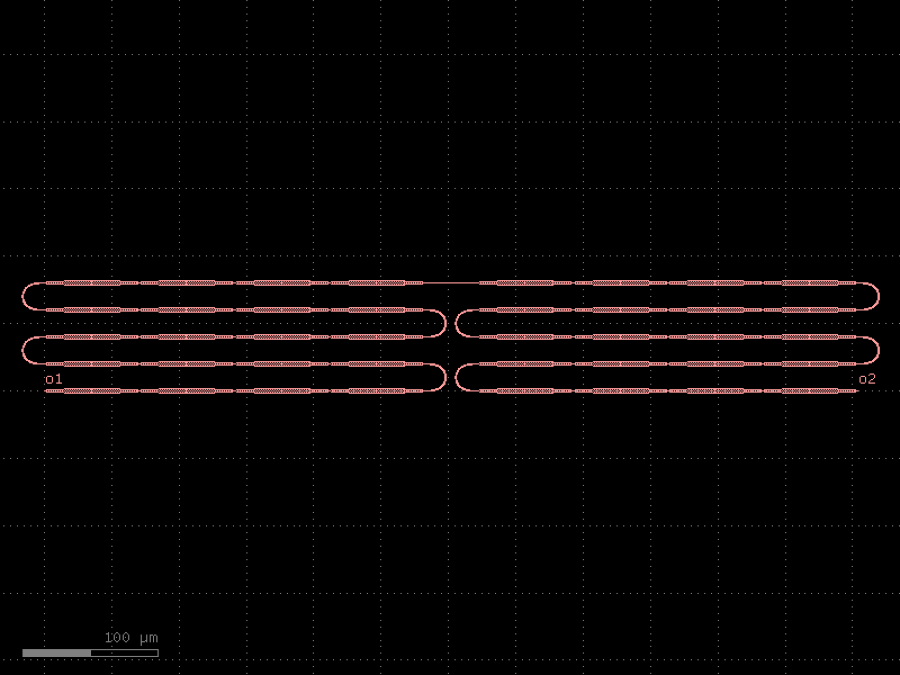
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cutback_component_mirror(component: ComponentSpec = 'taper_0p5_to_3_l36', cols: int = 4, rows: int = 5, port1: str = 'o1', port2: str = 'o2', bend180: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler180', *, mirror: bool = True, mirror1: bool = False, mirror2: bool = False, straight_length: float | None = None, straight_length_pair: float | None = None, straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns a daisy chain of components for measuring their loss.
Works only for components with 2 ports (input, output).
- Parameters
component– for cutback.cols– number of columns.rows– number of rows.port1– name of first optical port.port2– name of second optical port.bend180– ubend.mirror– Flips component. Useful when ‘o2’ is the port that you want to route to.mirror1– mirrors first component.mirror2– mirrors second component.straight_length– length of the straight section between cutbacks.straight_length_pair– length of the straight section between each component pair.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string or dict).straight– straight spec.kwargs– component settings.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cutback_component_mirror(component='taper_0p5_to_3_l36', cols=4, rows=5, port1='o1', port2='o2', bend180='bend_euler180', mirror=True, mirror1=False, mirror2=False, straight='straight', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()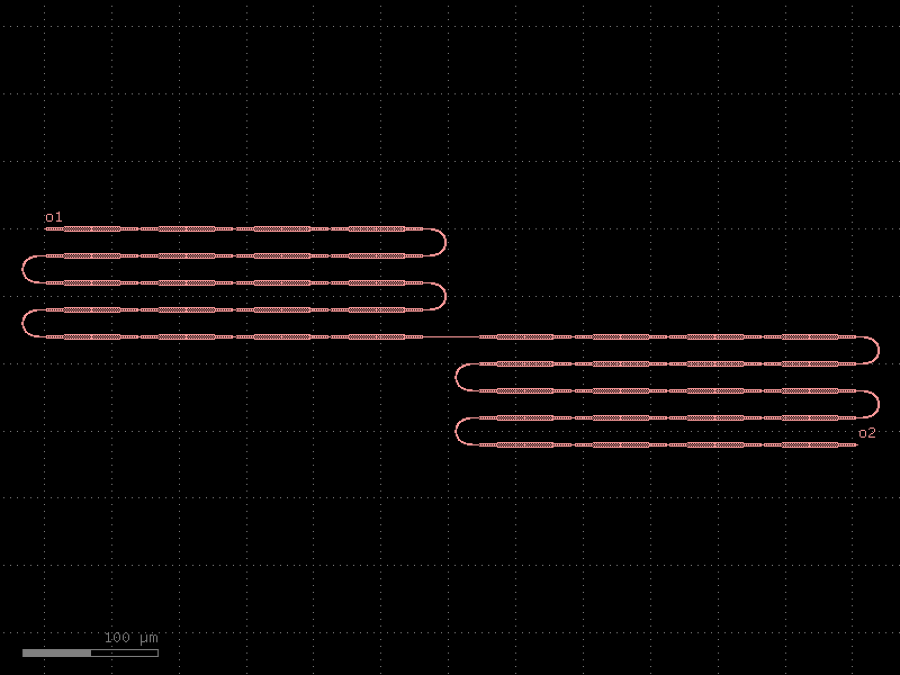
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.cutback_splitter(component: ComponentSpec = 'mmi1x2', cols: int = 4, rows: int = 5, port1: str = 'o1', port2: str = 'o2', port3: str = 'o3', bend180: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler180', mirror: bool = False, straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', straight_length: float | None = None, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns a daisy chain of splitters for measuring their loss.
- Parameters
component– for cutback.cols– number of columns.rows– number of rows.port1– name of first optical port.port2– name of second optical port.port3– name of third optical port.bend180– ubend.mirror– Flips component. Useful when ‘o2’ is the port that you want to route to.straight– waveguide spec to connect both sides.straight_length– length of the straight section between cutbacks.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string or dict).kwargs– cross_section settings.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cutback_splitter(component='mmi1x2', cols=4, rows=5, port1='o1', port2='o2', port3='o3', bend180='bend_euler180', mirror=False, straight='straight', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()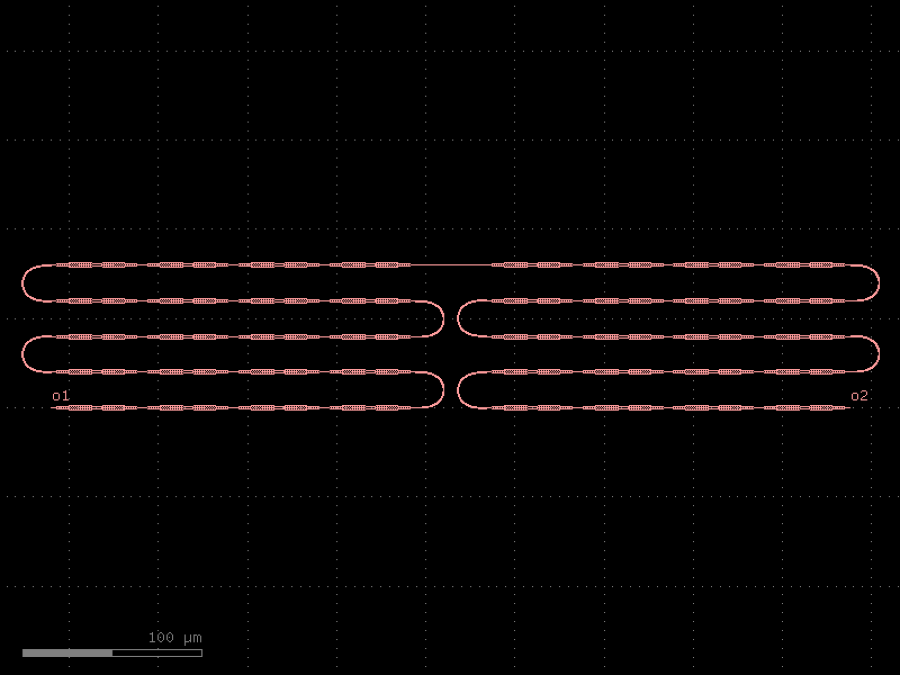
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.greek_cross(length: float = 30, layers: Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum] = ('WG', 'N'), widths: Sequence[float] = (2.0, 3.0), offsets: Sequence[float] | None = None, via_stack: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'via_stack_npp_m1', layer_index: int = 0)Component
Simple greek cross with via stacks at the endpoints.
Process control monitor for dopant sheet resistivity and linewidth variation.
- Parameters
length– length of cross arms.layers– list of layers.widths– list of widths (same order as layers).offsets– how much to extend each layer beyond the cross length negative shorter, positive longer.via_stack– via component to attach to the cross.layer_index– index of the layer to connect the via_stack to.
via_stack <-------> _________ length ________ | |<-------------------->| 2x | | | ↓ |<-->| | |======== width =======| |_______|<--> | ↑ |<-->|________ offset offsetReferences: - Walton, Anthony J.. “MICROELECTRONIC TEST STRUCTURES.” (1999). - W. Versnel, Analysis of the Greek cross, a Van der Pauw structure with finite
contacts, Solid-State Electronics, Volume 22, Issue 11, 1979, Pages 911-914, ISSN 0038-1101, Versnel (1979).
Enderling et al., “Sheet resistance measurement of non-standard cleanroom
materials using suspended Greek cross test structures,” IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 2-9, Feb. 2006, doi: 10.1109/TSM.2005.863248.
https://
download .tek .com /document /S530 _VanDerPauwSheetRstnce .pdf
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.greek_cross(length=30, layers=('WG', 'N'), widths=(2, 3), via_stack='via_stack_npp_m1', layer_index=0).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()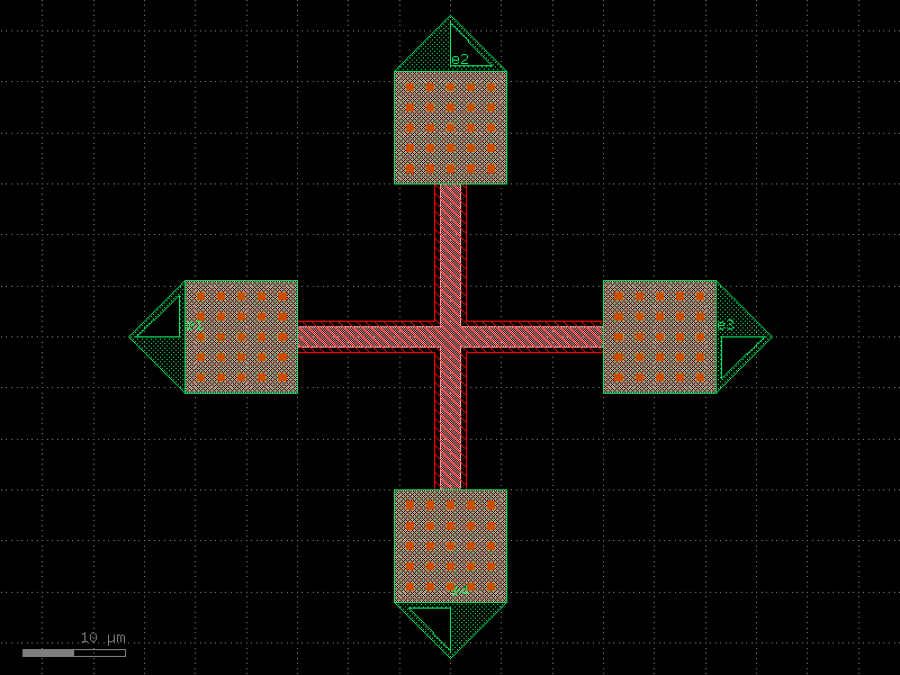
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.greek_cross_with_pads(pad: str | ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], ~gdsfactory.component.Component] | dict[str, ~typing.Any] | ~kfactory.kcell.DKCell = 'pad', pad_pitch: float = 150.0, greek_cross_component: str | ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], ~gdsfactory.component.Component] | dict[str, ~typing.Any] | ~kfactory.kcell.DKCell = 'greek_cross', pad_via: str | ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], ~gdsfactory.component.Component] | dict[str, ~typing.Any] | ~kfactory.kcell.DKCell = 'via_stack_m1_mtop', cross_section: ~gdsfactory.cross_section.CrossSection | str | dict[str, ~typing.Any] | ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], CrossSection] | ~kfactory.cross_section.SymmetricalCrossSection | ~kfactory.cross_section.DCrossSection = <function metal1>, pad_port_name: str = 'e4')Component
Greek cross under 4 DC pads, ready to test.
- Parameters
pad– component to use for probe pads.pad_pitch– spacing between pads.greek_cross_component– component to use for greek cross.pad_via– via to add to the pad.cross_section– cross-section for cross via to pad via wiring.pad_port_name– name of the port to connect to the greek cross.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.greek_cross_with_pads(pad='pad', pad_pitch=150, greek_cross_component='greek_cross', pad_via='via_stack_m1_mtop', pad_port_name='e4').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.litho_calipers(notch_size: tuple[float, float] = (2.0, 5.0), notch_spacing: float = 2.0, num_notches: int = 11, offset_per_notch: float = 0.1, row_spacing: float = 0.0, layer1: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', layer2: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'SLAB150')Component
Vernier caliper structure to test lithography alignment.
Only the middle finger is aligned and the rest are offset. adapted from phidl
- Parameters
notch_size– [xwidth, yheight].notch_spacing– in um.num_notches– number of notches.offset_per_notch– in um.row_spacing– 0layer1– layer.layer2– layer.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.litho_calipers(notch_size=(2, 5), notch_spacing=2, num_notches=11, offset_per_notch=0.1, row_spacing=0, layer1='WG', layer2='SLAB150').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.litho_ruler(height: float = 2, width: float = 0.5, spacing: float = 2.0, scale: tuple[float, ...] = (3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1), num_marks: int = 21, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG')Component
Ruler structure for lithographic measurement.
Includes marks of varying scales to allow for easy reading by eye.
based on phidl.geometry
- Parameters
height– Height of the ruling marks in um.width– Width of the ruling marks in um.spacing– Center-to-center spacing of the ruling marks in um.scale– Height scale pattern of marks.num_marks– Total number of marks to generate.layer– Specific layer to put the ruler geometry on.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.litho_ruler(height=2, width=0.5, spacing=2, scale=(3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1), num_marks=21, layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.litho_steps(line_widths: tuple[float, ...] = (1.0, 2.0, 4.0, 8.0, 16.0), line_spacing: float = 10.0, height: float = 100.0, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG')Component
Positive + negative tone linewidth test.
used for lithography resolution test patterning based on phidl
- Parameters
line_widths– in um.line_spacing– in um.height– in um.layer– Specific layer to put the ruler geometry on.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.litho_steps(line_widths=(1, 2, 4, 8, 16), line_spacing=10, height=100, layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()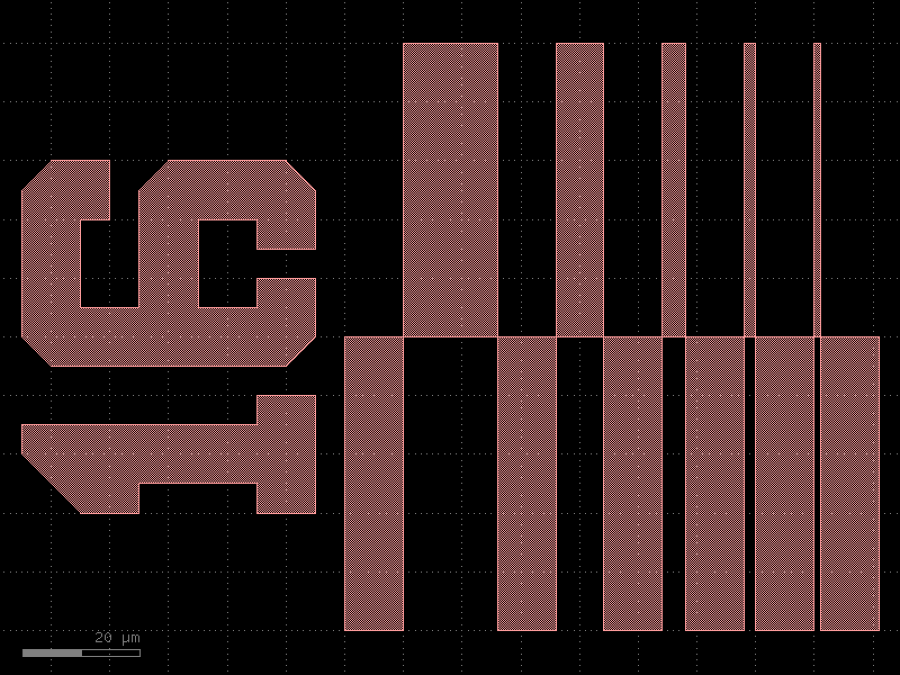
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.pixel(size: int = 1, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG')Component
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.pixel(size=1, layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.qrcode(data: str = 'mask01', psize: int = 1, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG')Component
Returns QRCode.
- Parameters
data– string to encode.psize– pixel size.layer– layer to use.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.qrcode(data='mask01', psize=1, layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.resistance_meander(pad_size: tuple[float, float] = (50.0, 50.0), num_squares: int = 1000, width: float = 1.0, res_layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'MTOP', pad_layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'MTOP')Component
Return meander to test resistance.
based on phidl.geometry
- Parameters
pad_size– Size of the two matched impedance pads (microns).num_squares– Number of squares comprising the resonator wire.width– The width of the squares (microns).res_layer– resistance layer.pad_layer– pad layer.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.resistance_meander(pad_size=(50, 50), num_squares=1000, width=1, res_layer='MTOP', pad_layer='MTOP').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.resistance_sheet(width: float = 10.0, layers: Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum] = ('HEATER',), layer_offsets: Sequence[float] = (0, 0.2), pad: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'via_stack_heater_mtop', pad_size: tuple[float, float] = (50.0, 50.0), pad_pitch: float = 100.0, ohms_per_square: float | None = None, pad_port_name: str = 'e4')Component
Returns Sheet resistance.
keeps connectivity for pads and first layer in layers
- Parameters
width– in um.layers– for the middle part.layer_offsets– from edge, positive: over, negative: inclusion.pad– function to create a pad.pad_size– in um.pad_pitch– in um.ohms_per_square– optional sheet resistance to compute info.resistance.pad_port_name– port name for the pad.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.resistance_sheet(width=10, layers=('HEATER',), layer_offsets=(0, 0.2), pad='via_stack_heater_mtop', pad_size=(50, 50), pad_pitch=100, pad_port_name='e4').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.staircase(component: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | Component = 'bend_euler', straight: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'straight', length_v: float = 5.0, length_h: float = 5.0, rows: int = 4, **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns staircase.
- Parameters
component– bend spec.straight– straight spec.length_v– vertical length.length_h– vertical length.rows– number of rows.cols– number of cols.kwargs– cross_section settings.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.staircase(component='bend_euler', straight='straight', length_v=5, length_h=5, rows=4).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()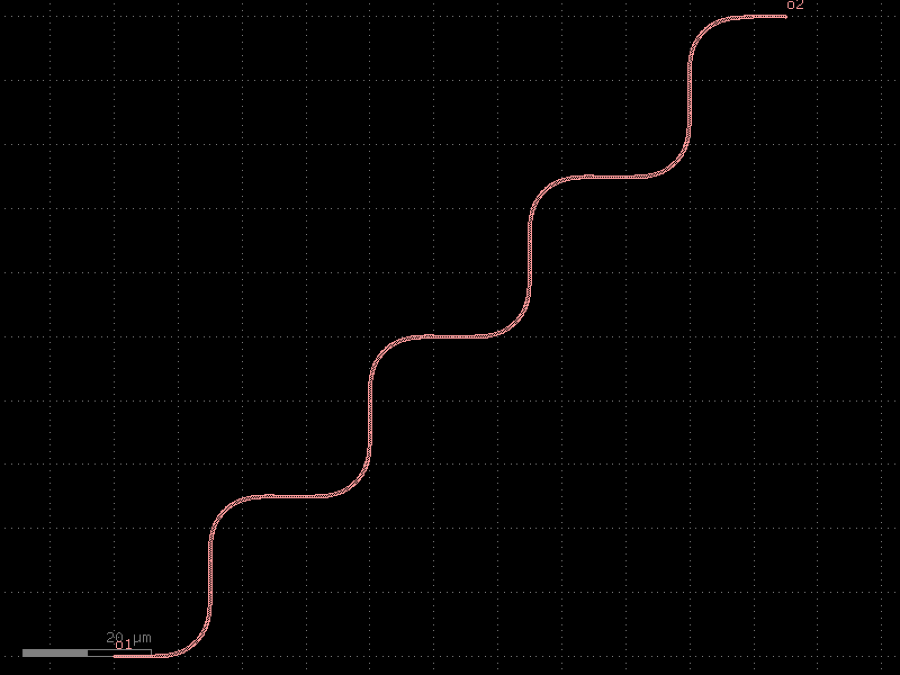
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.verniers(widths: Floats = (0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5), gap: float = 0.1, xsize: float = 100.0, layer_label: LayerSpec = 'TEXT', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_no_ports', **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns a component with verniers.
- Parameters
widths– list of widths.gap– gap between verniers.xsize– size of the component.layer_label– layer for the labels.straight– straight function.cross_section– cross_section spec.kwargs– straight settings.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.verniers(widths=(0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5), gap=0.1, xsize=100, layer_label='TEXT', straight='straight', cross_section='strip_no_ports').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.pcms.version_stamp(labels: tuple[str, ...] = ('demo_label',), with_qr_code: bool = False, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', pixel_size: int = 1, version: str | None = None, text_size: int = 10)Component
Component with module version and date.
- Parameters
labels– Iterable of labels.with_qr_code– Whether to add a QR code with the date.layer– Layer to use.pixel_size– Pixel size.version– Version string.text_size– Text size.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.version_stamp(labels=('demo_label',), with_qr_code=False, layer='WG', pixel_size=1, text_size=10).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
rings¶
- gdsfactory.components.rings.coupler_bend(radius: float = 10.0, coupler_gap: float = 0.2, coupling_angle_coverage: float = 120.0, cross_section_inner: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_outer: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', bend: AnyComponentFactory = <kfactory.decorators.WrappedVKCellFunc object>, bend_output: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler')Component
Compact curved coupler with bezier escape.
TODO: fix for euler bends.
- Parameters
radius– um.coupler_gap– um.coupling_angle_coverage– degrees.cross_section_inner– spec inner bend.cross_section_outer– spec outer bend.bend– for bend.bend_output– for bend.
r 4 | | | / ___3 | / / 2____/ / 1_____/
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler_bend(radius=10, coupler_gap=0.2, coupling_angle_coverage=120, cross_section_inner='strip', cross_section_outer='strip', bend_output='bend_euler').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()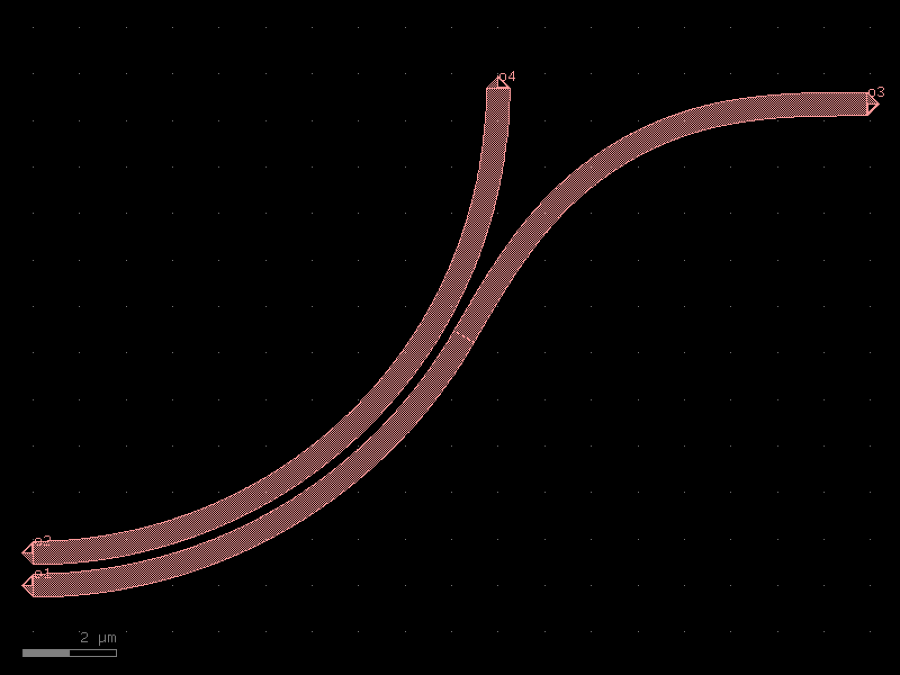
- gdsfactory.components.rings.coupler_ring_bend(radius: float = 10.0, coupler_gap: float = 0.2, coupling_angle_coverage: float = 90.0, length_x: float = 0.0, cross_section_inner: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_outer: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', bend: AnyComponentFactory = <kfactory.decorators.WrappedVKCellFunc object>, bend_output: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight')Component
Two back-to-back coupler_bend.
- Parameters
radius– um.coupler_gap– um.angle_inner– of the inner bend, from beginning to end. Depending on the bend chosen, gap may not be preserved.angle_outer– of the outer bend, from beginning to end. Depending on the bend chosen, gap may not be preserved.coupling_angle_coverage– degrees.length_x– horizontal straight length.cross_section_inner– spec inner bend.cross_section_outer– spec outer bend.bend– for bend.bend_output– for bend.straight– for straight.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.coupler_ring_bend(radius=10, coupler_gap=0.2, coupling_angle_coverage=90, length_x=0, cross_section_inner='strip', cross_section_outer='strip', bend_output='bend_euler', straight='straight').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()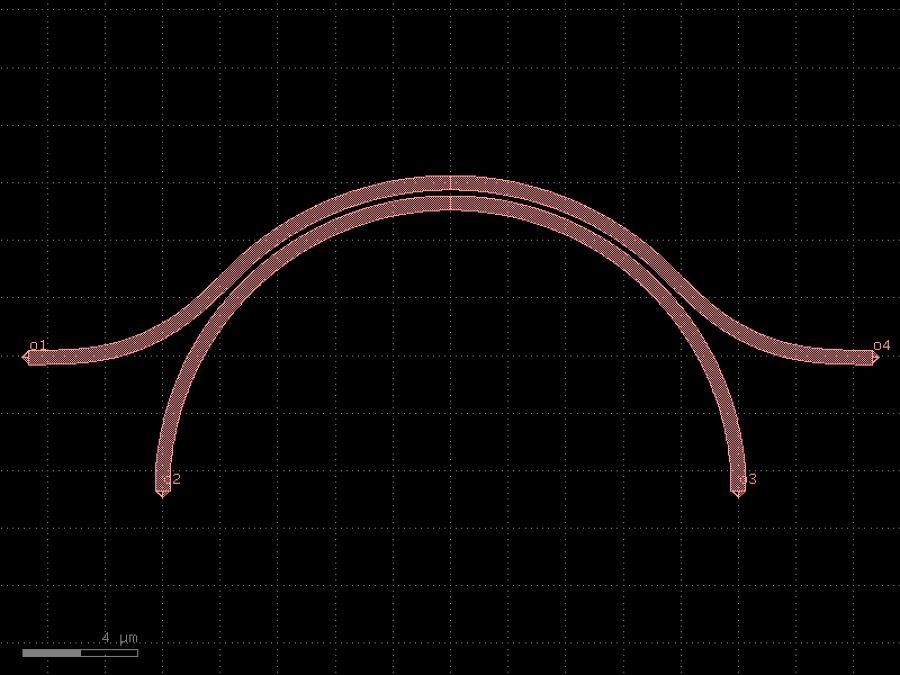
- gdsfactory.components.rings.disk(radius: float = 10.0, gap: float = 0.2, wrap_angle_deg: float = 180.0, parity: int = 1, cross_section: CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection = 'strip')Component
Disk Resonator.
- Parameters
radius– disk resonator radius.gap– Distance between the bus straight and resonator.wrap_angle_deg– Angle in degrees between 0 and 180. determines how much the bus straight wraps along the resonator. 0 corresponds to a straight bus straight. 180 corresponds to a bus straight wrapped around half of the resonator.parity(1or-1) – 1, resonator left from bus straight, -1 resonator to the right.cross_section– cross_section spec.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.disk(radius=10, gap=0.2, wrap_angle_deg=180, parity=1, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()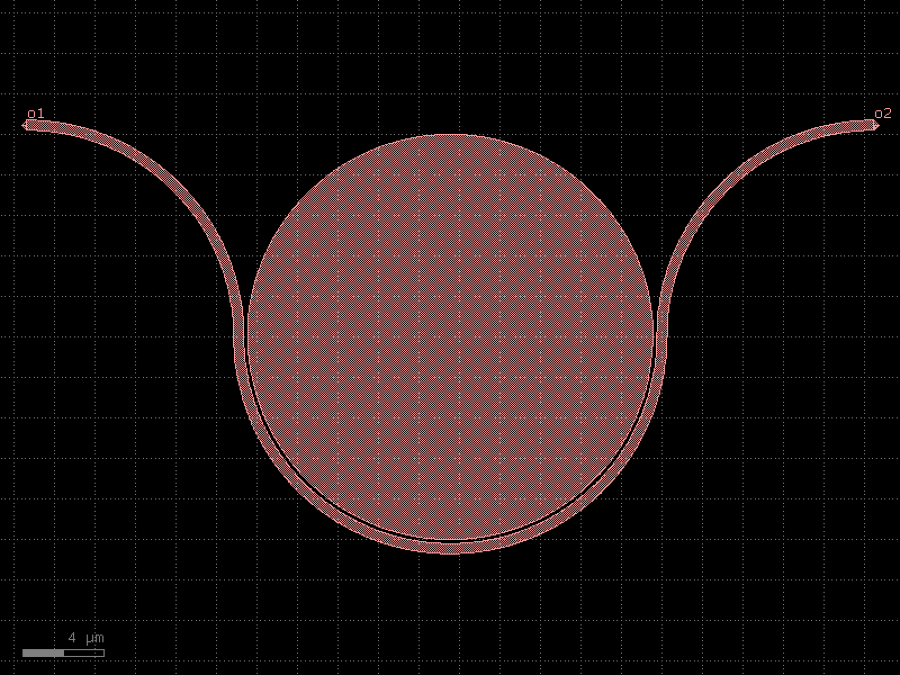
- gdsfactory.components.rings.disk_heater(radius: float = 10.0, gap: float = 0.2, wrap_angle_deg: float = 180.0, parity: int = 1, cross_section: CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection = 'strip', heater_layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'HEATER', via_stack: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'via_stack_heater_mtop', heater_width: float = 5.0, heater_extent: float = 2.0, via_width: float = 10.0, port_orientation: float | None = 90)Component
Disk Resonator with top metal heater.
- Parameters
radius– disk resonator radius.gap– Distance between the bus straight and resonator.wrap_angle_deg– Angle in degrees between 0 and 180. determines how much the bus straight wraps along the resonator. 0 corresponds to a straight bus straight. 180 corresponds to a bus straight wrapped around half of the resonator.parity(1or-1) – 1, resonator left from bus straight, -1 resonator to the right.cross_section– cross_section spec.heater_layer– layer of the heater.via_stack– via stack component.heater_width– width of the heater.heater_extent– length of heater beyond disk.via_width– size of the square via at the end of the heater.port_orientation– in degrees.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.disk_heater(radius=10, gap=0.2, wrap_angle_deg=180, parity=1, cross_section='strip', heater_layer='HEATER', via_stack='via_stack_heater_mtop', heater_width=5, heater_extent=2, via_width=10, port_orientation=90).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()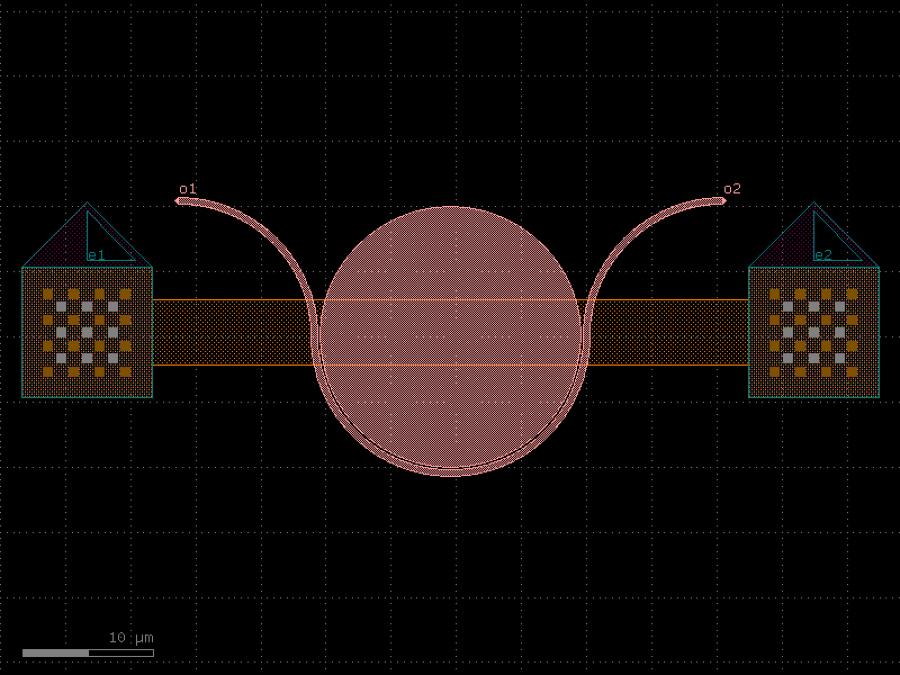
- gdsfactory.components.rings.ring(radius: float = 10.0, width: float = 0.5, angle_resolution: float = 2.5, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', angle: float = 360)Component
Returns a ring.
- Parameters
radius– ring radius.width– of the ring.angle_resolution– number of points per degree.layer– layer.angle– angular coverage of the ring
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ring(radius=10, width=0.5, angle_resolution=2.5, layer='WG', angle=360).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.rings.ring_crow(gaps: tuple[float, ...] = (0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2), radius: tuple[float, ...] = (10.0, 10.0, 10.0), bends: tuple[ComponentSpec, ...] | None = None, ring_cross_sections: tuple[CrossSectionSpec, ...] = ('strip', 'strip', 'strip'), length_x: float = 0, lengths_y: tuple[float, ...] = (0, 0, 0), input_straight_cross_section: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, output_straight_cross_section: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Coupled ring resonators.
- Parameters
gaps– gap between rings.radius– for each ring.bends– bend spec for each ring.ring_cross_sections– cross_section spec for each ring.length_x– ring coupler length.lengths_y– vertical straight length.input_straight_cross_section– cross_section spec for input and output straight. Defaults to cross_section.output_straight_cross_section– cross_section spec for input and output straight. Defaults to cross_section.cross_section– cross_section spec for input and output straight.
--==ct==-- gap[N-1] | | sl sr ring[N-1] | | --==cb==-- gap[N-2] . . . --==ct==-- | | sl sr lengths_y[1], ring[1] | | --==cb==-- gap[1] --==ct==-- | | sl sr lengths_y[0], ring[0] | | --==cb==-- gap[0] length_x
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ring_crow(gaps=(0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2), radius=(10, 10, 10), ring_cross_sections=('strip', 'strip', 'strip'), length_x=0, lengths_y=(0, 0, 0), cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.rings.ring_crow_couplers(radius: Sequence[float] = (10.0, 10.0, 10.0), bends: Sequence[ComponentSpec] = ('bend_circular', 'bend_circular', 'bend_circular'), ring_cross_sections: Sequence[CrossSectionSpec] = ('strip', 'strip', 'strip'), couplers: Sequence[ComponentSpec] = ('coupler', 'coupler', 'coupler', 'coupler'))Component
Coupled ring resonators with coupler components between gaps.
- Parameters
radius– for the bend and coupler.bends– bend specs.ring_cross_sections– cross_section for the ring.couplers– coupling component between rings and bus.
--==ct==-- gap[N-1] <------- couplers[N-1] | | sl sr ring[N-1] | | --==cb==-- gap[N-2] <------- couplers[N-2] . . . --==ct==-- | | sl sr lengths_y[1], ring[1] | | --==cb==-- gap[1] <------- couplers[1] --==ct==-- | | sl sr lengths_y[0], ring[0] | | --==cb==-- gap[0] <------- couplers[0] length_x
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ring_crow_couplers(radius=(10, 10, 10), bends=('bend_circular', 'bend_circular', 'bend_circular'), ring_cross_sections=('strip', 'strip', 'strip'), couplers=('coupler', 'coupler', 'coupler', 'coupler')).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()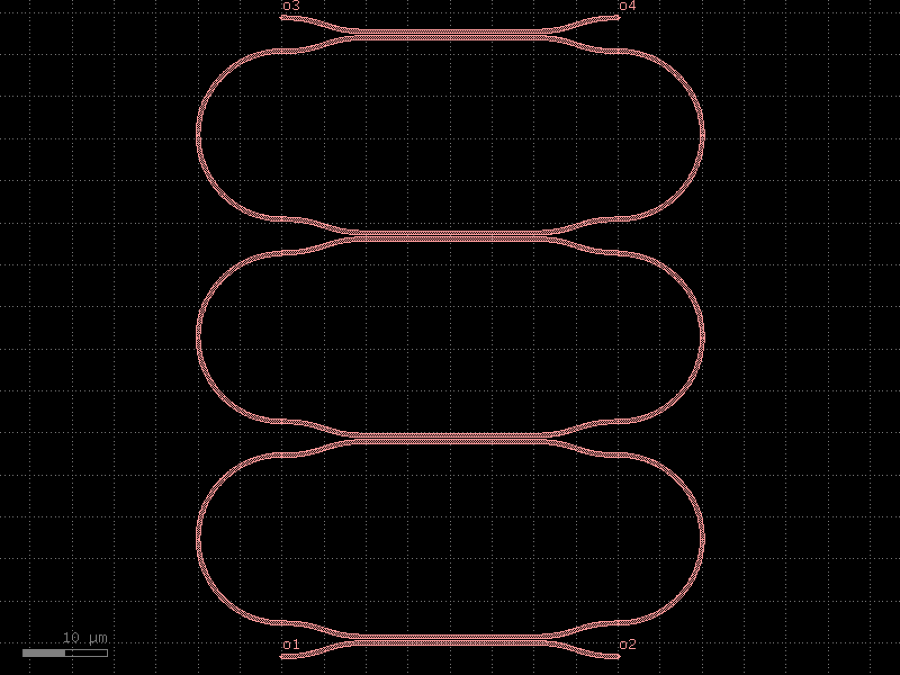
- gdsfactory.components.rings.ring_double(gap: float = 0.2, gap_top: float | None = None, gap_bot: float | None = None, radius: float = 10.0, length_x: float = 0.01, length_y: float = 0.01, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', coupler_ring: ComponentSpec = 'coupler_ring', coupler_ring_top: ComponentSpec | None = None, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns a double bus ring.
two couplers (ct: top, cb: bottom) connected with two vertical straights (sl: left, sr: right)
- Parameters
gap– gap between for coupler.gap_top– gap for the top coupler. Defaults to gap.gap_bot– gap for the bottom coupler. Defaults to gap.radius– for the bend and coupler.length_x– ring coupler length.length_y– vertical straight length.bend– 90 degrees bend spec.straight– straight spec.coupler_ring– ring coupler spec.coupler_ring_top– top ring coupler spec. Defaults to coupler_ring.cross_section– cross_section spec.
o2──────▲─────────o3 │gap_top xx──────▼─────────xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xx xxx x xxx xx xx▲ xx xx│length_y xx xx▼ xx xx xx length_x x xx ◄───────────────► x xx xxx xx xxx xxx──────▲─────────xxx │gap o1──────▼─────────o4
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ring_double(gap=0.2, radius=10, length_x=0.01, length_y=0.01, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', coupler_ring='coupler_ring', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()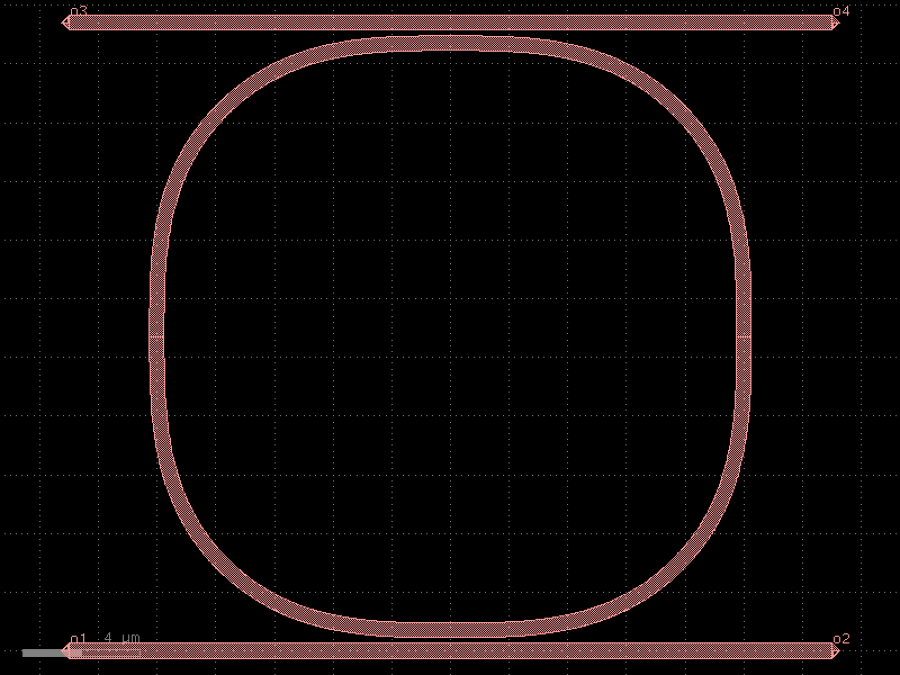
- gdsfactory.components.rings.ring_double_bend_coupler(radius: float = 5.0, gap: float = 0.2, coupling_angle_coverage: float = 70.0, bend: ComponentAllAngleFactory = <kfactory.decorators.WrappedVKCellFunc object>, length_x: float = 0.6, length_y: float = 0.6, cross_section_inner: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_outer: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns ring with double curved couplers.
- Parameters
radius– um.gap– um.coupling_angle_coverage– degrees.bend– for bend.length_x– horizontal straight length.length_y– vertical straight length.cross_section_inner– spec inner bend.cross_section_outer– spec outer bend.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ring_double_bend_coupler(radius=5, gap=0.2, coupling_angle_coverage=70, length_x=0.6, length_y=0.6, cross_section_inner='strip', cross_section_outer='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()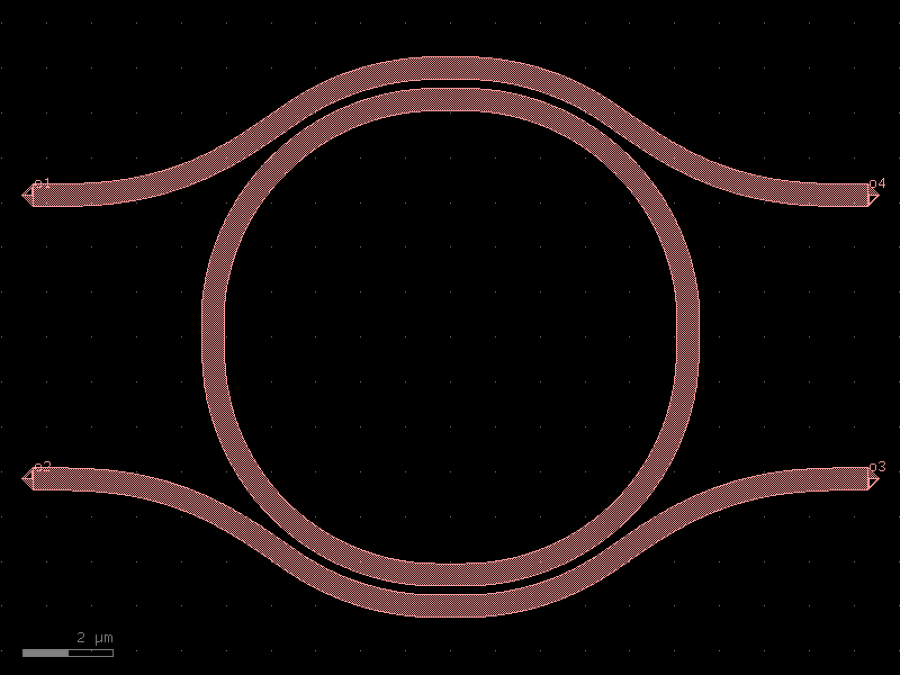
- gdsfactory.components.rings.ring_double_heater(gap: float = 0.2, gap_top: float | None = None, gap_bot: float | None = None, radius: float = 10.0, length_x: float = 1.0, length_y: float = 0.01, coupler_ring: ComponentSpec = 'coupler_ring', coupler_ring_top: ComponentSpec | None = None, straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', cross_section_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'heater_metal', cross_section_waveguide_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_heater_metal', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', via_stack: ComponentSpec = 'via_stack_heater_mtop_mini', port_orientation: AngleInDegrees | None = None, via_stack_offset: Float2 = (1, 0), with_drop: bool = True)Component
Returns a double bus ring with heater on top.
two couplers (ct: top, cb: bottom) connected with two vertical straights (sl: left, sr: right)
- Parameters
gap– gap between for coupler.gap_top– gap for the top coupler. Defaults to gap.gap_bot– gap for the bottom coupler. Defaults to gap.radius– for the bend and coupler.length_x– ring coupler length.length_y– vertical straight length.coupler_ring– ring coupler spec.coupler_ring_top– ring coupler spec for coupler away from vias (defaults to coupler_ring)straight– straight spec.bend– bend spec.cross_section_heater– for heater.cross_section_waveguide_heater– for waveguide with heater.cross_section– for regular waveguide.via_stack– for heater to routing metal.port_orientation– for electrical ports to promote from via_stack.via_stack_offset– x,y offset for via_stack.with_drop– adds drop ports.
o2──────▲─────────o3 │gap_top xx──────▼─────────xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xx xxx x xxx xx xx▲ xx xx│length_y xx xx▼ xx xx xx length_x x xx ◄───────────────► x xx xxx xx xxx xxx──────▲─────────xxx │gap o1──────▼─────────o4
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ring_double_heater(gap=0.2, radius=10, length_x=1, length_y=0.01, coupler_ring='coupler_ring', straight='straight', bend='bend_euler', cross_section_heater='heater_metal', cross_section_waveguide_heater='strip_heater_metal', cross_section='strip', via_stack='via_stack_heater_mtop_mini', via_stack_offset=(1, 0), with_drop=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()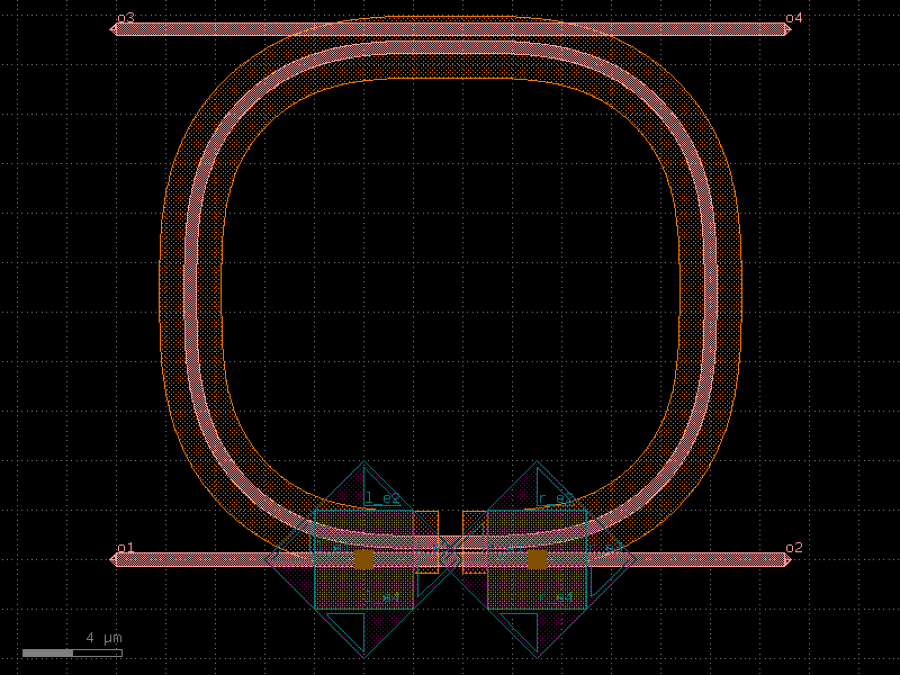
- gdsfactory.components.rings.ring_double_pn(add_gap: float = 0.3, drop_gap: float = 0.3, radius: float = 5.0, doping_angle: float = 85, cross_section: CrossSectionFactory = <function rib>, pn_cross_section: CrossSectionFactory = functools.partial(<function pn>, width_doping=2.425, width_slab=4.85, layer_via='VIAC', width_via=0.5, layer_metal='M1', width_metal=0.5), doped_heater: bool = True, doped_heater_angle_buffer: float = 10, doped_heater_layer: LayerSpec = 'NPP', doped_heater_width: float = 0.5, doped_heater_waveguide_offset: float = 2.175, heater_vias: ComponentSpec = functools.partial(<function via_stack>, size=(0.5, 0.5), layers=('M1', 'M2', 'M3'), vias=(functools.partial(<function via>, layer='VIAC', size=(0.1, 0.1), enclosure=0.1, pitch=0.2), functools.partial(<function via>, layer='VIA1', size=(0.1, 0.1), enclosure=0.1, pitch=0.2), None)), with_drop: bool = True, **kwargs: Any)gf.Component
Returns add-drop pn ring with optional doped heater.
- Parameters
add_gap– gap to add waveguide. Bottom gap.drop_gap– gap to drop waveguide. Top gap.radius– for the bend and coupler.doping_angle– angle in degrees representing portion of ring that is doped.length_x– ring coupler length.length_y– vertical straight length.cross_section– cross_section spec for non-PN doped rib waveguide sections.pn_cross_section– cross section of pn junction.doped_heater– boolean for if we include doped heater or not.doped_heater_angle_buffer– angle in degrees buffering heater from pn junction.doped_heater_layer– doping layer for heater.doped_heater_width– width of doped heater.doped_heater_waveguide_offset– distance from the center of the ring waveguide to the center of the doped heater.heater_vias– components specifications for heater viaswith_drop– boolean for if we include drop waveguide or not.kwargs– cross_section settings.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ring_double_pn(add_gap=0.3, drop_gap=0.3, radius=5, doping_angle=85, doped_heater=True, doped_heater_angle_buffer=10, doped_heater_layer='NPP', doped_heater_width=0.5, doped_heater_waveguide_offset=2.175, with_drop=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()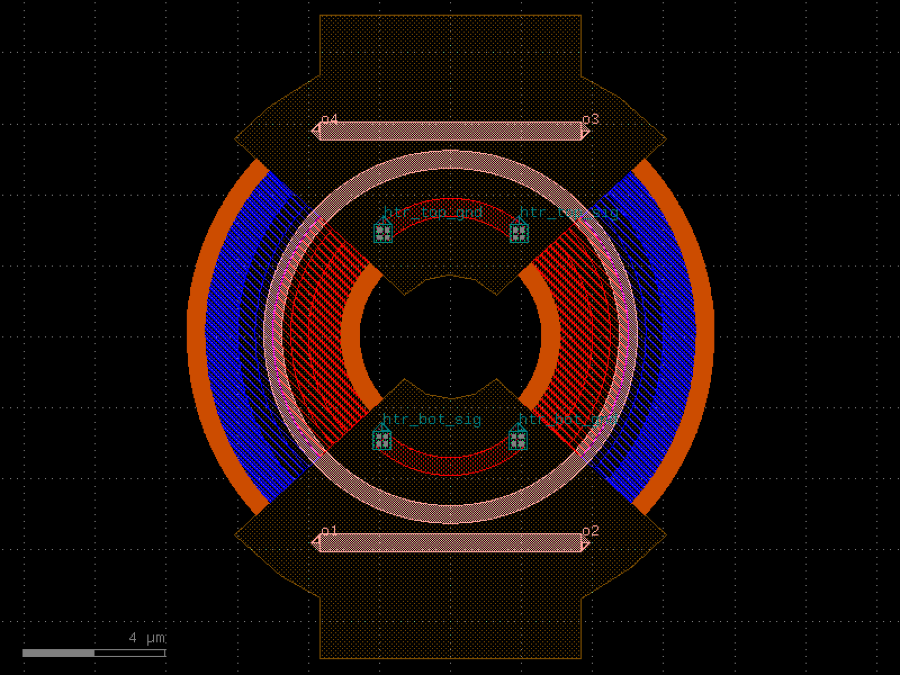
- gdsfactory.components.rings.ring_single(gap: float = 0.2, radius: float = 10.0, length_x: float = 4.0, length_y: float = 0.6, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', coupler_ring: ComponentSpec = 'coupler_ring', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')gf.Component
Returns a single ring.
ring coupler (cb: bottom) connects to two vertical straights (sl: left, sr: right), two bends (bl, br) and horizontal straight (wg: top)
- Parameters
gap– gap between for coupler.radius– for the bend and coupler.length_x– ring coupler length.length_y– vertical straight length.coupler_ring– ring coupler spec.bend– 90 degrees bend spec.straight– straight spec.coupler_ring– ring coupler spec.cross_section– cross_section spec.
xxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xx xxx x xxx xx xx▲ xx xx│length_y xx xx▼ xx xx xx length_x x xx ◄───────────────► x xx xxx xx xxx xxx──────▲─────────xxx │gap o1──────▼─────────o2
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ring_single(gap=0.2, radius=10, length_x=4, length_y=0.6, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', coupler_ring='coupler_ring', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()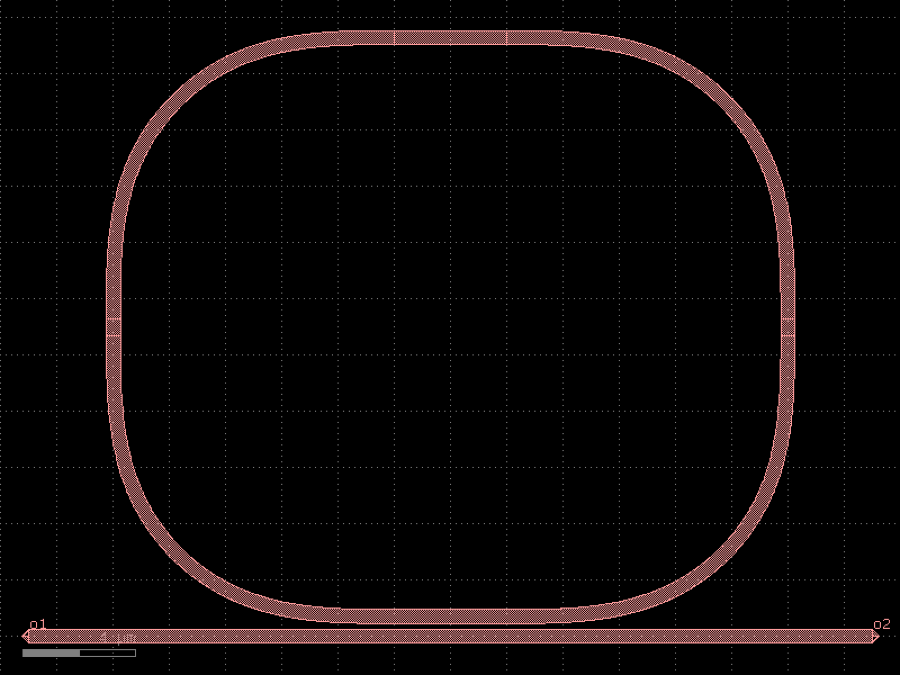
- gdsfactory.components.rings.ring_single_array(ring: ComponentSpec = 'ring_single', spacing: float = 5.0, list_of_dicts: tuple[dict[str, Any], ...] | None = None, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Ring of single bus connected with straights.
- Parameters
ring– ring function.spacing– between rings.list_of_dicts– settings for each ring.cross_section– spec.
______ ______ | | | | | | length_y | | | | | | --======-- spacing ----==gap==-- length_x
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ring_single_array(ring='ring_single', spacing=5, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.rings.ring_single_bend_coupler(radius: float = 5.0, gap: float = 0.2, coupling_angle_coverage: float = 180.0, bend_all_angle: AnyComponentFactory = <kfactory.decorators.WrappedVKCellFunc object>, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_circular', bend_output: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', length_x: float = 0.6, length_y: float = 0.6, cross_section_inner: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_outer: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns ring with curved coupler.
TODO: enable euler bends.
- Parameters
radius– um.gap– um.coupling_angle_coverage– degrees.angle_inner– of the inner bend, from beginning to end. Depending on the bend chosen, gap may not be preserved.angle_outer– of the outer bend, from beginning to end. Depending on the bend chosen, gap may not be preserved.bend_all_angle– for bend.bend– for bend.bend_output– for bend.length_x– horizontal straight length.length_y– vertical straight length.cross_section_inner– spec inner bend.cross_section_outer– spec outer bend.kwargs– cross_section settings.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ring_single_bend_coupler(radius=5, gap=0.2, coupling_angle_coverage=180, bend='bend_circular', bend_output='bend_euler', length_x=0.6, length_y=0.6, cross_section_inner='strip', cross_section_outer='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()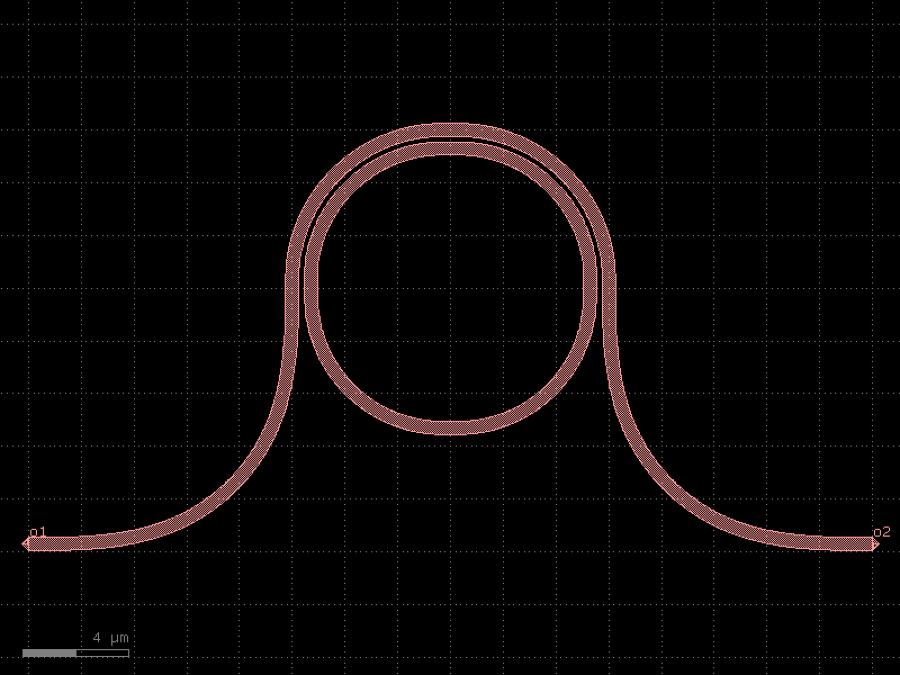
- gdsfactory.components.rings.ring_single_dut(component: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'straight', gap: float = 0.2, length_x: float = 4, length_y: float = 0, radius: float = 5.0, coupler: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'coupler_ring', bend: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'bend_euler', with_component: bool = True, port_name: str = 'o1', **kwargs: Any)Component
Single bus ring made of two couplers (ct: top, cb: bottom) connected.
with two vertical straights (wyl: left, wyr: right) (Component Under Test) in the middle to extract loss from quality factor.
- Parameters
component– device under test.gap– in um.length_x– in um.length_y– in um.radius– in um.coupler– coupler function.bend– bend function.with_component– True adds component. False adds waveguide.port_name– for component input.kwargs– cross_section settings.with_component– if False changes component for just a straight.
bl-wt-br | | length_y wl component | | --==cb==-- gap length_x
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ring_single_dut(component='straight', gap=0.2, length_x=4, length_y=0, radius=5, coupler='coupler_ring', bend='bend_euler', with_component=True, port_name='o1').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()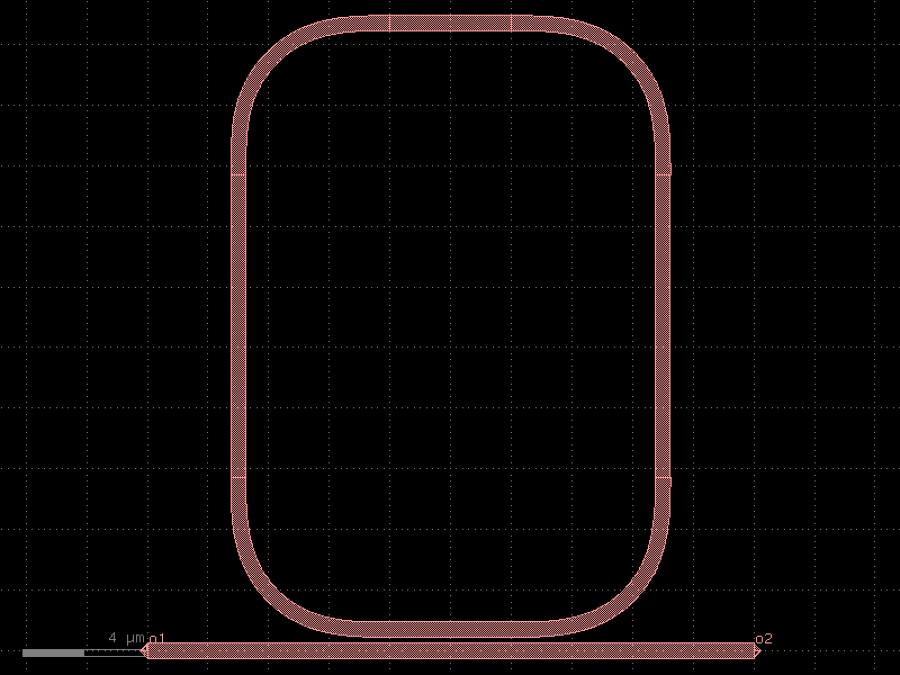
- gdsfactory.components.rings.ring_single_heater(gap: float = 0.2, gap_top: float | None = None, gap_bot: float | None = None, radius: float = 10.0, length_x: float = 1.0, length_y: float = 0.01, coupler_ring: ComponentSpec = 'coupler_ring', coupler_ring_top: ComponentSpec | None = None, straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', cross_section_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'heater_metal', cross_section_waveguide_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_heater_metal', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', via_stack: ComponentSpec = 'via_stack_heater_mtop_mini', port_orientation: AngleInDegrees | None = None, via_stack_offset: Float2 = (1, 0), *, with_drop: bool = False)Component
Returns a double bus ring with heater on top.
two couplers (ct: top, cb: bottom) connected with two vertical straights (sl: left, sr: right)
- Parameters
gap– gap between for coupler.gap_top– gap for the top coupler. Defaults to gap.gap_bot– gap for the bottom coupler. Defaults to gap.radius– for the bend and coupler.length_x– ring coupler length.length_y– vertical straight length.coupler_ring– ring coupler spec.coupler_ring_top– ring coupler spec for coupler away from vias (defaults to coupler_ring)straight– straight spec.bend– bend spec.cross_section_heater– for heater.cross_section_waveguide_heater– for waveguide with heater.cross_section– for regular waveguide.via_stack– for heater to routing metal.port_orientation– for electrical ports to promote from via_stack.via_stack_offset– x,y offset for via_stack.with_drop– adds drop ports.
o2──────▲─────────o3 │gap_top xx──────▼─────────xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xx xxx x xxx xx xx▲ xx xx│length_y xx xx▼ xx xx xx length_x x xx ◄───────────────► x xx xxx xx xxx xxx──────▲─────────xxx │gap o1──────▼─────────o4
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ring_single_heater(gap=0.2, radius=10, length_x=1, length_y=0.01, coupler_ring='coupler_ring', straight='straight', bend='bend_euler', cross_section_heater='heater_metal', cross_section_waveguide_heater='strip_heater_metal', cross_section='strip', via_stack='via_stack_heater_mtop_mini', via_stack_offset=(1, 0), with_drop=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.rings.ring_single_pn(gap: float = 0.3, radius: float = 5.0, doping_angle: float = 250, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = <function rib>, pn_cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = functools.partial(<function pn>, width_doping=2.425, width_slab=4.85, layer_via='VIAC', width_via=0.5, layer_metal='M1', width_metal=0.5), doped_heater: bool = True, doped_heater_angle_buffer: float = 10, doped_heater_layer: LayerSpec = 'NPP', doped_heater_width: float = 0.5, doped_heater_waveguide_offset: float = 1.175, heater_vias: ComponentSpec = functools.partial(<function via_stack>, size=(0.5, 0.5), layers=('M1', 'M2', 'M3'), vias=(functools.partial(<function via>, layer='VIAC', size=(0.1, 0.1), enclosure=0.1, pitch=0.2), functools.partial(<function via>, layer='VIA1', size=(0.1, 0.1), enclosure=0.1, pitch=0.2), None)), pn_vias: ComponentSpec = 'via_stack_slab_m3', pn_vias_width: float = 3)gf.Component
Returns single pn ring with optional doped heater.
- Parameters
gap– gap between for coupler.radius– for the bend and coupler.doping_angle– angle in degrees representing portion of ring that is doped.length_x– ring coupler length.length_y– vertical straight length.cross_section– cross_section spec for non-PN doped rib waveguide sections.pn_cross_section– cross section of pn junction.doped_heater– boolean for if we include doped heater or not.doped_heater_angle_buffer– angle in degrees buffering heater from pn junction.doped_heater_layer– doping layer for heater.doped_heater_width– width of doped heater.doped_heater_waveguide_offset– distance from the center of the ring waveguide to the center of the doped heater.heater_vias– components specifications for heater vias.pn_vias– components specifications for pn vias.pn_vias_width– width of pn vias.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ring_single_pn(gap=0.3, radius=5, doping_angle=250, doped_heater=True, doped_heater_angle_buffer=10, doped_heater_layer='NPP', doped_heater_width=0.5, doped_heater_waveguide_offset=1.175, pn_vias='via_stack_slab_m3', pn_vias_width=3).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
shapes¶
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.C(width: float = 1.0, size: tuple[float, float] = (10.0, 20.0), layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', port_type: str = 'electrical')Component
C geometry with ports on both ends.
based on phidl.
- Parameters
width– of the line.size– length and height of the base.layer– layer spec.port_type– optical or electrical.
______ | o1 | ___ | | | |___ ||<---> size[0] |______ o2
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.C(width=1, size=(10, 20), layer='WG', port_type='electrical').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.L(width: int | float = 1, size: tuple[int, int] = (10, 20), layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'MTOP', port_type: str = 'electrical')Component
Generates an ‘L’ geometry with ports on both ends.
Based on phidl.
- Parameters
width– of the line.size– length and height of the base.layer– spec.port_type– for port.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.L(width=1, size=(10, 20), layer='MTOP', port_type='electrical').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()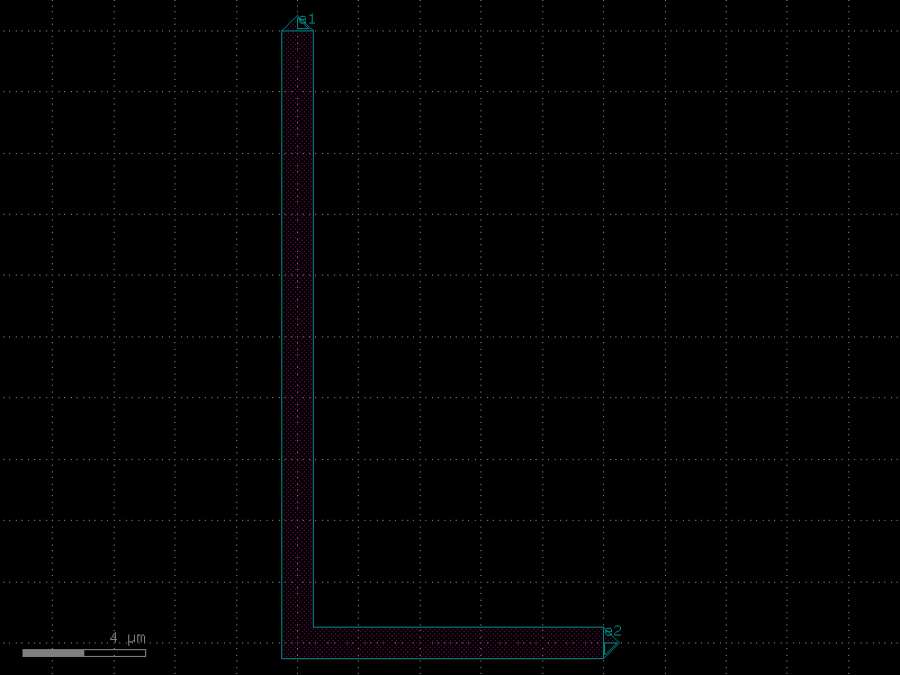
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.circle(radius: float = 10.0, angle_resolution: float = 2.5, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG')Component
Generate a circle geometry.
- Parameters
radius– of the circle.angle_resolution– number of degrees per point.layer– layer.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.circle(radius=10, angle_resolution=2.5, layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.compass(size: tuple[float, float] = (4.0, 2.0), layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', port_type: str | None = 'electrical', port_inclusion: float = 0.0, port_orientations: tuple[int, ...] | list[int] | None = (180, 90, 0, -90), auto_rename_ports: bool = True)Component
Rectangle with ports on each edge (north, south, east, and west).
- Parameters
size– rectangle size.layer– tuple (int, int).port_type– optical, electrical.port_inclusion– from edge.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.auto_rename_ports– auto rename ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.compass(size=(4, 2), layer='WG', port_type='electrical', port_inclusion=0, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90), auto_rename_ports=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.cross(length: float = 10.0, width: float = 3.0, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', port_type: str | None = None)Component
Returns a cross from two rectangles of length and width.
- Parameters
length– float Length of the cross from one end to the other.width– float Width of the arms of the cross.layer– layer for geometry.port_type– None, optical, electrical.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.cross(length=10, width=3, layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()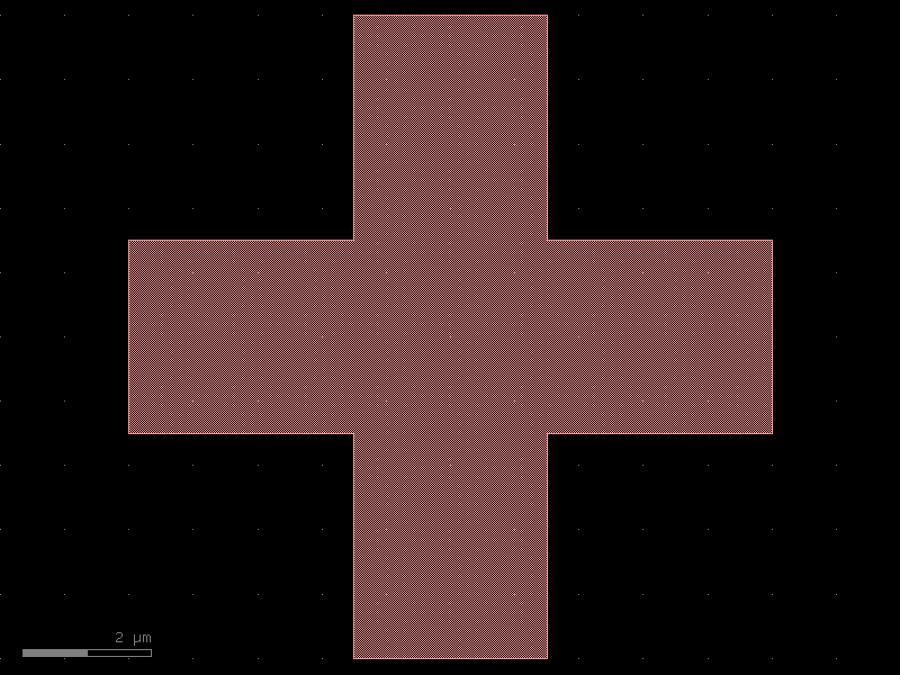
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.ellipse(radii: tuple[float, float] = (10.0, 5.0), angle_resolution: float = 2.5, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG')Component
Returns ellipse component.
- Parameters
radii– Semimajor and semiminor axis lengths of the ellipse.angle_resolution– number of degrees per point.layer– Specific layer(s) to put polygon geometry on.
The orientation of the ellipse is determined by the order of the radii variables; if the first element is larger, the ellipse will be horizontal and if the second element is larger, the ellipse will be vertical.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ellipse(radii=(10, 5), angle_resolution=2.5, layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.fiducial_squares(layers: Sequence[tuple[int, int]] = ((1, 0),), size: tuple[float, float] = (5, 5), offset: float = 0.14)Component
Returns fiducials with two squares.
- Parameters
layers– list of layers.size– in um.offset– in um.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.fiducial_squares(layers=((1, 0),), size=(5, 5), offset=0.14).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.hexagon(*, sides: int = 6, side_length: float = 10, layer: LayerSpec = 'WG', port_type: str | None = 'placement')Component
Returns a regular N-sided polygon, with ports on each edge.
- Parameters
sides– number of sides for the polygon.side_length– of the edges.layer– Specific layer to put polygon geometry on.port_type– optical, electrical.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.hexagon(sides=6, side_length=10, layer='WG', port_type='placement').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.marker_te(*, size: Size = (10.4, 10.4), layer: LayerSpec = 'TE', centered: bool = True, port_type: str | None = 'electrical', port_orientations: Ints | None = (180, 90, 0, -90))Component
Returns a rectangle.
- Parameters
size– (tuple) Width and height of rectangle.layer– Specific layer to put polygon geometry on.centered– True sets center to (0, 0), False sets south-west to (0, 0).port_type– optical, electrical.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None adds no ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.marker_te(size=(10.4, 10.4), layer='TE', centered=True, port_type='electrical', port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.marker_tm(*, size: Size = (10.4, 10.4), layer: LayerSpec = 'TM', centered: bool = True, port_type: str | None = 'electrical', port_orientations: Ints | None = (180, 90, 0, -90))Component
Returns a rectangle.
- Parameters
size– (tuple) Width and height of rectangle.layer– Specific layer to put polygon geometry on.centered– True sets center to (0, 0), False sets south-west to (0, 0).port_type– optical, electrical.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None adds no ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.marker_tm(size=(10.4, 10.4), layer='TM', centered=True, port_type='electrical', port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()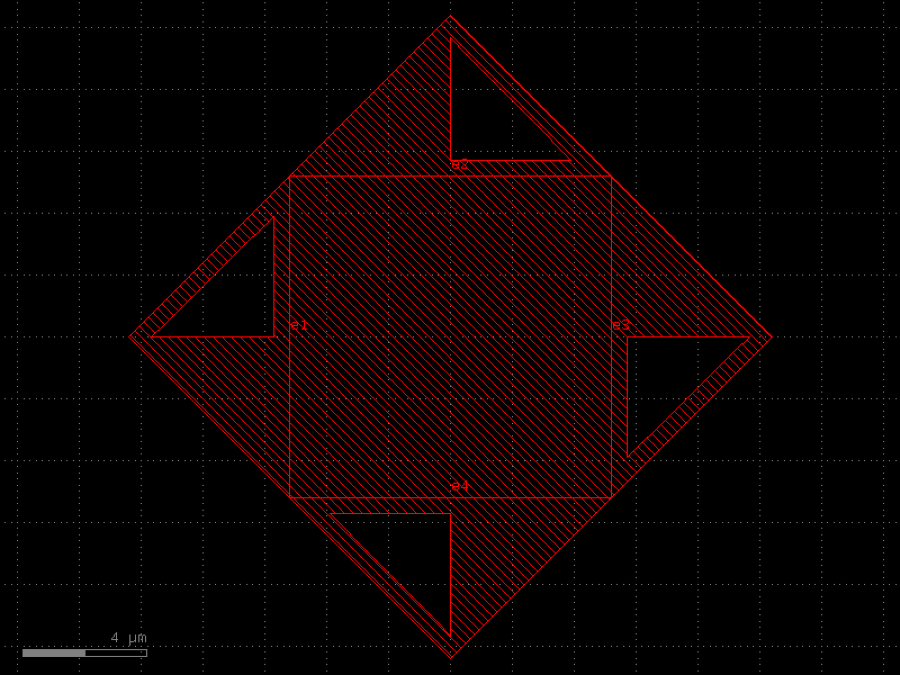
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.nxn(west: int = 1, east: int = 4, north: int = 0, south: int = 0, xsize: float = 8.0, ysize: float = 8.0, wg_width: float = 0.5, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', wg_margin: float = 1.0, **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns a nxn component with nxn ports (west, east, north, south).
- Parameters
west– number of west ports.east– number of east ports.north– number of north ports.south– number of south ports.xsize– size in X.ysize– size in Y.wg_width– width of the straight ports.layer– layer.wg_margin– margin from straight to component edge.kwargs– port_settings.
3 4 |___|_ 2 -| |- 5 | | 1 -|______|- 6 | | 8 7
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.nxn(west=1, east=4, north=0, south=0, xsize=8, ysize=8, wg_width=0.5, layer='WG', wg_margin=1).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.octagon(*, sides: int = 8, side_length: float = 10, layer: LayerSpec = 'WG', port_type: str | None = 'placement')Component
Returns a regular N-sided polygon, with ports on each edge.
- Parameters
sides– number of sides for the polygon.side_length– of the edges.layer– Specific layer to put polygon geometry on.port_type– optical, electrical.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.octagon(sides=8, side_length=10, layer='WG', port_type='placement').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.rectangle(size: tuple[float, float] = (4.0, 2.0), layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', centered: bool = False, port_type: str | None = 'electrical', port_orientations: tuple[int, ...] | list[int] | None = (180, 90, 0, -90))Component
Returns a rectangle.
- Parameters
size– (tuple) Width and height of rectangle.layer– Specific layer to put polygon geometry on.centered– True sets center to (0, 0), False sets south-west to (0, 0).port_type– optical, electrical.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None adds no ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.rectangle(size=(4, 2), layer='WG', centered=False, port_type='electrical', port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()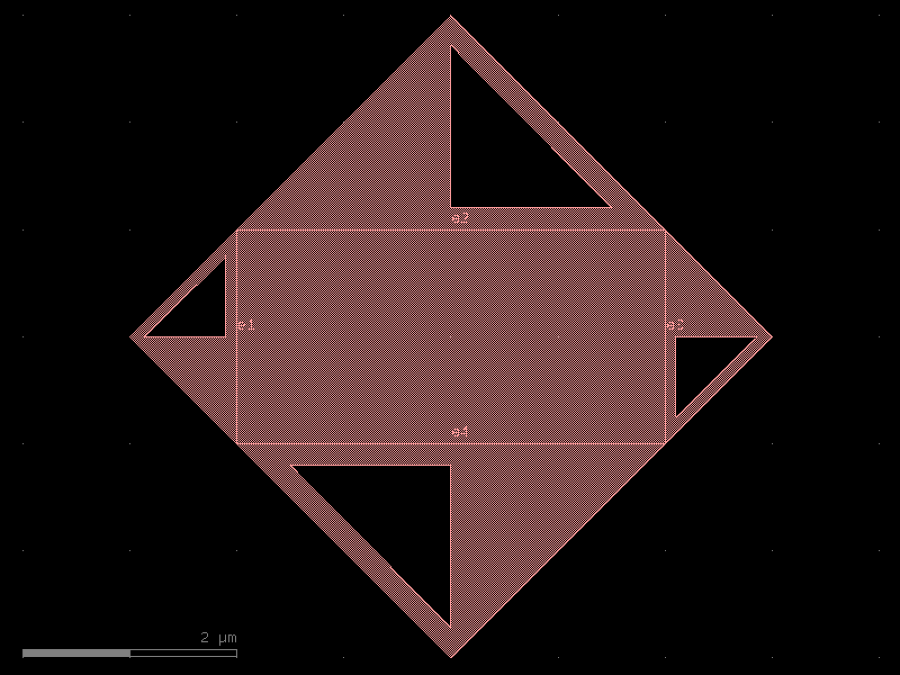
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.rectangles(size: tuple[float, float] = (4.0, 2.0), offsets: Sequence[float] | None = None, layers: Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum] = ('WG', 'SLAB150'), centered: bool = True, **kwargs: Any)Component
Returns overimposed rectangles.
- Parameters
size– (tuple) Width and height of rectangle.layers– Specific layer to put polygon geometry on.offsets– list of offsets. If None, all rectangles have a zero offset.centered– True sets center to (0, 0), False sets south-west of first rectangle to (0, 0).kwargs– additional arguments to pass to rectangle.
- Keyword Arguments
port_type– optical, electrical.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add.
┌──────────────┐ │ │ │ ┌──────┐ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ ├───► │ │ │offset │ └──────┘ │ │ │ └──────────────┘
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.rectangles(size=(4, 2), layers=('WG', 'SLAB150'), centered=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.regular_polygon(sides: int = 6, side_length: float = 10, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', port_type: str | None = 'placement')Component
Returns a regular N-sided polygon, with ports on each edge.
- Parameters
sides– number of sides for the polygon.side_length– of the edges.layer– Specific layer to put polygon geometry on.port_type– optical, electrical.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.regular_polygon(sides=6, side_length=10, layer='WG', port_type='placement').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()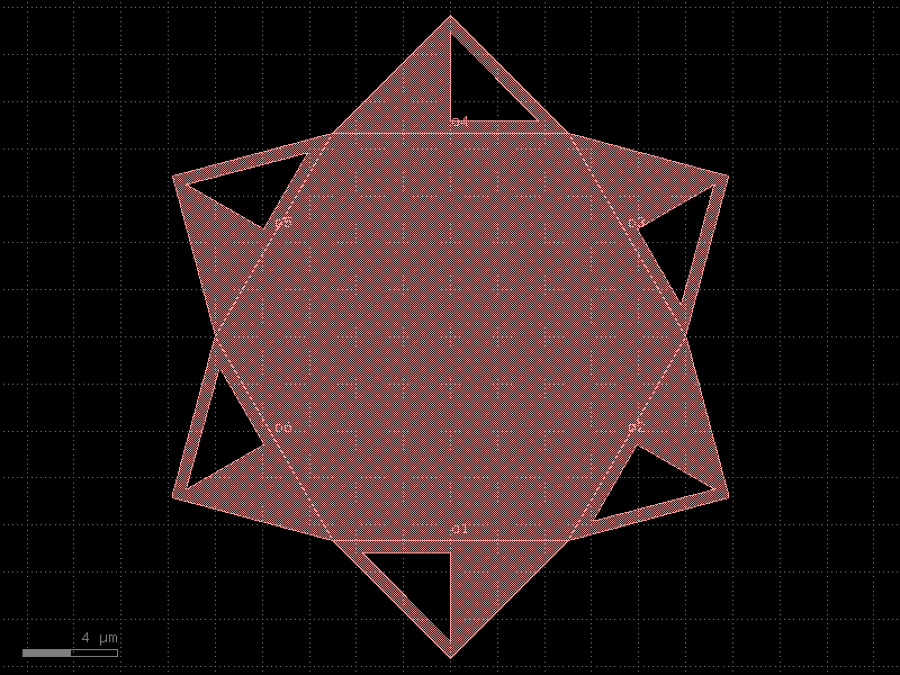
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.triangle(x: float = 10, xtop: float = 0, y: float = 20, ybot: float = 0, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG')Component
Return triangle.
- Parameters
x– base xsize.xtop– top xsize.y– ysize.ybot– bottom ysize.layer– layer.
xtop _ | \ | \ | \ y| \ | \ | \ |______|ybot x
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.triangle(x=10, xtop=0, y=20, ybot=0, layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()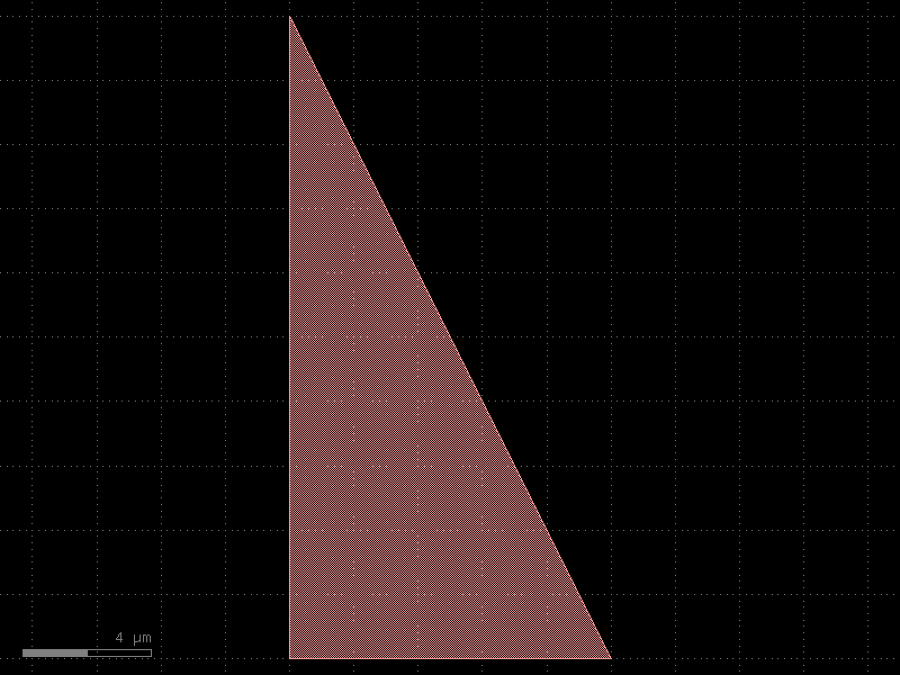
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.triangle2(spacing: float = 3, **kwargs: Any)Component
Return 2 triangles (bot, top).
- Parameters
spacing– between top and bottom.kwargs– triangle arguments.
- Keyword Arguments
x– base xsize.xtop– top xsize.y– ysize.ybot– bottom ysize.layer– layer.
_ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | | spacing | / | / | / | / | / |_/
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.triangle2(spacing=3).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.triangle2_thin(spacing: float = 3, **kwargs: Any)Component
Return 2 triangles (bot, top).
- Parameters
spacing– between top and bottom.kwargs– triangle arguments.
- Keyword Arguments
x– base xsize.xtop– top xsize.y– ysize.ybot– bottom ysize.layer– layer.
_ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | | spacing | / | / | / | / | / |_/
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.triangle2_thin(spacing=3).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.triangle4(**kwargs: Any)Component
Return 4 triangles.
- Parameters
kwargs– triangle arguments.- Keyword Arguments
x– base xsize.xtop– top xsize.y– ysize.ybot– bottom ysize.layer– layer.
/ | \ / | \ / | \ / | \ / | \ / | \ / | \ | | | \ | / \ | / \ | / \ | / \ | / \ |_/
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.triangle4().copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()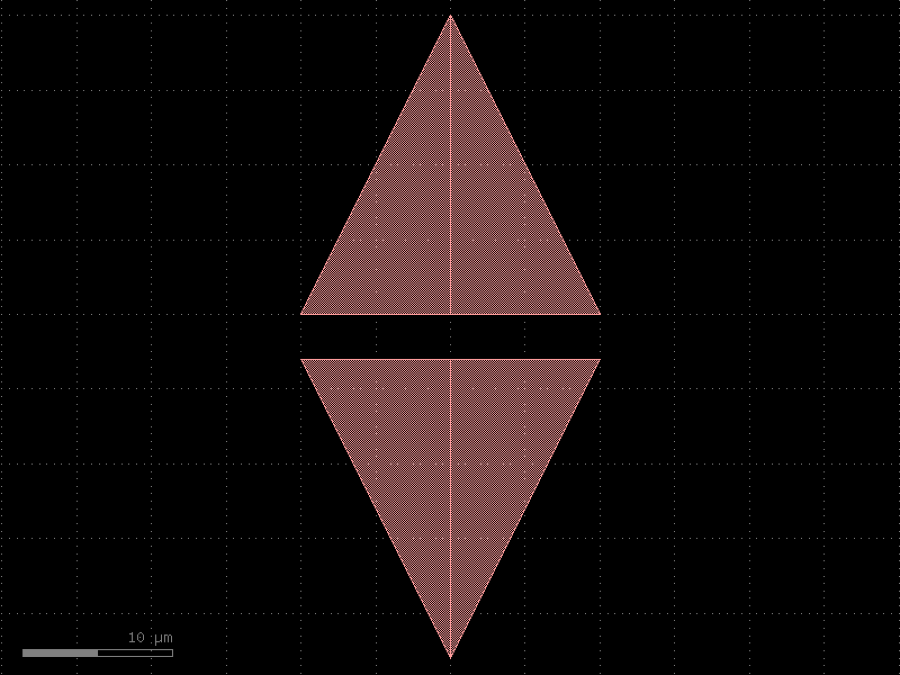
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.triangle4_thin(spacing: float = 3, **kwargs: Any)Component
Return 2 triangles (bot, top).
- Parameters
spacing– between top and bottom.kwargs– triangle arguments.
- Keyword Arguments
x– base xsize.xtop– top xsize.y– ysize.ybot– bottom ysize.layer– layer.
_ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | | spacing | / | / | / | / | / |_/
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.triangle4_thin(spacing=3).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()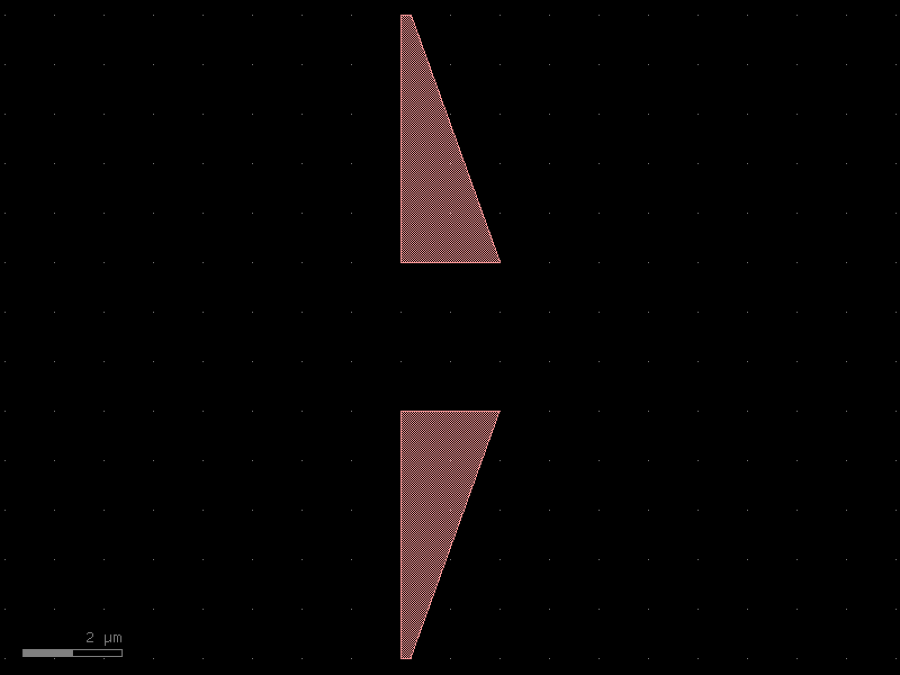
- gdsfactory.components.shapes.triangle_thin(*, x: float = 2, xtop: float = 0.2, y: float = 5, ybot: float = 0, layer: LayerSpec = 'WG')Component
Return triangle.
- Parameters
x– base xsize.xtop– top xsize.y– ysize.ybot– bottom ysize.layer– layer.
xtop _ | \ | \ | \ y| \ | \ | \ |______|ybot x
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.triangle_thin(x=2, xtop=0.2, y=5, ybot=0, layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
spirals¶
- gdsfactory.components.spirals.delay_snake(length: float = 1600.0, length0: float = 0.0, length2: float = 0.0, n: int = 2, bend180: ComponentSpec = functools.partial(<function bend_euler>, angle=180), cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', width: float | None = None)Component
Returns Snake with a starting bend and 180 bends.
- Parameters
length– total length.length0– start length.length2– end length.n– number of loops.bend180– ubend spec.cross_section– cross_section spec.width– width of the waveguide. If None, it will use the width of the cross_section.
| length0 | >---------\ \bend180.info['length'] / |-------------------/ | |------------------->------->| length2 | delta_length | |
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.delay_snake(length=1600, length0=0, length2=0, n=2, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.spirals.delay_snake2(length: float = 1600.0, length0: float = 0.0, length2: float = 0.0, n: int = 2, bend180: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler180', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', width: float | None = None)Component
Returns Snake with a starting straight and 180 bends.
Input faces west output faces east.
- Parameters
length– total length.length0– start length.length2– end length.n– number of loops.bend180– ubend spec.cross_section– cross_section spec.width– width of the waveguide. If None, it will use the width of the cross_section.
| length0 | length1 | >---------| | bend180.length |-------------------| | |------------------->------- | length2 | delta_length | |
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.delay_snake2(length=1600, length0=0, length2=0, n=2, bend180='bend_euler180', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()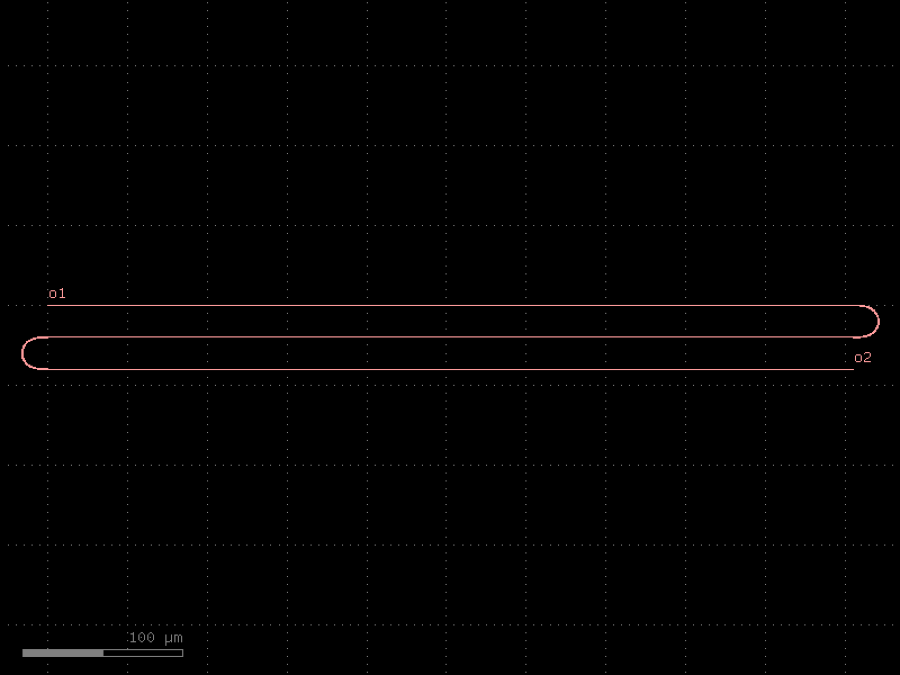
- gdsfactory.components.spirals.delay_snake_sbend(length: float = 100.0, length1: float = 0.0, length4: float = 0.0, radius: float = 5.0, waveguide_spacing: float = 5.0, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', sbend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_s', sbend_xsize: float = 100.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns compact Snake with sbend in the middle.
Input port faces west and output port faces east.
- Parameters
length– total length.length1– first straight section length in um.length4– fourth straight section length in um.radius– u bend radius in um.waveguide_spacing– waveguide pitch in um.bend– bend spec.sbend– sbend spec.sbend_xsize– sbend size.cross_section– cross_section spec.
length1 <---------------------------- length2 spacing | _______ | | \ | | \ | bend1 radius | \sbend | bend2| \ | | \ | | \__| | ---------------------->-----------> length3 length4 We adjust length2 and length3
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.delay_snake_sbend(length=100, length1=0, length4=0, radius=5, waveguide_spacing=5, bend='bend_euler', sbend='bend_s', sbend_xsize=100, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()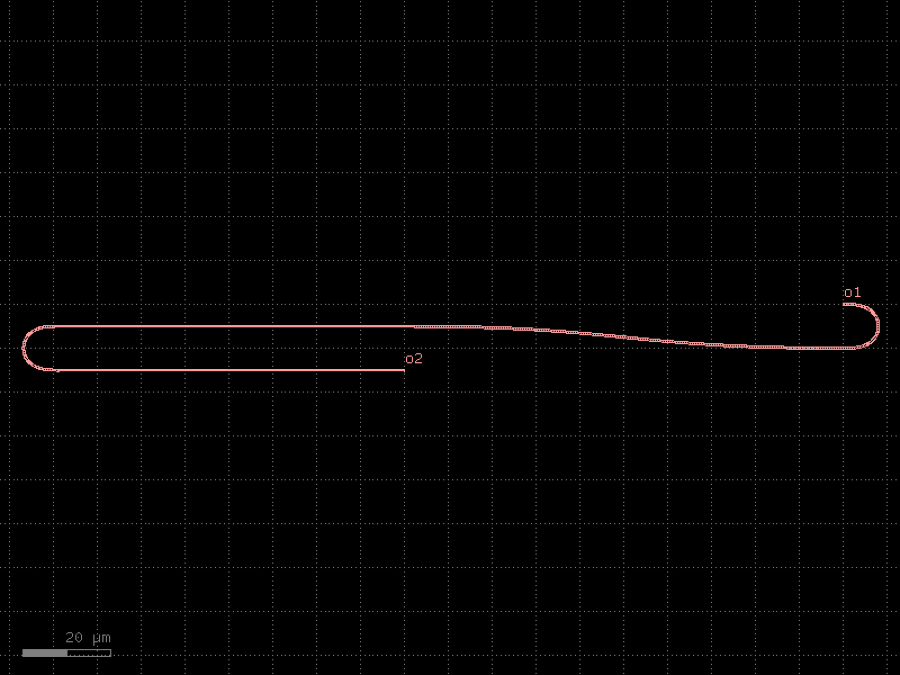
- gdsfactory.components.spirals.spiral(length: float = 100, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_euler', straight: ComponentSpec = 'straight', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', spacing: float = 3.0, n_loops: int = 6)gf.Component
Returns a spiral double (spiral in, and then out).
- Parameters
length– length of the spiral straight section.bend– bend component.straight– straight component.cross_section– cross_section component.spacing– spacing between the spiral loops.n_loops– number of loops.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.spiral(length=100, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', cross_section='strip', spacing=3, n_loops=6).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.spirals.spiral_double(min_bend_radius: float = 10.0, separation: float = 2.0, number_of_loops: float = 3, npoints: int = 1000, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_circular')gf.Component
Returns a spiral double (spiral in, and then out).
- Parameters
min_bend_radius– inner radius of the spiral.separation– separation between the loops.number_of_loops– number of loops per spiral.npoints– points for the spiral.cross_section– cross-section to extrude the structure with.bend– factory for the bends in the middle of the double spiral.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.spiral_double(min_bend_radius=10, separation=2, number_of_loops=3, npoints=1000, cross_section='strip', bend='bend_circular').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.spirals.spiral_inductor(width: float = 3.0, pitch: float = 3.0, turns: int = 16, outer_diameter: float = 800, tail: float = 50.0)Component
Generates a spiral inductor to make superconducting resonator for qubit readout.
See J. M. Hornibrook, J. I. Colless, A. C. Mahoney, X. G. Croot, S. Blanvillain, H. Lu, A. C. Gossard, D. J. Reilly; Frequency multiplexing for readout of spin qubits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 10 March 2014; 104 (10): 103108. Hornibrook et al. (2014)
- Parameters
width– width of the inductor track.pitch– distance between the inductor tracks.turns– number of full spriral turns.outer_diameter– size of the inductor.tail– length of the inner and outer tail.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.spiral_inductor(width=3, pitch=3, turns=16, outer_diameter=800, tail=50).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.spirals.spiral_racetrack(min_radius: float | None = None, straight_length: float = 20.0, spacings: Floats = (2, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2), straight: ComponentSpec = <function straight>, bend: ComponentSpec = <function bend_euler>, bend_s: ComponentSpec = 'bend_s', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_s: CrossSectionSpec | None = None, extra_90_deg_bend: bool = False, allow_min_radius_violation: bool = False)Component
Returns Racetrack-Spiral.
- Parameters
min_radius– smallest radius in um.straight_length– length of the straight segments in um.spacings– space between the center of neighboring waveguides in um.straight– factory to generate the straight segments.bend– factory to generate the bend segments.bend_s– factory to generate the s-bend segments.cross_section– cross-section of the waveguides.cross_section_s– cross-section of the s bend waveguide (optional).extra_90_deg_bend– if True, we add an additional straight + 90 degree bent at the output, so the output port is looking down.allow_min_radius_violation– if True, will allow the s-bend to have a smaller radius than the minimum radius.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.spiral_racetrack(straight_length=20, spacings=(2, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2), bend_s='bend_s', cross_section='strip', extra_90_deg_bend=False, allow_min_radius_violation=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()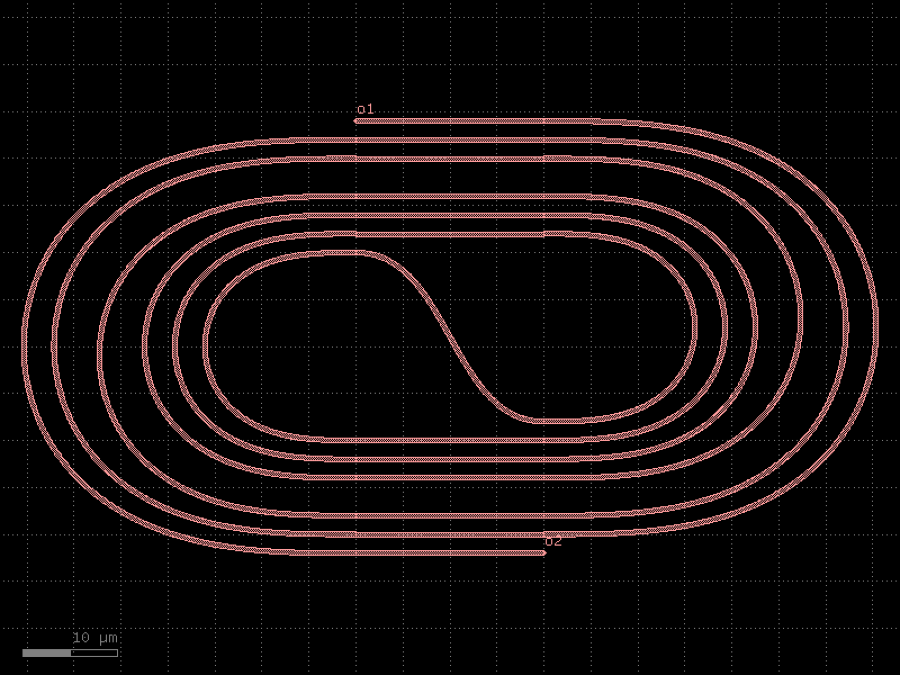
- gdsfactory.components.spirals.spiral_racetrack_fixed_length(length: float = 1000, in_out_port_spacing: float = 150, n_straight_sections: int = 8, min_radius: float | None = None, min_spacing: float = 5.0, straight: ComponentSpec = <function straight>, bend: ComponentSpec = 'bend_circular', bend_s: ComponentSpec = 'bend_s', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_s: CrossSectionSpec | None = None)Component
Returns Racetrack-Spiral with a specified total length.
The input and output ports are aligned in y. This class is meant to be used for generating interferometers with long waveguide lengths, where the most important parameter is the length difference between the arms.
- Parameters
length– total length of the spiral from input to output ports in um.in_out_port_spacing– spacing between input and output ports of the spiral in um.n_straight_sections– total number of straight sections for the racetrack spiral. Has to be even.min_radius– smallest radius in um.min_spacing– minimum center-center spacing between adjacent waveguides.straight– factory to generate the straight segments.bend– factory to generate the bend segments.bend_s– factory to generate the s-bend segments.cross_section– cross-section of the waveguides.cross_section_s– cross-section of the s bend waveguide (optional).
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.spiral_racetrack_fixed_length(length=1000, in_out_port_spacing=150, n_straight_sections=8, min_spacing=5, bend='bend_circular', bend_s='bend_s', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()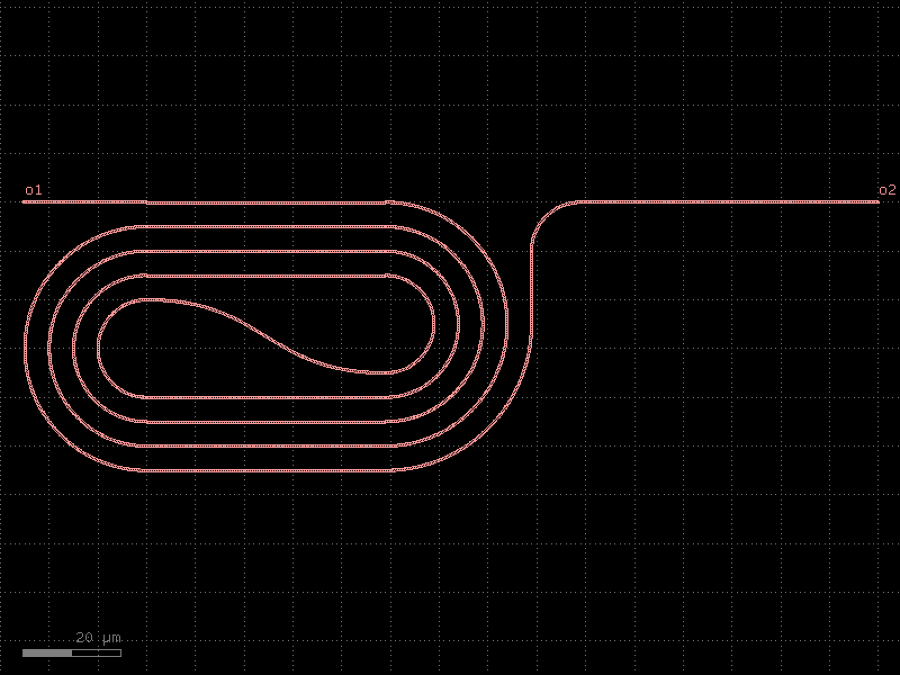
- gdsfactory.components.spirals.spiral_racetrack_heater_doped(min_radius: float | None = None, straight_length: float = 30, spacing: float = 2, num: int = 8, straight: ComponentSpec = <function straight>, bend: ComponentSpec = <function bend_euler>, bend_s: ComponentSpec = 'bend_s', waveguide_cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', heater_cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'npp')Component
Returns spiral racetrack with a heater between the loops.
based on Qiu et al. (2020) but with the heater between the loops.
- Parameters
min_radius– smallest radius in um. Defaults to the radius of the cross-section.straight_length– length of the straight segments in um.spacing– space between the center of neighboring waveguides in um.num– number.straight– factory to generate the straight segments.bend– factory to generate the bend segments.bend_s– factory to generate the s-bend segments.waveguide_cross_section– cross-section of the waveguides.heater_cross_section– cross-section of the heater.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.spiral_racetrack_heater_doped(straight_length=30, spacing=2, num=8, bend_s='bend_s', waveguide_cross_section='strip', heater_cross_section='npp').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()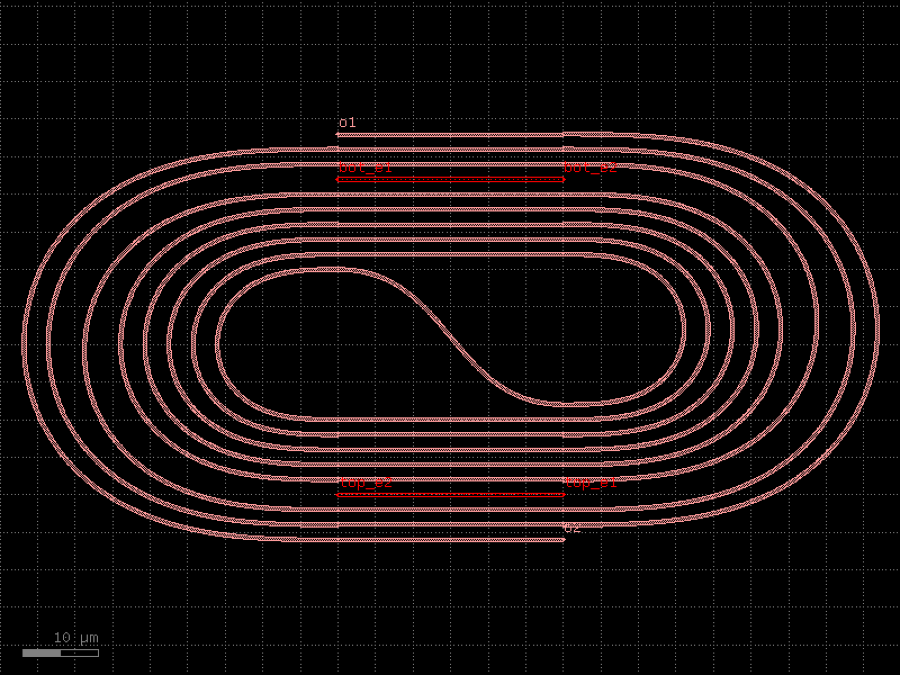
- gdsfactory.components.spirals.spiral_racetrack_heater_metal(min_radius: float | None = None, straight_length: float = 30, spacing: float = 2, num: int = 8, straight: ComponentSpec = <function straight>, bend: ComponentSpec = <function bend_euler>, bend_s: ComponentSpec = 'bend_s', waveguide_cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', heater_cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'heater_metal', via_stack: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_heater_mtop')Component
Returns spiral racetrack with a heater above.
based on Qiu et al. (2020) .
- Parameters
min_radius– smallest radius. Defaults to the radius of the cross-section.straight_length– length of the straight segments.spacing– space between the center of neighboring waveguides.num– number of loops.straight– factory to generate the straight segments.bend– factory to generate the bend segments.bend_s– factory to generate the s-bend segments.waveguide_cross_section– cross-section of the waveguides.heater_cross_section– cross-section of the heater.via_stack– via stack to connect the heater to the metal layer.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.spiral_racetrack_heater_metal(straight_length=30, spacing=2, num=8, bend_s='bend_s', waveguide_cross_section='strip', heater_cross_section='heater_metal', via_stack='via_stack_heater_mtop').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
superconductors¶
- gdsfactory.components.superconductors.hline(length: float = 10.0, width: float = 0.5, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', port_type: str = 'optical')Component
Horizontal line straight, with ports on east and west sides.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.hline(length=10, width=0.5, layer='WG', port_type='optical').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.superconductors.optimal_90deg(width: float = 100, num_pts: int = 15, length_adjust: float = 1, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = (1, 0))Component
Returns optimally-rounded 90 degree bend that is sharp on the outer corner.
- Parameters
width– Width of the ports on either side of the bend.num_pts– The number of points comprising the curved section of the bend.length_adjust– Adjusts the length of the non-curved portion of the bend.layer– Specific layer(s) to put polygon geometry on.
Notes
Optimal structure from Clem & Berggren (2011) Clem, J., & Berggren, K. (2011). Geometry-dependent critical currents in superconducting nanocircuits. Physical Review B, 84(17), 1-27.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.optimal_90deg(width=100, num_pts=15, length_adjust=1, layer=(1, 0)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.superconductors.optimal_hairpin(width: float = 0.2, pitch: float = 0.6, length: float = 10, turn_ratio: float = 4, num_pts: int = 50, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = (1, 0))Component
Returns an optimally-rounded hairpin geometry, with a 180 degree turn.
based on phidl.geometry
- Parameters
width– Width of the hairpin leads.pitch– Distance between the two hairpin leads. Must be greater than width.length– Length of the hairpin from the connectors to the opposite end of the curve.turn_ratio– int or float Specifies how much of the hairpin is dedicated to the 180 degree turn. A turn_ratio of 10 will result in 20% of the hairpin being comprised of the turn.num_pts– Number of points constituting the 180 degree turn.layer– Specific layer(s) to put polygon geometry on.
Notes
Hairpin pitch must be greater than width.
Optimal structure from Clem & Berggren (2011) Clem, J., & Berggren, K. (2011). Geometry-dependent critical currents in superconducting nanocircuits. Physical Review B, 84(17), 1-27.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.optimal_hairpin(width=0.2, pitch=0.6, length=10, turn_ratio=4, num_pts=50, layer=(1, 0)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()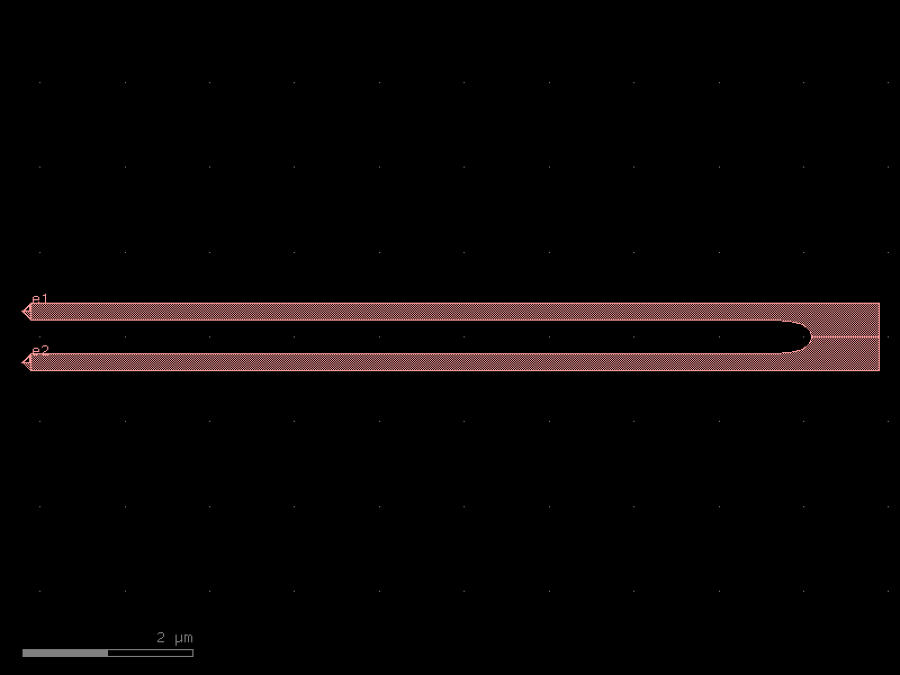
- gdsfactory.components.superconductors.optimal_step(start_width: float = 10, end_width: float = 22, num_pts: int = 50, width_tol: float = 0.001, anticrowding_factor: float = 1.2, symmetric: bool = False, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = (1, 0))Component
Returns an optimally-rounded step geometry.
- Parameters
start_width– Width of the connector on the left end of the step.end_width– Width of the connector on the right end of the step.num_pts– number of points comprising the entire step geometry.width_tol– Point at which to terminate the calculation of the optimal stepanticrowding_factor– Factor to reduce current crowding by elongating the structure and reducing the curvaturesymmetric– If True, adds a mirrored copy of the step across the x-axis to the geometry and adjusts the width of the ports.layer– layer spec to put polygon geometry on.
based on phidl.geometry Optimal structure from Clem & Berggren (2011) Clem, J., & Berggren, K. (2011). Geometry-dependent critical currents in superconducting nanocircuits. Physical Review B, 84(17), 1-27.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.optimal_step(start_width=10, end_width=22, num_pts=50, width_tol=0.001, anticrowding_factor=1.2, symmetric=False, layer=(1, 0)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.superconductors.snspd(wire_width: float = 0.2, wire_pitch: float = 0.6, size: tuple[float, float] = (10, 8), num_squares: int | None = None, turn_ratio: float = 4, terminals_same_side: bool = False, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = (1, 0), port_type: str = 'electrical')Component
Creates an optimally-rounded SNSPD.
- Parameters
wire_width– Width of the wire.wire_pitch– Distance between two adjacent wires. Must be greater than width.size– Float2 (width, height) of the rectangle formed by the outer boundary of the SNSPD.num_squares– int | None = None Total number of squares inside the SNSPD length.turn_ratio– float Specifies how much of the SNSPD width is dedicated to the 180 degree turn. A turn_ratio of 10 will result in 20% of the width being comprised of the turn.terminals_same_side– If True, both ports will be located on the same side of the SNSPD.layer– layer spec to put polygon geometry on.port_type– type of port to add to the component.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.snspd(wire_width=0.2, wire_pitch=0.6, size=(10, 8), turn_ratio=4, terminals_same_side=False, layer=(1, 0), port_type='electrical').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
tapers¶
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.ramp(length: float = 10.0, width1: float = 5.0, width2: float | None = 8.0, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG')Component
Return a ramp component.
Based on phidl.
- Parameters
length– Length of the ramp section.width1– Width of the start of the ramp section.width2– Width of the end of the ramp section (defaults to width1).layer– Specific layer to put polygon geometry on.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.ramp(length=10, width1=5, width2=8, layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()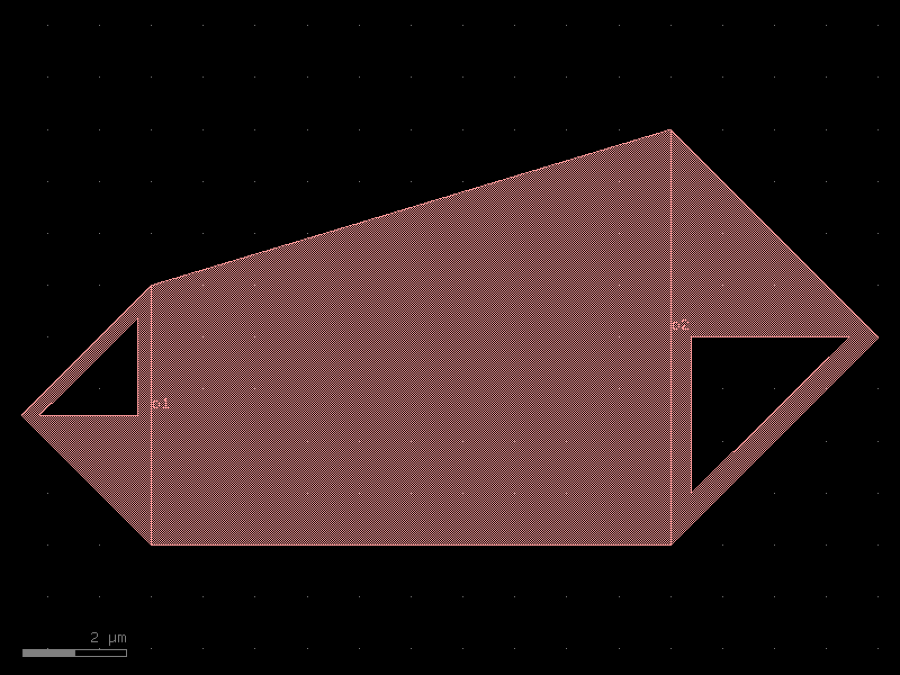
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper(length: float = 10.0, width1: float = 0.5, width2: float | None = None, layer: LayerSpec | None = None, port: Port | None = None, with_two_ports: bool = True, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', port_names: tuple[str, str] = ('o1', 'o2'), port_types: tuple[str, str] = ('optical', 'optical'), with_bbox: bool = True)Component
Linear taper, which tapers only the main cross section section.
- Parameters
length– taper length.width1– width of the west/left port.width2– width of the east/right port. Defaults to width1.layer– layer for the taper.port– can taper from a port instead of defining width1.with_two_ports– includes a second port. False for terminator and edge coupler fiber interface.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).port_names– input and output port names. Second name only used if with_two_ports.port_types– input and output port types. Second type only used if with_two_ports.with_bbox– box in bbox_layers and bbox_offsets to avoid DRC sharp edges.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper(length=10, width1=0.5, with_two_ports=True, cross_section='strip', port_names=('o1', 'o2'), port_types=('optical', 'optical'), with_bbox=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_0p5_to_3_l36(*, filepath: Path = PosixPath('/home/runner/work/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/components/tapers/csv_data/taper_strip_0p5_3_36.csv'), cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns taper from CSV file.
- Parameters
filepath– for CSV file.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_0p5_to_3_l36(cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()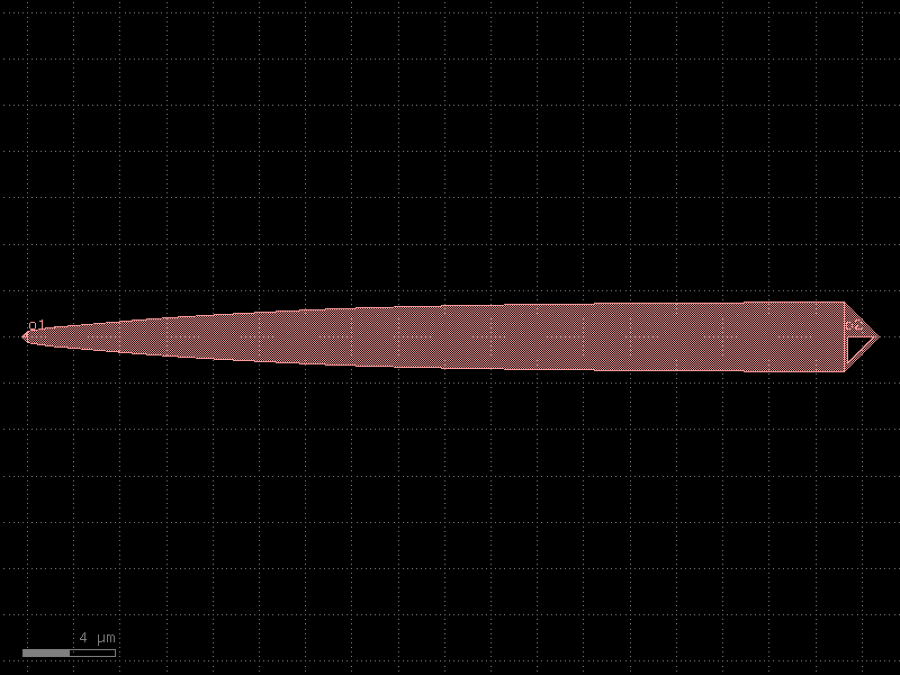
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_adiabatic(width1: float = 0.5, width2: float = 5.0, length: float = 0, neff_w: Callable[[float], float] = <function neff_TE1550SOI_220nm>, alpha: float = 1, wavelength: float = 1.55, npoints: int = 200, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', max_length: float = 200)gf.Component
Returns a straight adiabatic_taper from an effective index callable.
- Parameters
width1– initial width.width2– final width.length– 0 uses the optimized length, and otherwise the optimal shape is compressed/stretched to the specified length.neff_w– a callable that returns the effective index as a function of width - By default, will use a compact model of neff(y) for fundamental 1550 nm TE mode of 220nm-thick core with 3.45 index, fully clad with 1.44 index. Many coefficients are needed to capture the behaviour.alpha– parameter that scales the rate of width change. - closer to 0 means longer and more adiabatic; - 1 is the intuitive limit beyond which higher order modes are excited; - [2] reports good performance up to 1.4 for fundamental TE in SOI (for multiple core thicknesses)wavelength– wavelength in um.npoints– number of points for sampling.cross_section– cross_section specification.max_length– maximum length for the taper.
References
[1] Burns, W. K., et al. “Optical waveguide parabolic coupling horns.” Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 30, no. 1, 1 Jan. 1977, pp. 28-30, doi:10.1063/1.89199. [2] Fu, Yunfei, et al. “Efficient adiabatic silicon-on-insulator waveguide taper.” Photonics Res., vol. 2, no. 3, 1 June 2014, pp. A41-A44, doi:10.1364/PRJ.2.000A41. npoints: number of points for sampling
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_adiabatic(width1=0.5, width2=5, length=0, alpha=1, wavelength=1.55, npoints=200, cross_section='strip', max_length=200).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()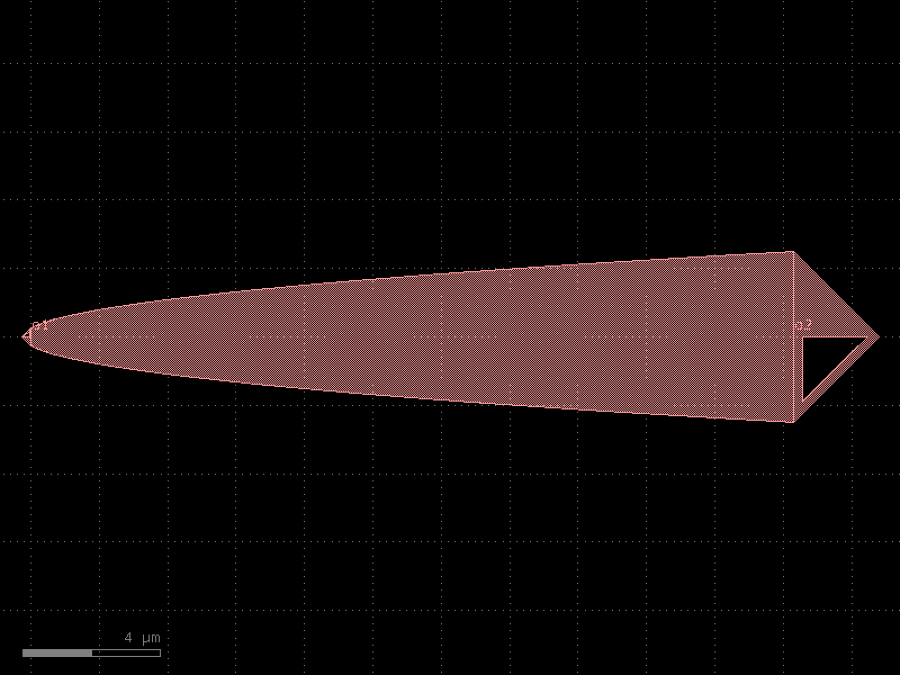
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_cross_section(cross_section1: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_rib_tip', cross_section2: CrossSectionSpec = 'rib2', length: float = 10, npoints: int = 100, linear: bool = False, width_type: str = 'sine')Component
Returns taper transition between cross_section1 and cross_section2.
- Parameters
cross_section1– start cross_section factory.cross_section2– end cross_section factory.length– transition length.npoints– number of points.linear– shape of the transition, sine when False.width_type– shape of the transition ONLY IF linear is False
_____________________ / _______/______________________ / cross_section1 | cross_section2 ______\_______________________ \ \_____________________
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_cross_section(cross_section1='strip_rib_tip', cross_section2='rib2', length=10, npoints=100, linear=False, width_type='sine').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()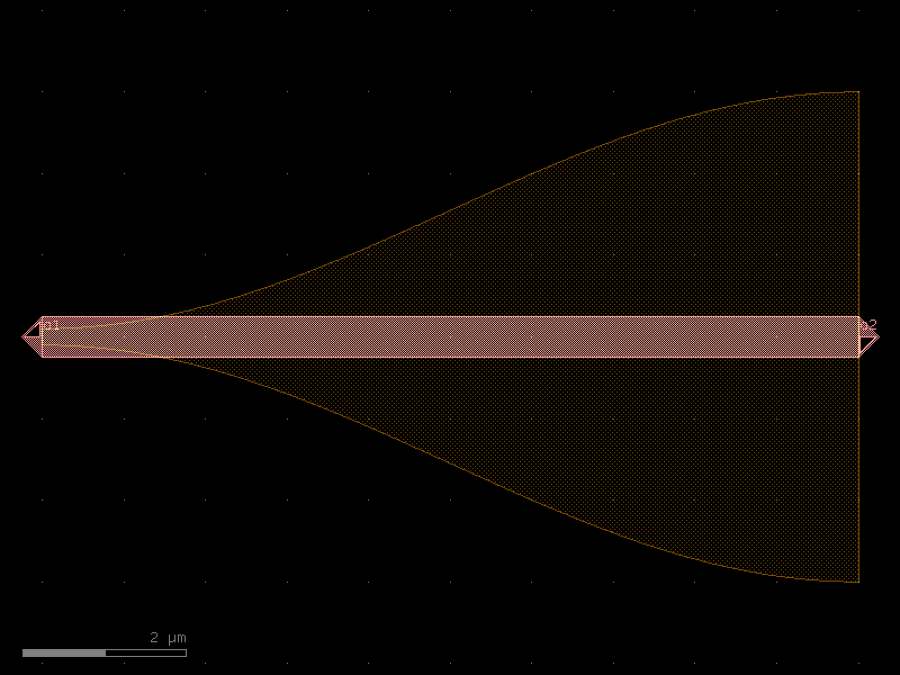
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_cross_section_linear(cross_section1: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_rib_tip', cross_section2: CrossSectionSpec = 'rib2', length: float = 10, *, npoints: int = 2, linear: bool = True, width_type: str = 'sine')Component
Returns taper transition between cross_section1 and cross_section2.
- Parameters
cross_section1– start cross_section factory.cross_section2– end cross_section factory.length– transition length.npoints– number of points.linear– shape of the transition, sine when False.width_type– shape of the transition ONLY IF linear is False
_____________________ / _______/______________________ / cross_section1 | cross_section2 ______\_______________________ \ \_____________________
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_cross_section_linear(cross_section1='strip_rib_tip', cross_section2='rib2', length=10, npoints=2, linear=True, width_type='sine').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()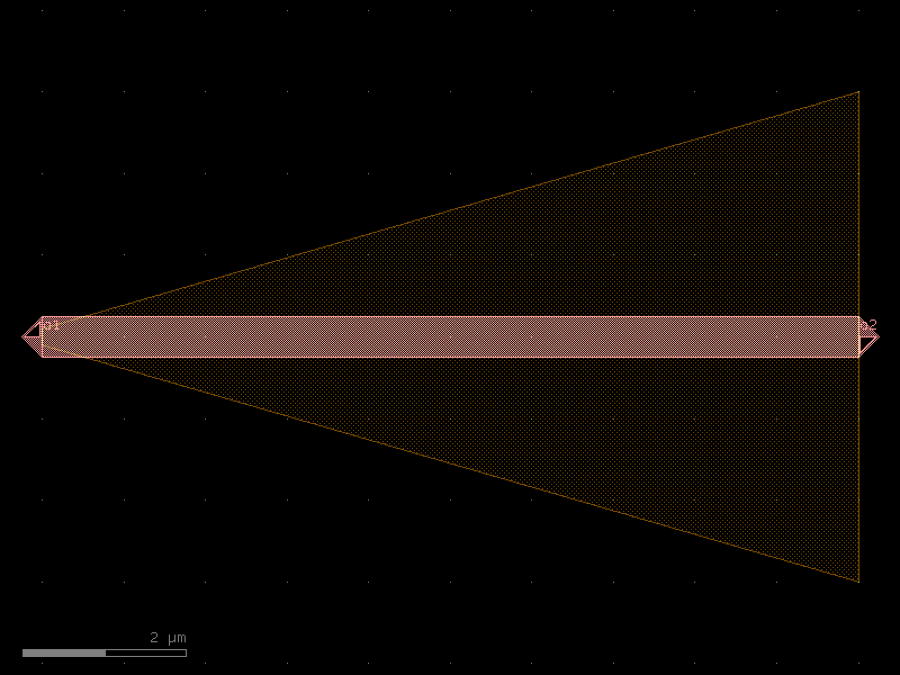
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_cross_section_parabolic(cross_section1: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_rib_tip', cross_section2: CrossSectionSpec = 'rib2', length: float = 10, *, npoints: int = 101, linear: bool = False, width_type: str = 'parabolic')Component
Returns taper transition between cross_section1 and cross_section2.
- Parameters
cross_section1– start cross_section factory.cross_section2– end cross_section factory.length– transition length.npoints– number of points.linear– shape of the transition, sine when False.width_type– shape of the transition ONLY IF linear is False
_____________________ / _______/______________________ / cross_section1 | cross_section2 ______\_______________________ \ \_____________________
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_cross_section_parabolic(cross_section1='strip_rib_tip', cross_section2='rib2', length=10, npoints=101, linear=False, width_type='parabolic').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()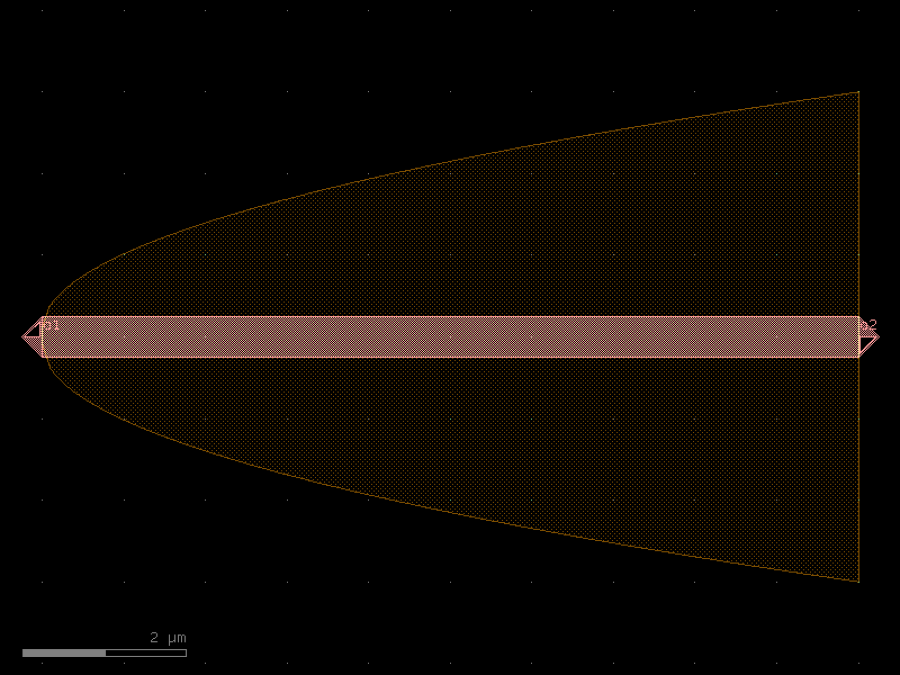
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_cross_section_sine(cross_section1: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_rib_tip', cross_section2: CrossSectionSpec = 'rib2', length: float = 10, *, npoints: int = 101, linear: bool = False, width_type: str = 'sine')Component
Returns taper transition between cross_section1 and cross_section2.
- Parameters
cross_section1– start cross_section factory.cross_section2– end cross_section factory.length– transition length.npoints– number of points.linear– shape of the transition, sine when False.width_type– shape of the transition ONLY IF linear is False
_____________________ / _______/______________________ / cross_section1 | cross_section2 ______\_______________________ \ \_____________________
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_cross_section_sine(cross_section1='strip_rib_tip', cross_section2='rib2', length=10, npoints=101, linear=False, width_type='sine').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()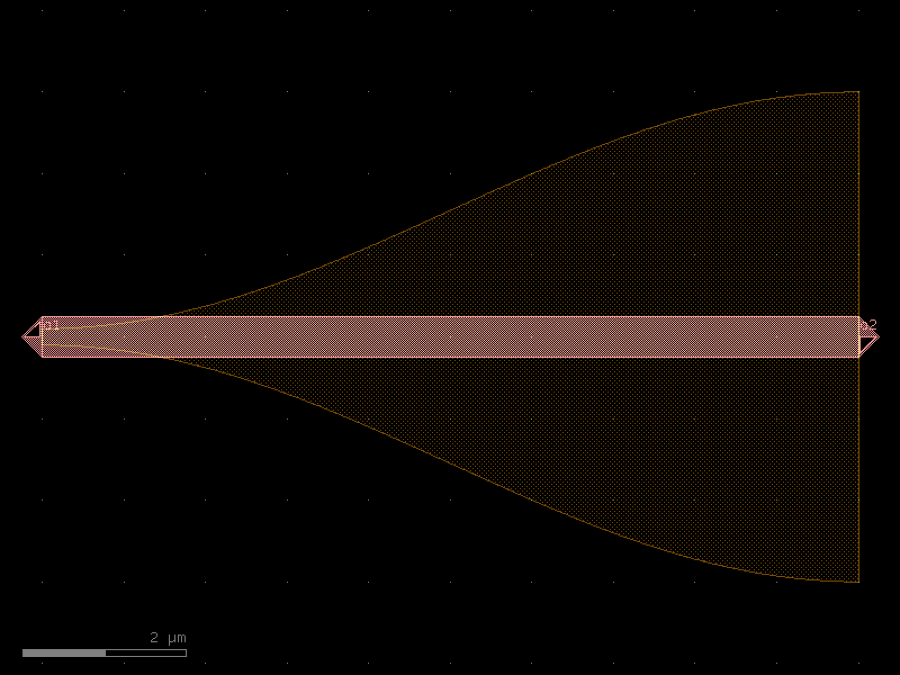
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_electrical(length: float = 10.0, width1: float = 0.5, width2: float | None = None, layer: LayerSpec | None = None, port: Port | None = None, with_two_ports: bool = True, *, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'metal_routing', port_names: tuple[str, str] = ('e1', 'e2'), port_types: tuple[str, str] = ('electrical', 'electrical'), with_bbox: bool = True)Component
Linear taper, which tapers only the main cross section section.
- Parameters
length– taper length.width1– width of the west/left port.width2– width of the east/right port. Defaults to width1.layer– layer for the taper.port– can taper from a port instead of defining width1.with_two_ports– includes a second port. False for terminator and edge coupler fiber interface.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).port_names– input and output port names. Second name only used if with_two_ports.port_types– input and output port types. Second type only used if with_two_ports.with_bbox– box in bbox_layers and bbox_offsets to avoid DRC sharp edges.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_electrical(length=10, width1=0.5, with_two_ports=True, cross_section='metal_routing', port_names=('e1', 'e2'), port_types=('electrical', 'electrical'), with_bbox=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_from_csv(filepath: Path = PosixPath('/home/runner/work/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/components/tapers/csv_data/taper_strip_0p5_3_36.csv'), cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns taper from CSV file.
- Parameters
filepath– for CSV file.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_from_csv(cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()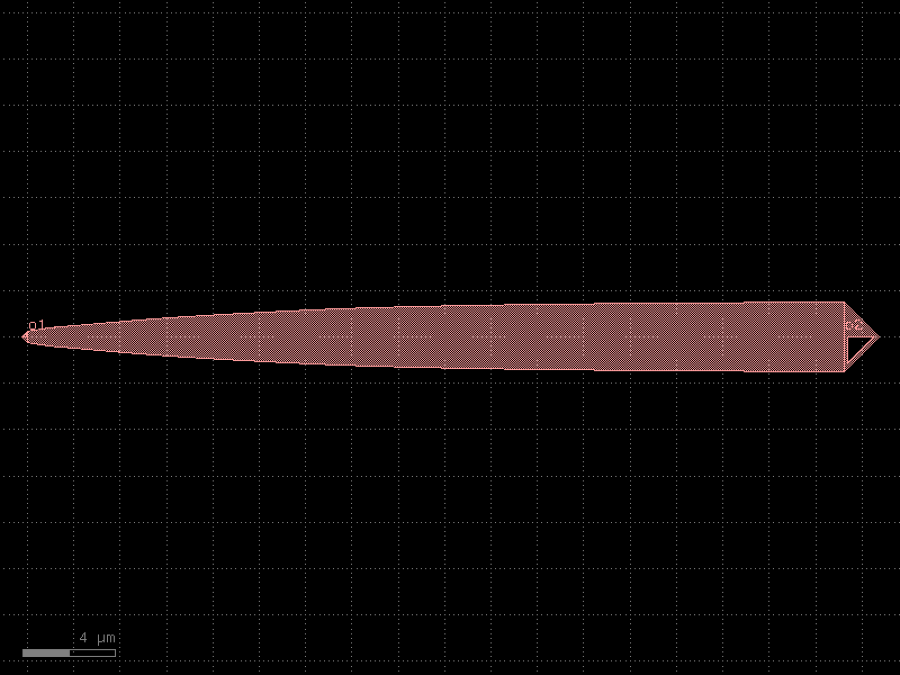
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_nc_sc(width1: float = 1, width2: float = 0.5, length: float = 20, layer_wg: LayerSpec = 'WG', layer_nitride: LayerSpec = 'WGN', width_tip_nitride: float = 0.15, width_tip_silicon: float = 0.15, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Taper from nitride to strip.
- Parameters
width1– nitride width.width2– silicon width.length– taper length.layer_wg– nitride layer.layer_nitride– strip layer.width_tip_nitride– tip width for nitride.width_tip_silicon– tip width for strip.cross_section– cross_section specification.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_nc_sc(width1=1, width2=0.5, length=20, layer_wg='WG', layer_nitride='WGN', width_tip_nitride=0.15, width_tip_silicon=0.15, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_parabolic(length: float = 20, width1: float = 0.5, width2: float = 5.0, exp: float = 0.5, npoints: int = 100, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG')Component
Returns a parabolic_taper.
- Parameters
length– in um.width1– in um.width2– in um.exp– exponent.npoints– number of points.layer– layer spec.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_parabolic(length=20, width1=0.5, width2=5, exp=0.5, npoints=100, layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()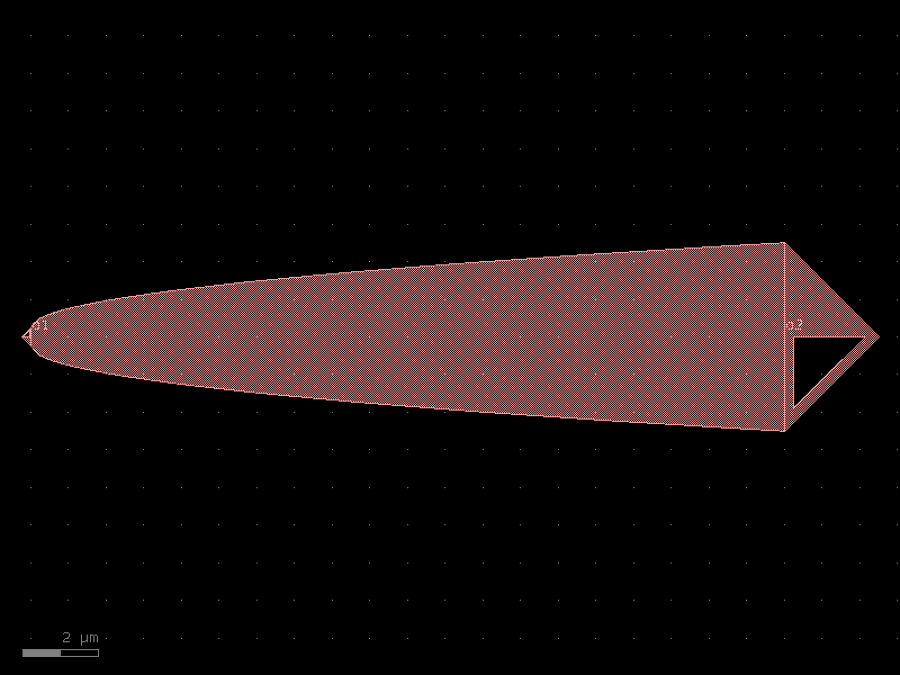
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_sc_nc(width1: float = 0.5, width2: float = 1, length: float = 20, layer_wg: LayerSpec = 'WG', layer_nitride: LayerSpec = 'WGN', width_tip_nitride: float = 0.15, width_tip_silicon: float = 0.15, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Taper from strip to nitride.
- Parameters
width1– strip width.width2– nitride width.length– taper length.layer_wg– strip layer.layer_nitride– nitride layer.width_tip_nitride– tip width for nitride.width_tip_silicon– tip width for strip.cross_section– cross_section specification.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_sc_nc(width1=0.5, width2=1, length=20, layer_wg='WG', layer_nitride='WGN', width_tip_nitride=0.15, width_tip_silicon=0.15, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_strip_to_ridge(length: float = 10.0, width1: float = 0.5, width2: float = 0.5, w_slab1: float = 0.15, w_slab2: float = 6.0, layer_wg: LayerSpec = 'WG', layer_slab: LayerSpec = 'SLAB90', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', use_slab_port: bool = False)Component
Linear taper from strip to rib.
- Parameters
length– taper length (um).width1– in um.width2– in um.w_slab1– slab width in um.w_slab2– slab width in um.layer_wg– for input waveguide.layer_slab– for output waveguide with slab.cross_section– for input waveguide.use_slab_port– if True adds a second port for the slab.
__________________________ / | _______/____________|______________ / | width1 |w_slab1 | w_slab2 width2 ______\_____________|______________ \ | \__________________________
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_strip_to_ridge(length=10, width1=0.5, width2=0.5, w_slab1=0.15, w_slab2=6, layer_wg='WG', layer_slab='SLAB90', cross_section='strip', use_slab_port=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()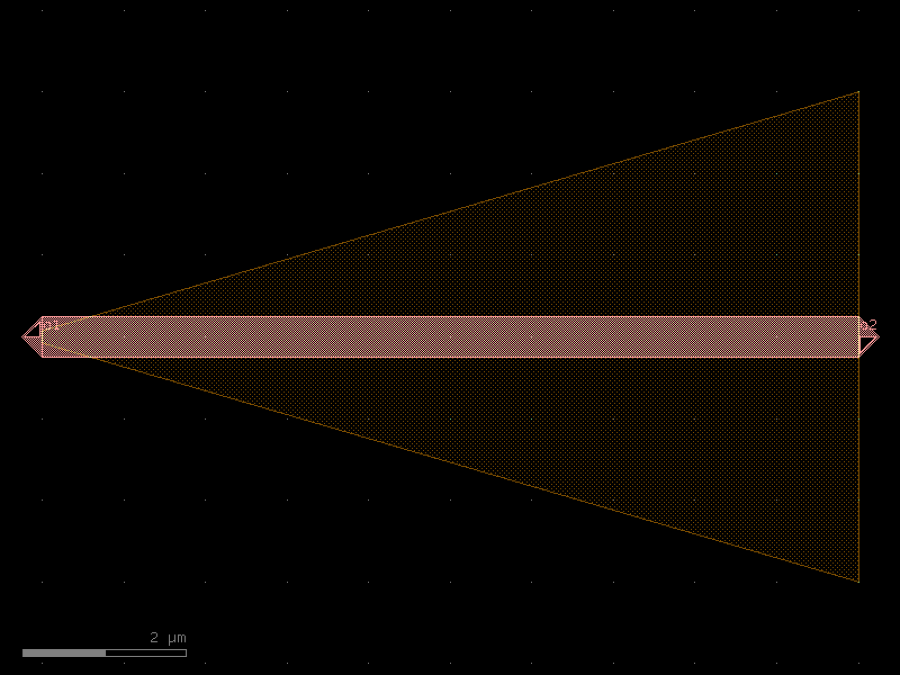
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_strip_to_ridge_trenches(length: float = 10.0, width: float = 0.5, slab_offset: float = 3.0, trench_width: float = 2.0, trench_layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'DEEP_ETCH', layer_wg: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', trench_offset: float = 0.1)Component
Defines taper using trenches to define the etch.
- Parameters
length– in um.width– in um.slab_offset– in um.trench_width– in um.trench_layer– trench layer.layer_wg– waveguide layer.trench_offset– after waveguide in um.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_strip_to_ridge_trenches(length=10, width=0.5, slab_offset=3, trench_width=2, trench_layer='DEEP_ETCH', layer_wg='WG', trench_offset=0.1).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()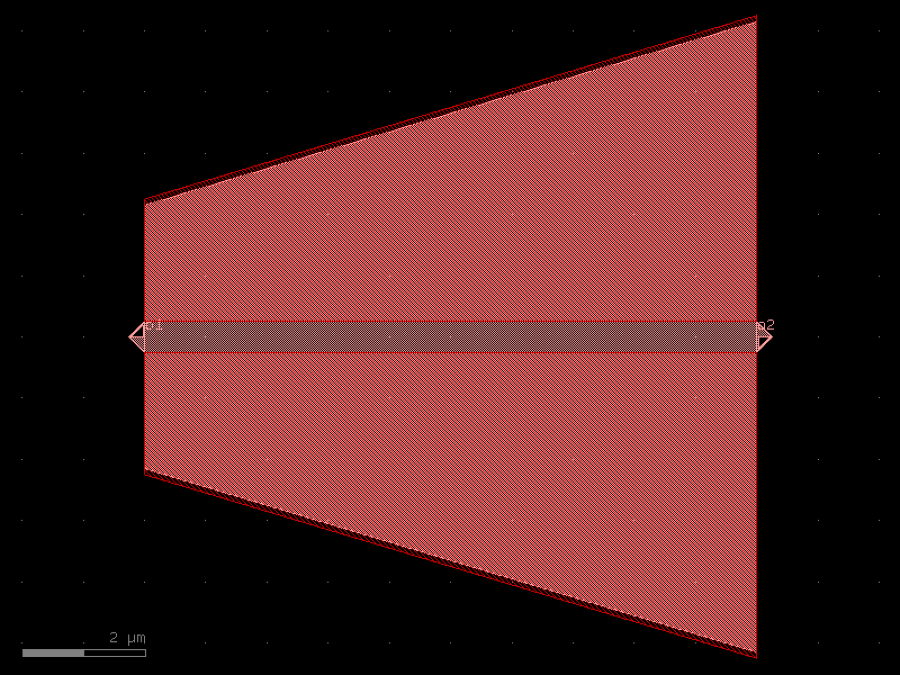
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_strip_to_slab150(length: float = 10.0, width1: float = 0.5, width2: float = 0.5, w_slab1: float = 0.15, w_slab2: float = 6.0, layer_wg: LayerSpec = 'WG', *, layer_slab: LayerSpec = 'SLAB150', cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', use_slab_port: bool = False)Component
Linear taper from strip to rib.
- Parameters
length– taper length (um).width1– in um.width2– in um.w_slab1– slab width in um.w_slab2– slab width in um.layer_wg– for input waveguide.layer_slab– for output waveguide with slab.cross_section– for input waveguide.use_slab_port– if True adds a second port for the slab.
__________________________ / | _______/____________|______________ / | width1 |w_slab1 | w_slab2 width2 ______\_____________|______________ \ | \__________________________
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_strip_to_slab150(length=10, width1=0.5, width2=0.5, w_slab1=0.15, w_slab2=6, layer_wg='WG', layer_slab='SLAB150', cross_section='strip', use_slab_port=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()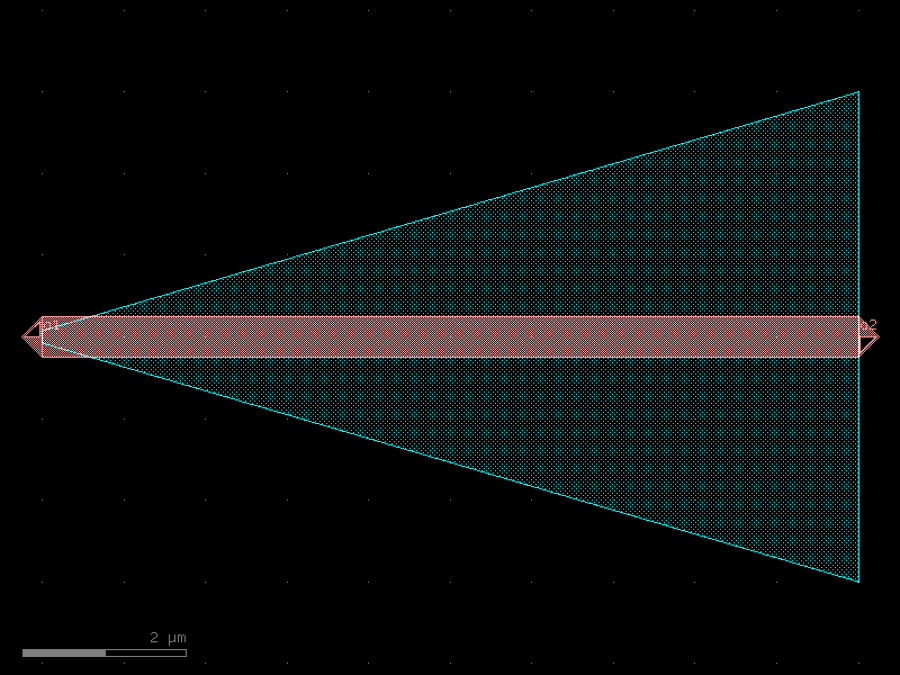
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_w10_l100(*, filepath: Path = PosixPath('/home/runner/work/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/components/tapers/csv_data/taper_strip_0p5_10_100.csv'), cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns taper from CSV file.
- Parameters
filepath– for CSV file.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_w10_l100(cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()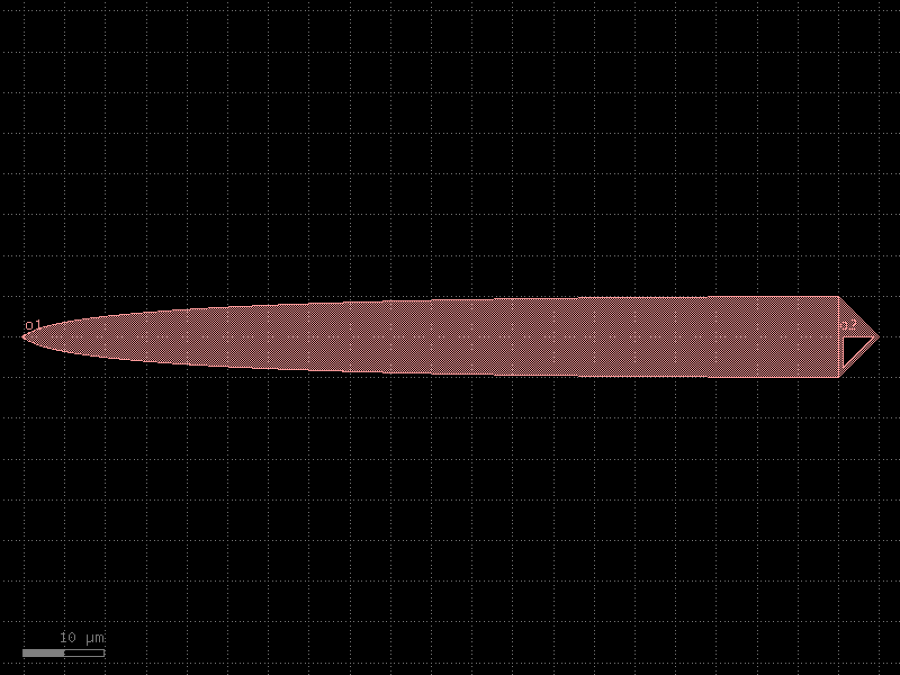
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_w10_l150(*, filepath: Path = PosixPath('/home/runner/work/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/components/tapers/csv_data/taper_strip_0p5_10_150.csv'), cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns taper from CSV file.
- Parameters
filepath– for CSV file.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_w10_l150(cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_w10_l200(*, filepath: Path = PosixPath('/home/runner/work/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/components/tapers/csv_data/taper_strip_0p5_10_200.csv'), cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns taper from CSV file.
- Parameters
filepath– for CSV file.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_w10_l200(cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_w11_l200(*, filepath: Path = PosixPath('/home/runner/work/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/components/tapers/csv_data/taper_strip_0p5_11_200.csv'), cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns taper from CSV file.
- Parameters
filepath– for CSV file.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_w11_l200(cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.tapers.taper_w12_l200(*, filepath: Path = PosixPath('/home/runner/work/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/components/tapers/csv_data/taper_strip_0p5_12_200.csv'), cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns taper from CSV file.
- Parameters
filepath– for CSV file.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.taper_w12_l200(cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()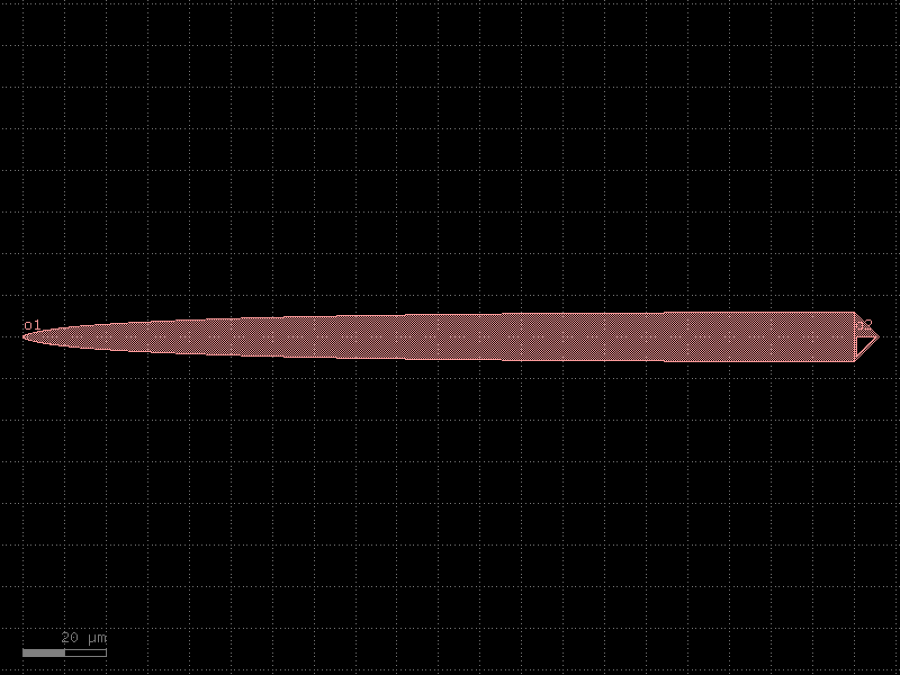
texts¶
- gdsfactory.components.texts.pixel_array(pixels: str = '\n XXX\nX X\nXXXXX\nX X\nX X\n\n', pixel_size: float = 10.0, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'M1')Component
Returns a pixel component from a string representing the pixels.
- Parameters
pixels– string representing the pixelspixel_size– width/height for each pixellayer– layer for each pixel
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.pixel_array(pixels='\n XXX\nX X\nXXXXX\nX X\nX X\n\n', pixel_size=10, layer='M1').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.texts.text(text: str = 'abcd', size: float = 10.0, position: tuple[float, float] = (0, 0), justify: str = 'left', layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG')Component
Text shapes.
- Parameters
text– string.size– in um.position– x, y position.justify– left, right, center.layer– for the text.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.text(text='abcd', size=10, position=(0, 0), justify='left', layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.texts.text_freetype(text: str = 'a', size: int = 10, justify: str = 'left', font: str | Path = PosixPath('/home/runner/work/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/gdsfactory/components/texts/fonts/OCR-A.ttf'), layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', layers: Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum] | None = None)Component
Returns text Component.
- Parameters
text– string.size– in um.justify– left, right, center.font– Font face to use. Default DEPLOF does not require additional libraries, otherwise freetype load fonts. You can choose font by name (e.g. “Times New Roman”), or by file OTF or TTF filepath.layer– list of layers to use for the text.layers– list of layers to use for the text.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.text_freetype(text='a', size=10, justify='left', layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.texts.text_klayout(text: str = 'a', layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', layers: Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum] | None = None, bbox_layers: Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum] | None = None)Component
Returns a text component.
- Parameters
text– string.layer– text layer.layers– layers for the text.bbox_layers– layers for the text bounding box.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.text_klayout(text='a', layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.texts.text_lines(text: tuple[str, ...] = ('Chip', '01'), size: float = 0.4, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG')Component
Returns a Component from a text lines.
- Parameters
text– list of strings.size– text size.layer– text layer.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.text_lines(text=('Chip', '01'), size=0.4, layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.texts.text_rectangular(text: str = 'abcd', size: float = 10.0, position: tuple[float, float] = (0.0, 0.0), justify: str = 'left', layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | ~kfactory.layer.LayerEnum | None = 'WG', layers: ~collections.abc.Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | ~kfactory.layer.LayerEnum] | None = None, font: ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], dict[str, str]] = <functools._lru_cache_wrapper object>)Component
Pixel based font, guaranteed to be manhattan, without acute angles.
- Parameters
text– string.size– pixel size.position– coordinate.justify– left, right or center.layer– for text.layers– optional for duplicating the text.font– function that returns dictionary of characters.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.text_rectangular(text='abcd', size=10, position=(0, 0), justify='left', layer='WG').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.texts.text_rectangular_multi_layer(text: str = 'abcd', layers: ~collections.abc.Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | ~kfactory.layer.LayerEnum] = ('WG', 'M1', 'M2', 'MTOP'), text_factory: str | ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], ~gdsfactory.component.Component] | dict[str, ~typing.Any] | ~kfactory.kcell.DKCell = <function text_rectangular>, **kwargs: ~typing.Any)Component
Returns rectangular text in different layers.
- Parameters
text– string of text.layers– list of layers to replicate the text.text_factory– function to create the text Components.kwargs– keyword arguments for text_factory.
- Keyword Arguments
size– pixel size.position– coordinate.justify– left, right or center.font– function that returns dictionary of characters.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.text_rectangular_multi_layer(text='abcd', layers=('WG', 'M1', 'M2', 'MTOP')).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()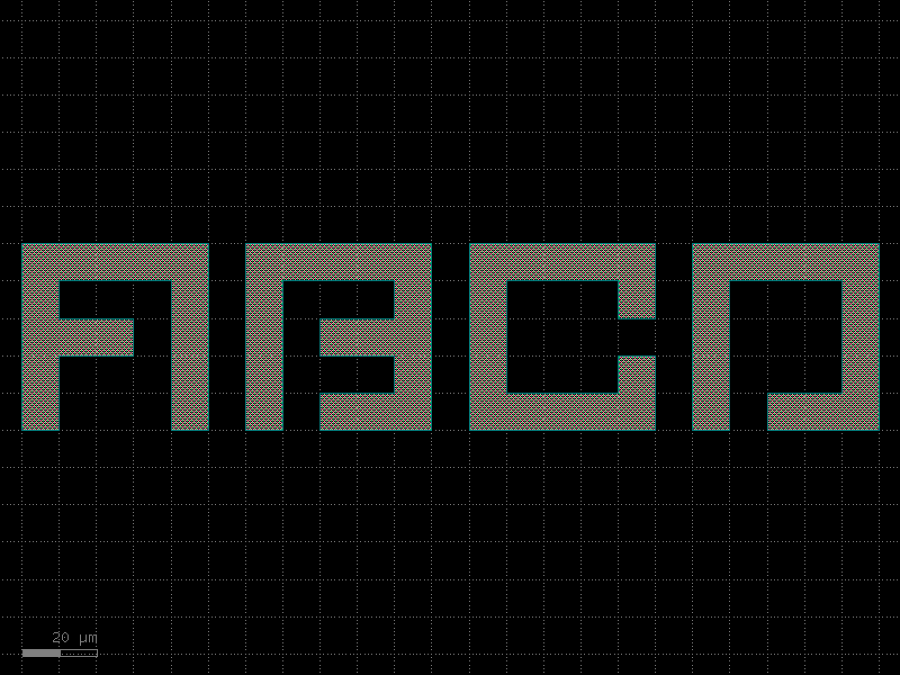
vias¶
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via(size: tuple[float, float] = (0.7, 0.7), enclosure: float = 1.0, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'VIAC', bbox_layers: Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum] | None = None, bbox_offset: float = 0, bbox_offsets: Sequence[float] | None = None, pitch: float = 2, column_pitch: float | None = None, row_pitch: float | None = None)Component
Rectangular via.
- Parameters
size– in x and y direction.enclosure– inclusion of via.layer– via layer.bbox_layers– layers for the bounding box.bbox_offset– in um.bbox_offsets– List of offsets for each bbox_layer.pitch– pitch between vias.column_pitch– Optional pitch between columns of vias. Default is pitch.row_pitch– Optional pitch between rows of vias. Default is pitch.
enclosure _________________________________________ |<---> | | gap[0] size[0] | | <------> <-----> | | ______ ______ | | | | | | | | | | | | size[1] | | |______| |______| | | <-------------> | | pitch | |_______________________________________|
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via(size=(0.7, 0.7), enclosure=1, layer='VIAC', bbox_offset=0, pitch=2).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_chain(num_vias: int = 100, cols: int = 10, via: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'via1', contact: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'via_stack_m2_m3', layers_bot: Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum] = ('M1',), layers_top: Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum] = ('M2',), offsets_top: tuple[float, ...] = (0,), offsets_bot: tuple[float, ...] = (0,), via_min_enclosure: float = 1.0, min_metal_spacing: float = 1.0, contact_offset: float = 0.0)Component
Via chain to extract via resistance.
- Parameters
num_vias– number of vias.cols– number of column pairs.via– via component.contact– contact component.layers_bot– list of bottom layers.layers_top– list of top layers.offsets_top– list of top layer offsets.offsets_bot– list of bottom layer offsets.via_min_enclosure– via_min_enclosure.min_metal_spacing– min_metal_spacing.contact_offset– contact offset.
side view: min_metal_spacing ┌────────────────────────────────────┐ ┌────────────────────────────────────┐ │ layers_top │ │ │ │ │◄───────────► │ │ └─────────────┬─────┬────────────────┘ └───────────────┬─────┬──────────────┘ │ │ via_enclosure │ │ │ │◄───────────────► │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │width│ │ │ ◄─────► │ │ │ │ │ │ ┌─────────────┴─────┴───────────────────────────────────────────────┴─────┴───────────────┐ │ layers_bot │ │ │ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ ◄─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────► 2*e + w + min_metal_spacing + 2*e + w
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_chain(num_vias=100, cols=10, via='via1', contact='via_stack_m2_m3', layers_bot=('M1',), layers_top=('M2',), offsets_top=(0,), offsets_bot=(0,), via_min_enclosure=1, min_metal_spacing=1, contact_offset=0).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()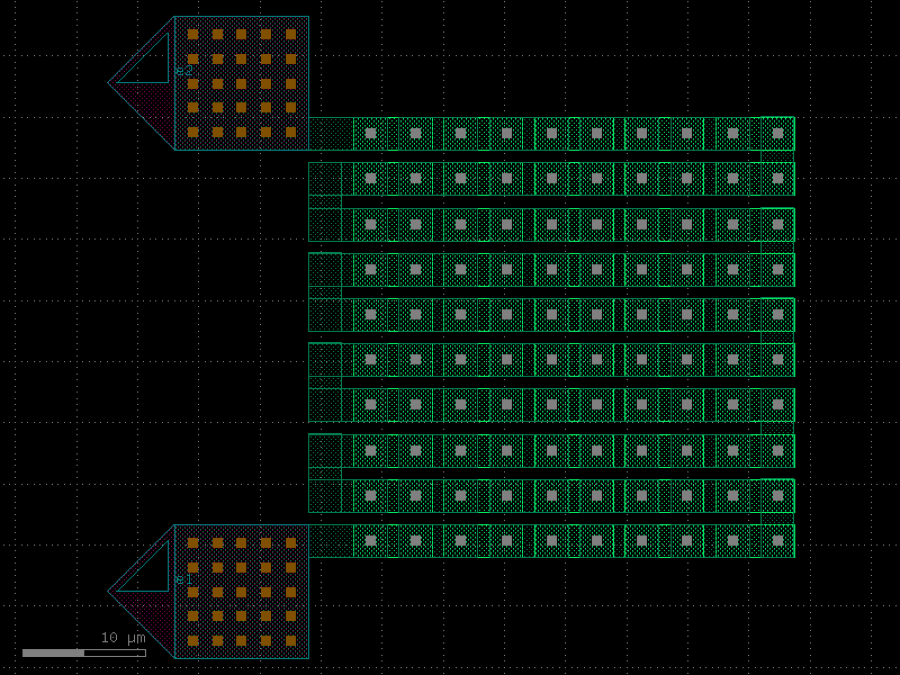
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_circular(radius: float = 0.35, enclosure: float = 1.0, layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'VIAC', pitch: float | None = 2, column_pitch: float | None = None, row_pitch: float | None = None, angle_resolution: float = 2.5)Component
Circular via.
- Parameters
radius– in um.enclosure– inclusion of via in um for the layer above.layer– via layer.pitch– pitch between vias.column_pitch– Optional pitch between columns of vias. Default is pitch.row_pitch– Optional pitch between rows of vias. Default is pitch.angle_resolution– number of degrees per point.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_circular(radius=0.35, enclosure=1, layer='VIAC', pitch=2, angle_resolution=2.5).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_corner(cross_section: MultiCrossSectionAngleSpec = ((<function metal2>, (0, 180)), (<function metal3>, (90, 270))), vias: tuple[ComponentSpec] = ('via1', ), layers_labels: tuple[str, ...] = ('m2', 'm3'), **kwargs: Any)gf.Component
Returns Corner via.
Use in place of wire_corner to route between two layers.
- Parameters
cross_section– list of cross_section, orientation pairs.vias– vias to use to fill the rectangles.layers_labels– Labels to use for each layer.kwargs– cross_section settings.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_corner(cross_section=(({'function': 'metal2', 'module': 'gdsfactory.cross_section'}, (0, 180)), ({'function': 'metal3', 'module': 'gdsfactory.cross_section'}, (90, 270))), layers_labels=('m2', 'm3')).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack(size: tuple[float, float] = (11.0, 11.0), layers: Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum] = ('M1', 'M2', 'MTOP'), layer_offsets: Sequence[float] | tuple[float | tuple[float, float], ...] | None = None, vias: Sequence[str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | None] = ('via1', 'via2', None), layer_to_port_orientations: dict[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum, list[int]] | None = None, correct_size: bool = True, slot_horizontal: bool = False, slot_vertical: bool = False, port_orientations: tuple[int, ...] | list[int] | None = (180, 90, 0, -90))Component
Rectangular via array stack.
You can use it to connect different metal layers or metals to silicon. You can use the naming convention via_stack_layerSource_layerDestination contains 4 ports (e1, e2, e3, e4)
also know as Via array http://
www .vlsi -expert .com /2017 /12 /vias .html - Parameters
size– of the layers.layers– layers on which to draw rectangles.layer_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size. If a tuple, it is the offset in x and y.vias– vias to use to fill the rectangles.layer_to_port_orientations– dictionary of layer to port_orientations.correct_size– if True, if the specified dimensions are too small it increases them to the minimum possible to fit a via.slot_horizontal– if True, then vias are horizontal.slot_vertical– if True, then vias are vertical.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack(size=(11, 11), layers=('M1', 'M2', 'MTOP'), correct_size=True, slot_horizontal=False, slot_vertical=False, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack_corner45(width: float = 10, layers: Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum | None] = ('M1', 'M2', 'MTOP'), layer_offsets: Sequence[float] | None = None, vias: Sequence[str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | None] = ('via1', 'via2', None), layer_port: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum | None = None, correct_size: bool = True)Component
Rectangular via array stack at a 45 degree angle.
- Parameters
width– of the corner45.layers– layers on which to draw rectangles.layer_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size.vias– vias to use to fill the rectangles.layer_port– if None assumes port is on the last layer.correct_size– if True, if the specified dimensions are too small it increases them to the minimum possible to fit a via.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack_corner45(width=10, layers=('M1', 'M2', 'MTOP'), correct_size=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()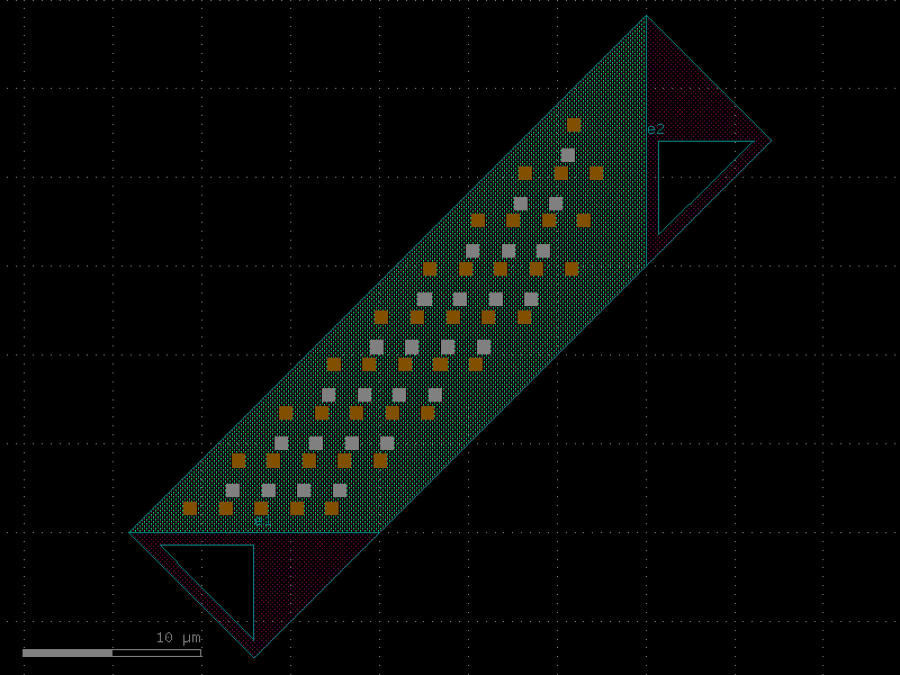
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack_corner45_extended(corner: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'via_stack_corner45', via_stack: str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell = 'via_stack', width: float = 3, length: float = 10)Component
Rectangular via array stack at a 45 degree angle.
- Parameters
corner– corner component.via_stack– for the via stack.width– of the corner45.length– of the straight.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack_corner45_extended(corner='via_stack_corner45', via_stack='via_stack', width=3, length=10).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack_heater_mtop_mini(*, size: Size = (4, 4), layers: LayerSpecs = ('HEATER', 'M2', 'MTOP'), layer_offsets: Floats | tuple[float | tuple[float, float], ...] | None = None, vias: Sequence[ComponentSpec | None] = (None, 'via1', 'via2'), layer_to_port_orientations: dict[LayerSpec, list[int]] | None = None, correct_size: bool = True, slot_horizontal: bool = False, slot_vertical: bool = False, port_orientations: Ints | None = (180, 90, 0, -90))Component
Rectangular via array stack.
You can use it to connect different metal layers or metals to silicon. You can use the naming convention via_stack_layerSource_layerDestination contains 4 ports (e1, e2, e3, e4)
also know as Via array http://
www .vlsi -expert .com /2017 /12 /vias .html - Parameters
size– of the layers.layers– layers on which to draw rectangles.layer_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size. If a tuple, it is the offset in x and y.vias– vias to use to fill the rectangles.layer_to_port_orientations– dictionary of layer to port_orientations.correct_size– if True, if the specified dimensions are too small it increases them to the minimum possible to fit a via.slot_horizontal– if True, then vias are horizontal.slot_vertical– if True, then vias are vertical.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack_heater_mtop_mini(size=(4, 4), layers=('HEATER', 'M2', 'MTOP'), correct_size=True, slot_horizontal=False, slot_vertical=False, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack_m1_m3(size: Size = (11.0, 11.0), *, layers: LayerSpecs = ('M1', 'M2', 'MTOP'), layer_offsets: Floats | tuple[float | tuple[float, float], ...] | None = None, vias: Sequence[ComponentSpec | None] = ('via1', 'via2', None), layer_to_port_orientations: dict[LayerSpec, list[int]] | None = None, correct_size: bool = True, slot_horizontal: bool = False, slot_vertical: bool = False, port_orientations: Ints | None = (180, 90, 0, -90))Component
Rectangular via array stack.
You can use it to connect different metal layers or metals to silicon. You can use the naming convention via_stack_layerSource_layerDestination contains 4 ports (e1, e2, e3, e4)
also know as Via array http://
www .vlsi -expert .com /2017 /12 /vias .html - Parameters
size– of the layers.layers– layers on which to draw rectangles.layer_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size. If a tuple, it is the offset in x and y.vias– vias to use to fill the rectangles.layer_to_port_orientations– dictionary of layer to port_orientations.correct_size– if True, if the specified dimensions are too small it increases them to the minimum possible to fit a via.slot_horizontal– if True, then vias are horizontal.slot_vertical– if True, then vias are vertical.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack_m1_m3(size=(11, 11), layers=('M1', 'M2', 'MTOP'), correct_size=True, slot_horizontal=False, slot_vertical=False, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack_m1_mtop(size: Size = (11.0, 11.0), *, layers: LayerSpecs = ('M1', 'M2', 'MTOP'), layer_offsets: Floats | tuple[float | tuple[float, float], ...] | None = None, vias: Sequence[ComponentSpec | None] = ('via1', 'via2', None), layer_to_port_orientations: dict[LayerSpec, list[int]] | None = None, correct_size: bool = True, slot_horizontal: bool = False, slot_vertical: bool = False, port_orientations: Ints | None = (180, 90, 0, -90))Component
Rectangular via array stack.
You can use it to connect different metal layers or metals to silicon. You can use the naming convention via_stack_layerSource_layerDestination contains 4 ports (e1, e2, e3, e4)
also know as Via array http://
www .vlsi -expert .com /2017 /12 /vias .html - Parameters
size– of the layers.layers– layers on which to draw rectangles.layer_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size. If a tuple, it is the offset in x and y.vias– vias to use to fill the rectangles.layer_to_port_orientations– dictionary of layer to port_orientations.correct_size– if True, if the specified dimensions are too small it increases them to the minimum possible to fit a via.slot_horizontal– if True, then vias are horizontal.slot_vertical– if True, then vias are vertical.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack_m1_mtop(size=(11, 11), layers=('M1', 'M2', 'MTOP'), correct_size=True, slot_horizontal=False, slot_vertical=False, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack_m2_m3(size: Size = (11.0, 11.0), *, layers: LayerSpecs = ('M2', 'MTOP'), layer_offsets: Floats | tuple[float | tuple[float, float], ...] | None = None, vias: Sequence[ComponentSpec | None] = ('via2', None), layer_to_port_orientations: dict[LayerSpec, list[int]] | None = None, correct_size: bool = True, slot_horizontal: bool = False, slot_vertical: bool = False, port_orientations: Ints | None = (180, 90, 0, -90))Component
Rectangular via array stack.
You can use it to connect different metal layers or metals to silicon. You can use the naming convention via_stack_layerSource_layerDestination contains 4 ports (e1, e2, e3, e4)
also know as Via array http://
www .vlsi -expert .com /2017 /12 /vias .html - Parameters
size– of the layers.layers– layers on which to draw rectangles.layer_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size. If a tuple, it is the offset in x and y.vias– vias to use to fill the rectangles.layer_to_port_orientations– dictionary of layer to port_orientations.correct_size– if True, if the specified dimensions are too small it increases them to the minimum possible to fit a via.slot_horizontal– if True, then vias are horizontal.slot_vertical– if True, then vias are vertical.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack_m2_m3(size=(11, 11), layers=('M2', 'MTOP'), correct_size=True, slot_horizontal=False, slot_vertical=False, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack_npp_m1(size: Size = (11.0, 11.0), *, layers: LayerSpecs = ('WG', 'NPP', 'M1'), layer_offsets: Floats | tuple[float | tuple[float, float], ...] | None = None, vias: Sequence[ComponentSpec | None] = (None, None, 'viac'), layer_to_port_orientations: dict[LayerSpec, list[int]] | None = None, correct_size: bool = True, slot_horizontal: bool = False, slot_vertical: bool = False, port_orientations: Ints | None = (180, 90, 0, -90))Component
Rectangular via array stack.
You can use it to connect different metal layers or metals to silicon. You can use the naming convention via_stack_layerSource_layerDestination contains 4 ports (e1, e2, e3, e4)
also know as Via array http://
www .vlsi -expert .com /2017 /12 /vias .html - Parameters
size– of the layers.layers– layers on which to draw rectangles.layer_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size. If a tuple, it is the offset in x and y.vias– vias to use to fill the rectangles.layer_to_port_orientations– dictionary of layer to port_orientations.correct_size– if True, if the specified dimensions are too small it increases them to the minimum possible to fit a via.slot_horizontal– if True, then vias are horizontal.slot_vertical– if True, then vias are vertical.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack_npp_m1(size=(11, 11), layers=('WG', 'NPP', 'M1'), correct_size=True, slot_horizontal=False, slot_vertical=False, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack_slab_m1(size: Size = (11.0, 11.0), *, layers: LayerSpecs = ('SLAB90', 'M1'), layer_offsets: Floats | tuple[float | tuple[float, float], ...] | None = None, vias: Sequence[ComponentSpec | None] = ('viac', 'via1'), layer_to_port_orientations: dict[LayerSpec, list[int]] | None = None, correct_size: bool = True, slot_horizontal: bool = False, slot_vertical: bool = False, port_orientations: Ints | None = (180, 90, 0, -90))Component
Rectangular via array stack.
You can use it to connect different metal layers or metals to silicon. You can use the naming convention via_stack_layerSource_layerDestination contains 4 ports (e1, e2, e3, e4)
also know as Via array http://
www .vlsi -expert .com /2017 /12 /vias .html - Parameters
size– of the layers.layers– layers on which to draw rectangles.layer_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size. If a tuple, it is the offset in x and y.vias– vias to use to fill the rectangles.layer_to_port_orientations– dictionary of layer to port_orientations.correct_size– if True, if the specified dimensions are too small it increases them to the minimum possible to fit a via.slot_horizontal– if True, then vias are horizontal.slot_vertical– if True, then vias are vertical.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack_slab_m1(size=(11, 11), layers=('SLAB90', 'M1'), correct_size=True, slot_horizontal=False, slot_vertical=False, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack_slab_m1_horizontal(size: Size = (11.0, 11.0), *, layers: LayerSpecs = ('SLAB90', 'M1'), layer_offsets: Floats | tuple[float | tuple[float, float], ...] | None = None, vias: Sequence[ComponentSpec | None] = ('viac', 'via1'), layer_to_port_orientations: dict[LayerSpec, list[int]] | None = None, correct_size: bool = True, slot_horizontal: bool = True, slot_vertical: bool = False, port_orientations: Ints | None = (180, 90, 0, -90))Component
Rectangular via array stack.
You can use it to connect different metal layers or metals to silicon. You can use the naming convention via_stack_layerSource_layerDestination contains 4 ports (e1, e2, e3, e4)
also know as Via array http://
www .vlsi -expert .com /2017 /12 /vias .html - Parameters
size– of the layers.layers– layers on which to draw rectangles.layer_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size. If a tuple, it is the offset in x and y.vias– vias to use to fill the rectangles.layer_to_port_orientations– dictionary of layer to port_orientations.correct_size– if True, if the specified dimensions are too small it increases them to the minimum possible to fit a via.slot_horizontal– if True, then vias are horizontal.slot_vertical– if True, then vias are vertical.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack_slab_m1_horizontal(size=(11, 11), layers=('SLAB90', 'M1'), correct_size=True, slot_horizontal=True, slot_vertical=False, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()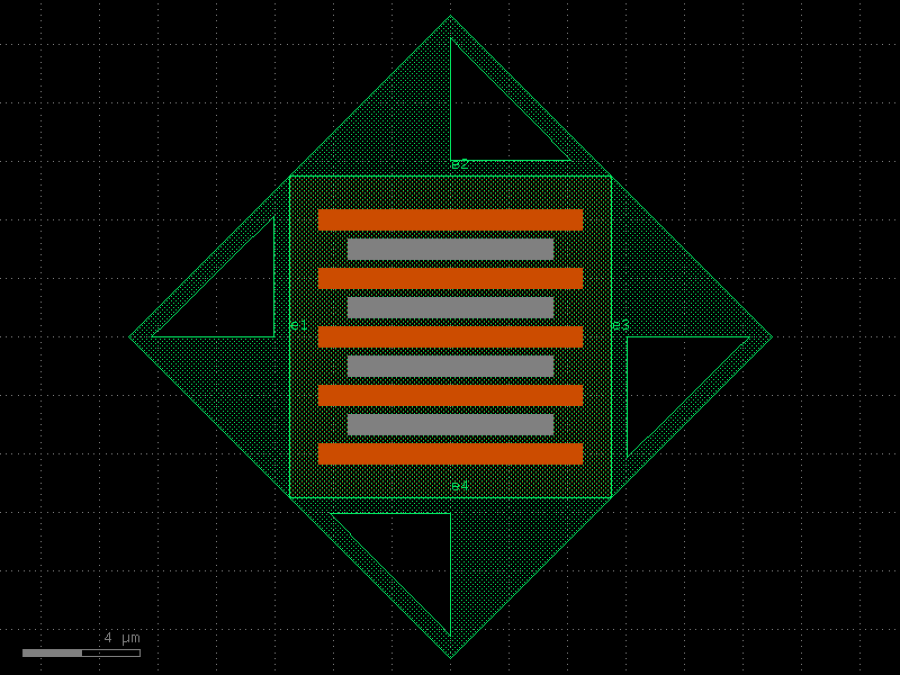
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack_slab_m2(size: Size = (11.0, 11.0), *, layers: LayerSpecs = ('SLAB90', 'M1', 'M2'), layer_offsets: Floats | tuple[float | tuple[float, float], ...] | None = None, vias: Sequence[ComponentSpec | None] = ('viac', 'via1', None), layer_to_port_orientations: dict[LayerSpec, list[int]] | None = None, correct_size: bool = True, slot_horizontal: bool = False, slot_vertical: bool = False, port_orientations: Ints | None = (180, 90, 0, -90))Component
Rectangular via array stack.
You can use it to connect different metal layers or metals to silicon. You can use the naming convention via_stack_layerSource_layerDestination contains 4 ports (e1, e2, e3, e4)
also know as Via array http://
www .vlsi -expert .com /2017 /12 /vias .html - Parameters
size– of the layers.layers– layers on which to draw rectangles.layer_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size. If a tuple, it is the offset in x and y.vias– vias to use to fill the rectangles.layer_to_port_orientations– dictionary of layer to port_orientations.correct_size– if True, if the specified dimensions are too small it increases them to the minimum possible to fit a via.slot_horizontal– if True, then vias are horizontal.slot_vertical– if True, then vias are vertical.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack_slab_m2(size=(11, 11), layers=('SLAB90', 'M1', 'M2'), correct_size=True, slot_horizontal=False, slot_vertical=False, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()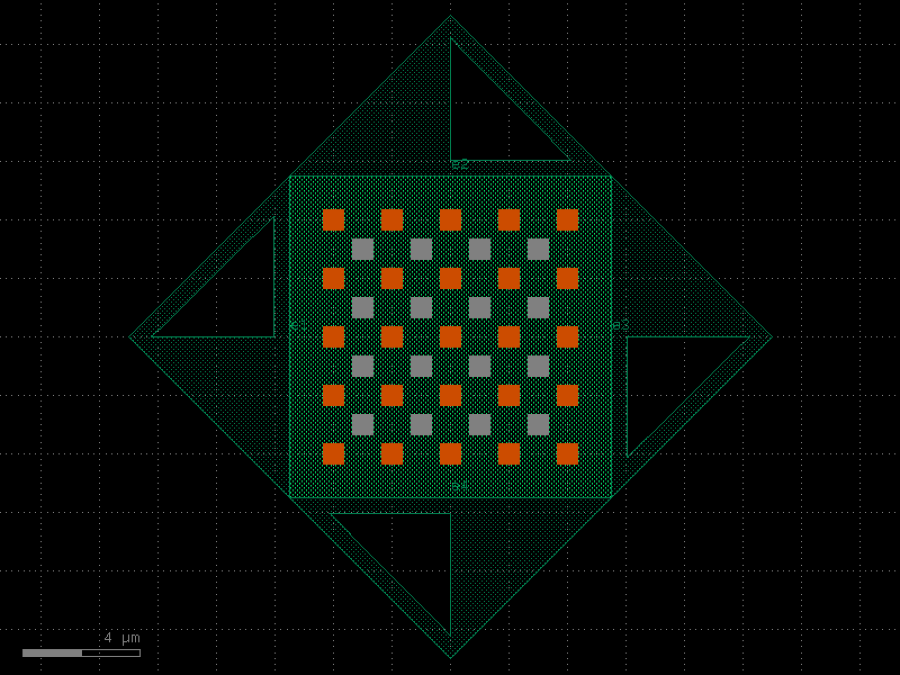
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack_slab_npp_m3(size: Size = (11.0, 11.0), *, layers: LayerSpecs = ('SLAB90', 'NPP', 'M1'), layer_offsets: Floats | tuple[float | tuple[float, float], ...] | None = None, vias: Sequence[ComponentSpec | None] = (None, None, 'viac'), layer_to_port_orientations: dict[LayerSpec, list[int]] | None = None, correct_size: bool = True, slot_horizontal: bool = False, slot_vertical: bool = False, port_orientations: Ints | None = (180, 90, 0, -90))Component
Rectangular via array stack.
You can use it to connect different metal layers or metals to silicon. You can use the naming convention via_stack_layerSource_layerDestination contains 4 ports (e1, e2, e3, e4)
also know as Via array http://
www .vlsi -expert .com /2017 /12 /vias .html - Parameters
size– of the layers.layers– layers on which to draw rectangles.layer_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size. If a tuple, it is the offset in x and y.vias– vias to use to fill the rectangles.layer_to_port_orientations– dictionary of layer to port_orientations.correct_size– if True, if the specified dimensions are too small it increases them to the minimum possible to fit a via.slot_horizontal– if True, then vias are horizontal.slot_vertical– if True, then vias are vertical.port_orientations– list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack_slab_npp_m3(size=(11, 11), layers=('SLAB90', 'NPP', 'M1'), correct_size=True, slot_horizontal=False, slot_vertical=False, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()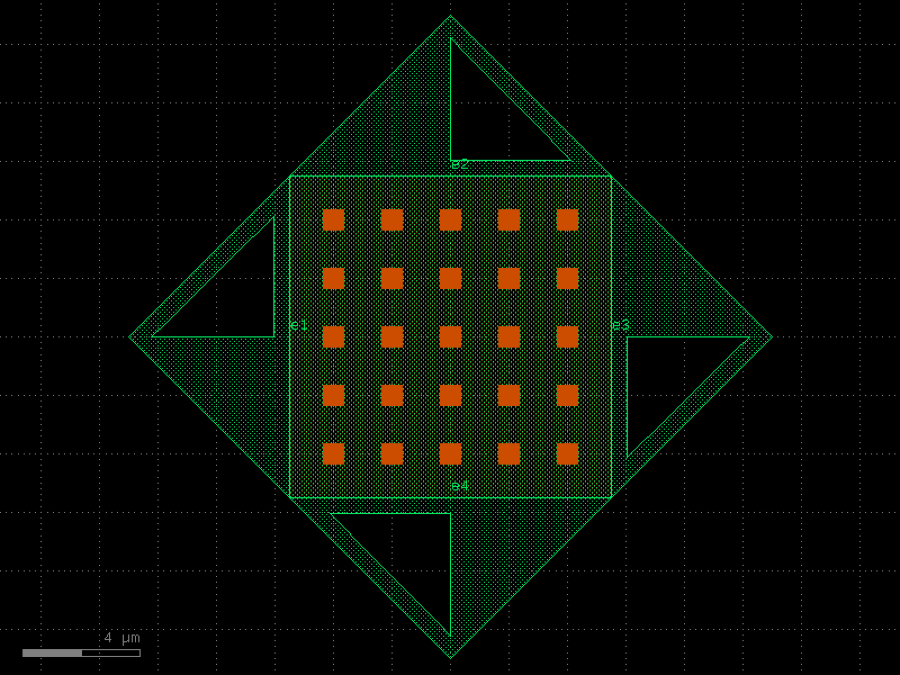
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack_with_offset(layers: Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum] = ('PPP', 'M1'), size: tuple[float, float] | None = (10, 10), sizes: Sequence[tuple[float, float]] | None = None, layer_offsets: Sequence[float] | None = None, vias: Sequence[str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | None] = (None, 'viac'), offsets: Sequence[float] | None = None, layer_to_port_orientations: dict[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum, list[int]] | None = None)Component
Rectangular layer transition with offset between layers.
- Parameters
layers– layer specs between vias.size– for all vias array.sizes– Optional size for each via array. Overrides size.layer_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size.vias– via spec for previous layer. None for no via.offsets– optional offset for each layer relatively to the previous one. By default it only offsets by size[1] if there is a via.layer_to_port_orientations– Optional dictionary with layer to port orientations.
side view __________________________ | | | | layers[2] |__________________________| vias[2] = None | | | layer_offsets[1]+size | layers[1] |__________________________| | | vias[1] ___|_____|__ | | | sizes[0] | layers[0] |____________| vias[0] = None
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack_with_offset(layers=('PPP', 'M1'), size=(10, 10)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()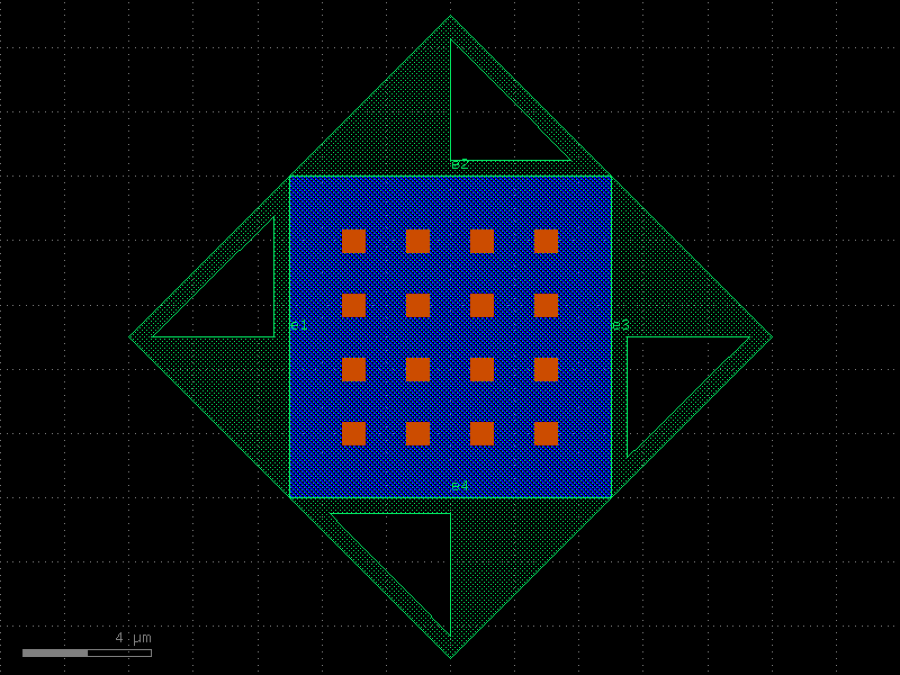
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack_with_offset_m1_m3(*, layers: LayerSpecs = ('M1', 'M2', 'MTOP'), size: Size | None = (10, 10), sizes: Sequence[Size] | None = None, layer_offsets: Sequence[float] | None = None, vias: Sequence[ComponentSpec | None] = (None, 'via1', 'via2'), offsets: Sequence[float] | None = None, layer_to_port_orientations: dict[LayerSpec, list[int]] | None = None)Component
Rectangular layer transition with offset between layers.
- Parameters
layers– layer specs between vias.size– for all vias array.sizes– Optional size for each via array. Overrides size.layer_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size.vias– via spec for previous layer. None for no via.offsets– optional offset for each layer relatively to the previous one. By default it only offsets by size[1] if there is a via.layer_to_port_orientations– Optional dictionary with layer to port orientations.
side view __________________________ | | | | layers[2] |__________________________| vias[2] = None | | | layer_offsets[1]+size | layers[1] |__________________________| | | vias[1] ___|_____|__ | | | sizes[0] | layers[0] |____________| vias[0] = None
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack_with_offset_m1_m3(layers=('M1', 'M2', 'MTOP'), size=(10, 10)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()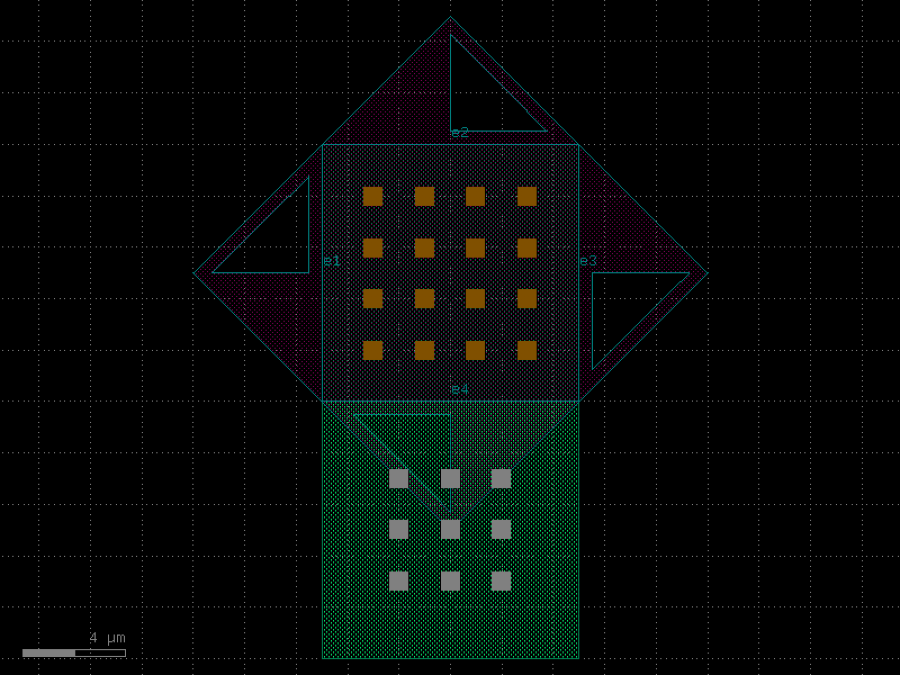
- gdsfactory.components.vias.via_stack_with_offset_ppp_m1(*, layers: LayerSpecs = ('PPP', 'M1'), size: Size | None = (10, 10), sizes: Sequence[Size] | None = None, layer_offsets: Sequence[float] | None = None, vias: Sequence[ComponentSpec | None] = (None, 'viac'), offsets: Sequence[float] | None = None, layer_to_port_orientations: dict[LayerSpec, list[int]] | None = None)Component
Rectangular layer transition with offset between layers.
- Parameters
layers– layer specs between vias.size– for all vias array.sizes– Optional size for each via array. Overrides size.layer_offsets– Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size.vias– via spec for previous layer. None for no via.offsets– optional offset for each layer relatively to the previous one. By default it only offsets by size[1] if there is a via.layer_to_port_orientations– Optional dictionary with layer to port orientations.
side view __________________________ | | | | layers[2] |__________________________| vias[2] = None | | | layer_offsets[1]+size | layers[1] |__________________________| | | vias[1] ___|_____|__ | | | sizes[0] | layers[0] |____________| vias[0] = None
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.via_stack_with_offset_ppp_m1(layers=('PPP', 'M1'), size=(10, 10)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()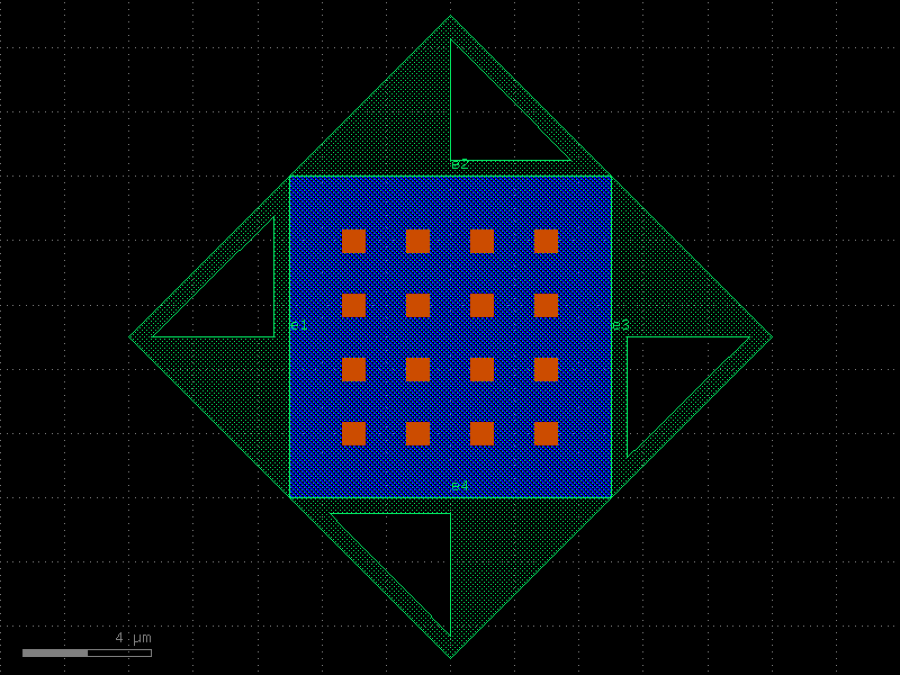
waveguides¶
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.crossing(arm: str | ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], ~gdsfactory.component.Component] | dict[str, ~typing.Any] | ~kfactory.kcell.DKCell = <function crossing_arm>)Component
Waveguide crossing.
- Parameters
arm– arm spec.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.crossing().copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()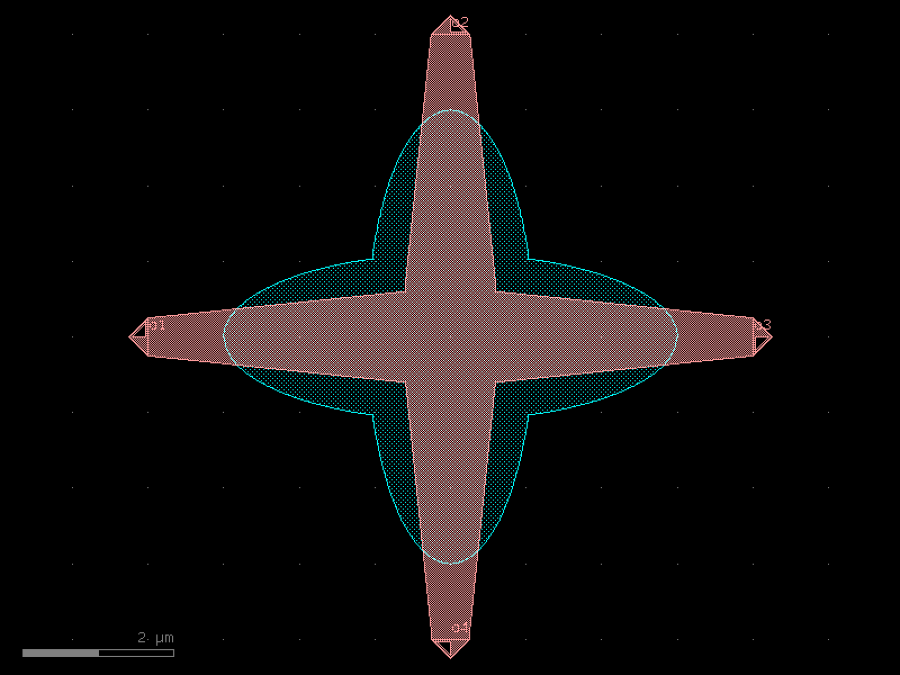
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.crossing45(crossing: ComponentSpec = <function crossing>, port_spacing: float = 40.0, dx: Delta | None = None, alpha: float = 0.08, npoints: int = 101, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_bends: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Returns 45deg crossing with bends.
- Parameters
crossing– crossing function.port_spacing– target I/O port spacing.dx– target length.alpha– optimization parameter. diminish it for tight bends, increase it if raises assertion angle errorsnpoints– number of points.cross_section– cross_section spec.cross_section_bends– cross_section spec.
The 45 Degree crossing CANNOT be kept as an SRef since we only allow for multiples of 90Deg rotations in SRef.
---- ---- \ / X / \ --- ----
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.crossing45(port_spacing=40, alpha=0.08, npoints=101, cross_section='strip', cross_section_bends='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()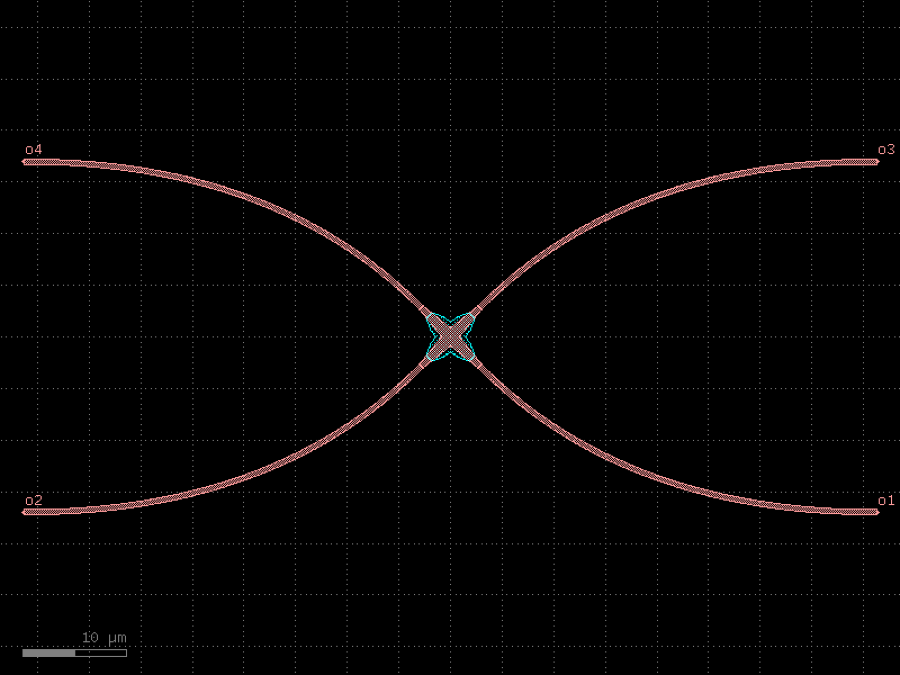
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.crossing_etched(width: float = 0.5, r1: float = 3.0, r2: float = 1.1, w: float = 1.2, L: float = 3.4, layer_wg: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'WG', layer_slab: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum = 'SLAB150')Component
Waveguide crossing.
Full crossing has to be on WG layer (to start with a 220nm slab). Then we etch the ellipses down to 150nm slabs and we keep linear taper at 220nm.
- Parameters
width– input waveguides width.r1– radii.r2– radii.w– wide width.L– length.layer_wg– waveguide layer.layer_slab– shallow etch layer.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.crossing_etched(width=0.5, r1=3, r2=1.1, w=1.2, L=3.4, layer_wg='WG', layer_slab='SLAB150').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()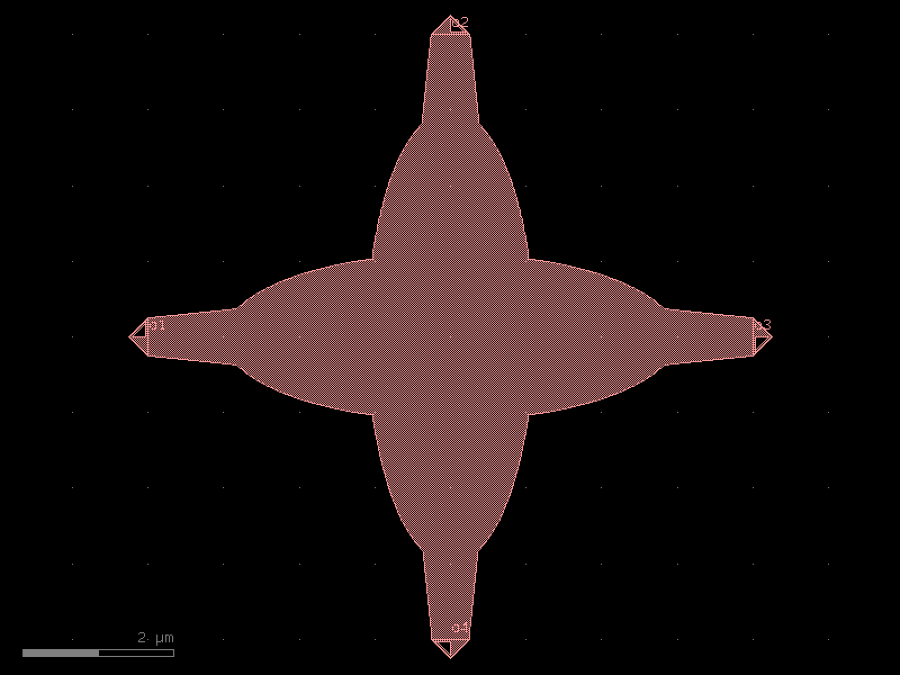
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.crossing_linear_taper(width1: float = 2.5, width2: float = 0.5, length: float = 3, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', taper: ComponentSpec = 'taper')Component
Returns Crossing based on a taper.
The default is a dummy taper.
- Parameters
width1– input width.width2– output width.length– taper length.cross_section– cross_section spec.taper– taper spec.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.crossing_linear_taper(width1=2.5, width2=0.5, length=3, cross_section='strip', taper='taper').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()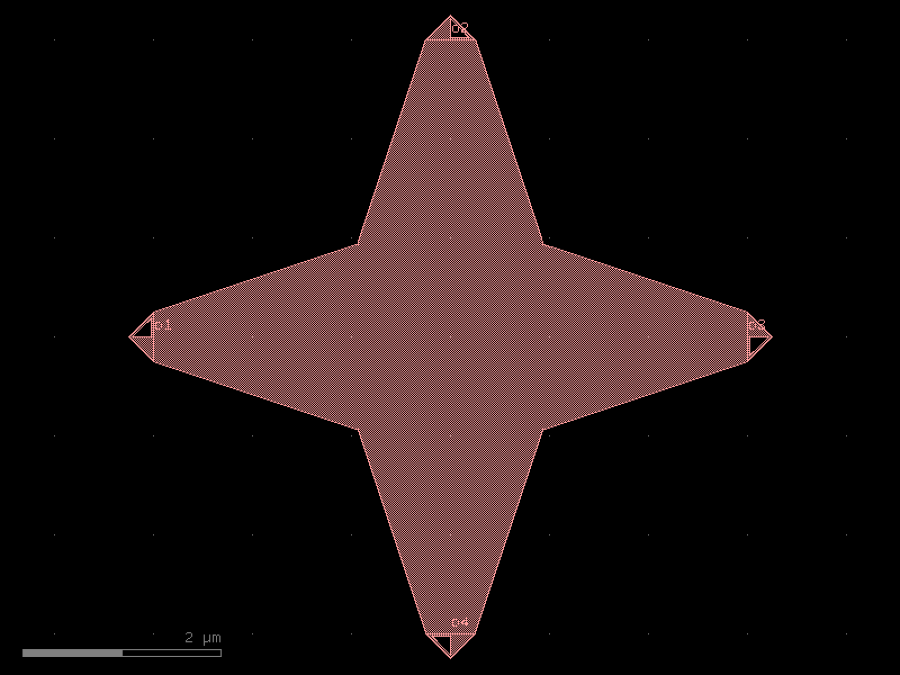
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight(length: float = 10.0, npoints: int = 2, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', width: float | None = None)Component
Returns a Straight waveguide.
- Parameters
length– straight length (um).npoints– number of points.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string or dict).width– width of the waveguide. If None, it will use the width of the cross_section.
o1 -------------- o2 length
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight(length=10, npoints=2, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_array(n: int = 4, spacing: float = 4.0, length: float = 10.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip')Component
Array of straights connected with grating couplers.
useful to align the 4 corners of the chip
- Parameters
n– number of straights.spacing– edge to edge straight spacing.length– straight length (um).cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string or dict).
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_array(n=4, spacing=4, length=10, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_heater_doped_rib(length: float = 320.0, nsections: int = 3, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_rib_tip', cross_section_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'rib_heater_doped', via_stack: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_slab_npp_m3', via_stack_metal: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_m1_mtop', via_stack_metal_size: Size = (10.0, 10.0), via_stack_size: Size = (10.0, 10.0), taper: ComponentSpec | None = 'taper_cross_section', heater_width: float = 2.0, heater_gap: float = 0.8, via_stack_gap: float = 0.0, width: float = 0.5, xoffset_tip1: float = 0.2, xoffset_tip2: float = 0.4)Component
Returns a doped thermal phase shifter.
dimensions from Jacques et al. (2019)
- Parameters
length– of the waveguide in um.nsections– between via_stacks.cross_section– for the input/output ports.cross_section_heater– for the heater.via_stack– optional function to connect the heater strip.via_stack_metal– function to connect the metal area.via_stack_metal_size– x, y size in um.via_stack_size– x, y size in um.taper– optional taper spec.heater_width– in um.heater_gap– in um.via_stack_gap– from edge of via_stack to waveguide.width– waveguide width on the ridge.xoffset_tip1– distance in um from input taper to via_stack.xoffset_tip2– distance in um from output taper to via_stack.
length |<--------------------------------------------->| | length_section | | <---------------------------> | | length_via_stack | | <-------> taper| | __________ _________ | | | | | | | | | via_stack|__________________| | | | | size | heater width | | | | /|__________|__________________|________|\ | | / | heater_gap | \ | |/ |______________________________________| \ | \ |_______________width__________________| / \ | | / \|_____________heater_gap______________ |/ | | | | | |____heater_width____| | | | | | |________| |________| taper cross_section_heater |<------width------>| ____________________ heater_gap slab_gap top_via_stack | |<---------->| bot_via_stack <--> ___ ______________________| |___________________________|___ | | | undoped Si | | | | |layer_heater| intrinsic region |layer_heater | | |___|____________|__________________________________________|______________|___| <------------> heater_width <------------------------------------------------------------------------------> slab_width
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_heater_doped_rib(length=320, nsections=3, cross_section='strip_rib_tip', cross_section_heater='rib_heater_doped', via_stack='via_stack_slab_npp_m3', via_stack_metal='via_stack_m1_mtop', via_stack_metal_size=(10, 10), via_stack_size=(10, 10), taper='taper_cross_section', heater_width=2, heater_gap=0.8, via_stack_gap=0, width=0.5, xoffset_tip1=0.2, xoffset_tip2=0.4).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_heater_doped_strip(length: float = 320.0, nsections: int = 3, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_heater_doped', cross_section_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'rib_heater_doped', via_stack: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_npp_m1', via_stack_metal: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_m1_mtop', via_stack_metal_size: Size = (10.0, 10.0), via_stack_size: Size = (10.0, 10.0), taper: ComponentSpec | None = 'taper_cross_section', heater_width: float = 2.0, heater_gap: float = 0.8, via_stack_gap: float = 0.0, width: float = 0.5, xoffset_tip1: float = 0.2, xoffset_tip2: float = 0.4)Component
Top view.
- Parameters
length– of the waveguide in um.nsections– between via_stacks.cross_section– for the input/output ports.cross_section_heater– for the heater.via_stack– optional function to connect the heater strip.via_stack_metal– function to connect the metal area.via_stack_metal_size– x, y size in um.via_stack_size– x, y size in um.taper– optional taper spec.heater_width– in um.heater_gap– in um.via_stack_gap– from edge of via_stack to waveguide.width– waveguide width on the ridge.xoffset_tip1– distance in um from input taper to via_stack.xoffset_tip2– distance in um from output taper to via_stack.
cross_section .. code:
|<------width------>| ____________ ___________________ ______________ | | | undoped Si | | | |layer_heater| | intrinsic region |<----------->| layer_heater | |____________| |___________________| |______________| <------------> heater_gap heater_width
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_heater_doped_strip(length=320, nsections=3, cross_section='strip_heater_doped', cross_section_heater='rib_heater_doped', via_stack='via_stack_npp_m1', via_stack_metal='via_stack_m1_mtop', via_stack_metal_size=(10, 10), via_stack_size=(10, 10), taper='taper_cross_section', heater_width=2, heater_gap=0.8, via_stack_gap=0, width=0.5, xoffset_tip1=0.2, xoffset_tip2=0.4).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()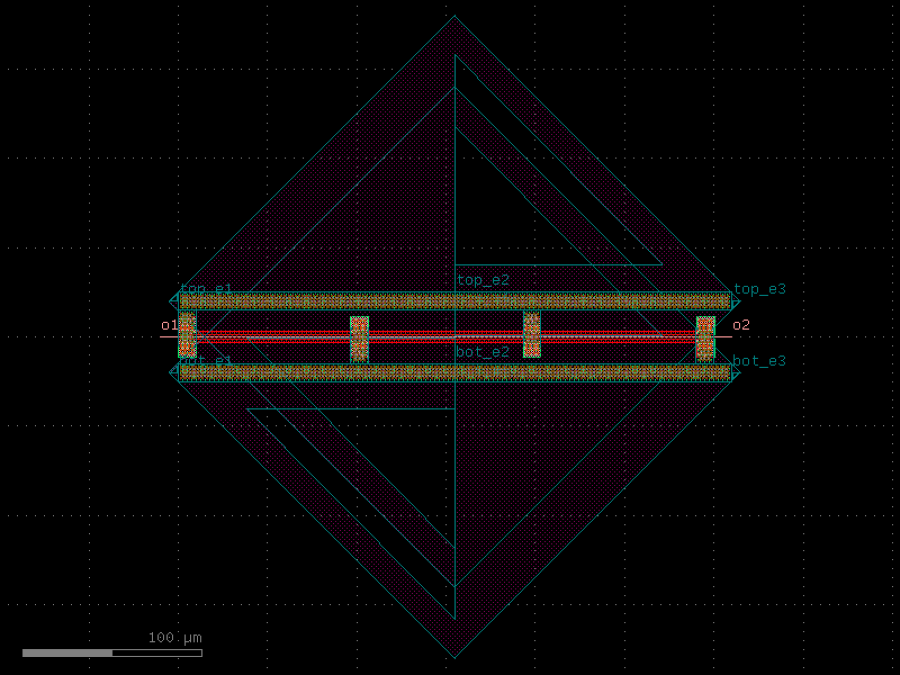
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_heater_meander(length: float = 300.0, spacing: float = 2.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', heater_width: float = 2.5, extension_length: float = 15.0, layer_heater: LayerSpec = 'HEATER', radius: float | None = None, via_stack: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_heater_mtop', port_orientation1: float | None = None, port_orientation2: float | None = None, heater_taper_length: float = 10.0, straight_widths: Floats | None = None, taper_length: float = 10.0, n: int | None = 3)Component
Returns a meander based heater.
based on SungWon Chung, Makoto Nakai, and Hossein Hashemi, Low-power thermo-optic silicon modulator for large-scale photonic integrated systems Opt. Express 27, 13430-13459 (2019) https://
www .osapublishing .org /oe /abstract .cfm ?URI = oe -27 -9 -13430 - Parameters
length– total length of the optical path.spacing– waveguide spacing (center to center).cross_section– for waveguide.heater_width– for heater.extension_length– of input and output optical ports.layer_heater– for top heater, if None, it does not add a heater.radius– for the meander bends. Defaults to cross_section radius.via_stack– for the heater to via_stack metal.port_orientation1– in degrees. None adds all orientations.port_orientation2– in degrees. None adds all orientations.heater_taper_length– minimizes current concentrations from heater to via_stack.straight_widths– widths of the straight sections.taper_length– from the cross_section.n– number of straight sections.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_heater_meander(length=300, spacing=2, cross_section='strip', heater_width=2.5, extension_length=15, layer_heater='HEATER', via_stack='via_stack_heater_mtop', heater_taper_length=10, taper_length=10, n=3).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_heater_meander_doped(length: float = 300.0, spacing: float = 2.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', heater_width: float = 1.5, extension_length: float = 15.0, layers_doping: LayerSpecs = ('P', 'PP', 'PPP'), radius: float = 5.0, via_stack: ComponentSpec | None = functools.partial(<function via_stack>, size=(1.5, 1.5), layers=('M1', 'M2'), vias=(functools.partial(<function via>, layer='VIAC', size=(0.1, 0.1), pitch=0.2, enclosure=0.1), functools.partial(<function via>, layer='VIA1', size=(0.1, 0.1), pitch=0.2, enclosure=0.1))), port_orientation1: float | None = None, port_orientation2: float | None = None, straight_widths: Floats = (0.8, 0.9, 0.8), taper_length: float = 10)Component
Returns a meander based heater.
based on SungWon Chung, Makoto Nakai, and Hossein Hashemi, Low-power thermo-optic silicon modulator for large-scale photonic integrated systems Opt. Express 27, 13430-13459 (2019) https://
www .osapublishing .org /oe /abstract .cfm ?URI = oe -27 -9 -13430 - Parameters
length– total length of the optical path.spacing– waveguide spacing (center to center).cross_section– for waveguide.heater_width– for heater.extension_length– of input and output optical ports.layers_doping– doping layers to be used for heater.radius– for the meander bends.via_stack– for the heater to via_stack metal.port_orientation1– in degrees. None adds all orientations.port_orientation2– in degrees. None adds all orientations.straight_widths– width of the straight sections.taper_length– from the cross_section.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_heater_meander_doped(length=300, spacing=2, cross_section='strip', heater_width=1.5, extension_length=15, layers_doping=('P', 'PP', 'PPP'), radius=5, straight_widths=(0.8, 0.9, 0.8), taper_length=10).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_heater_metal(length: float = 320.0, *, length_undercut_spacing: float = 0, length_undercut: float = 5, length_straight: float = 0.1, length_straight_input: float = 0.1, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'heater_metal', cross_section_waveguide_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_heater_metal', cross_section_heater_undercut: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_heater_metal_undercut', with_undercut: bool = False, via_stack: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_heater_mtop', port_orientation1: int | None = None, port_orientation2: int | None = None, heater_taper_length: float = 5.0, ohms_per_square: float | None = None)Component
Returns a thermal phase shifter.
dimensions from Jacques et al. (2019)
- Parameters
length– of the waveguide.length_undercut_spacing– from undercut regions.length_undercut– length of each undercut section.length_straight– length of the straight waveguide.length_straight_input– from input port to where trenches start.cross_section– for waveguide ports.cross_section_heater– for heated sections. heater metal only.cross_section_waveguide_heater– for heated sections.cross_section_heater_undercut– for heated sections with undercut.with_undercut– isolation trenches for higher efficiency.via_stack– via stack.port_orientation1– left via stack port orientation. None adds all orientations.port_orientation2– right via stack port orientation. None adds all orientations.heater_taper_length– minimizes current concentrations from heater to via_stack.ohms_per_square– to calculate resistance.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_heater_metal(length=320, length_undercut_spacing=0, length_undercut=5, length_straight=0.1, length_straight_input=0.1, cross_section='strip', cross_section_heater='heater_metal', cross_section_waveguide_heater='strip_heater_metal', cross_section_heater_undercut='strip_heater_metal_undercut', with_undercut=False, via_stack='via_stack_heater_mtop', heater_taper_length=5).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_heater_metal_90_90(length: float = 320.0, *, length_undercut_spacing: float = 0, length_undercut: float = 5, length_straight: float = 0.1, length_straight_input: float = 0.1, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'heater_metal', cross_section_waveguide_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_heater_metal', cross_section_heater_undercut: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_heater_metal_undercut', with_undercut: bool = False, via_stack: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_heater_mtop', port_orientation1: int | None = 90, port_orientation2: int | None = 90, heater_taper_length: float = 5.0, ohms_per_square: float | None = None)Component
Returns a thermal phase shifter.
dimensions from Jacques et al. (2019)
- Parameters
length– of the waveguide.length_undercut_spacing– from undercut regions.length_undercut– length of each undercut section.length_straight– length of the straight waveguide.length_straight_input– from input port to where trenches start.cross_section– for waveguide ports.cross_section_heater– for heated sections. heater metal only.cross_section_waveguide_heater– for heated sections.cross_section_heater_undercut– for heated sections with undercut.with_undercut– isolation trenches for higher efficiency.via_stack– via stack.port_orientation1– left via stack port orientation. None adds all orientations.port_orientation2– right via stack port orientation. None adds all orientations.heater_taper_length– minimizes current concentrations from heater to via_stack.ohms_per_square– to calculate resistance.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_heater_metal_90_90(length=320, length_undercut_spacing=0, length_undercut=5, length_straight=0.1, length_straight_input=0.1, cross_section='strip', cross_section_heater='heater_metal', cross_section_waveguide_heater='strip_heater_metal', cross_section_heater_undercut='strip_heater_metal_undercut', with_undercut=False, via_stack='via_stack_heater_mtop', port_orientation1=90, port_orientation2=90, heater_taper_length=5).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()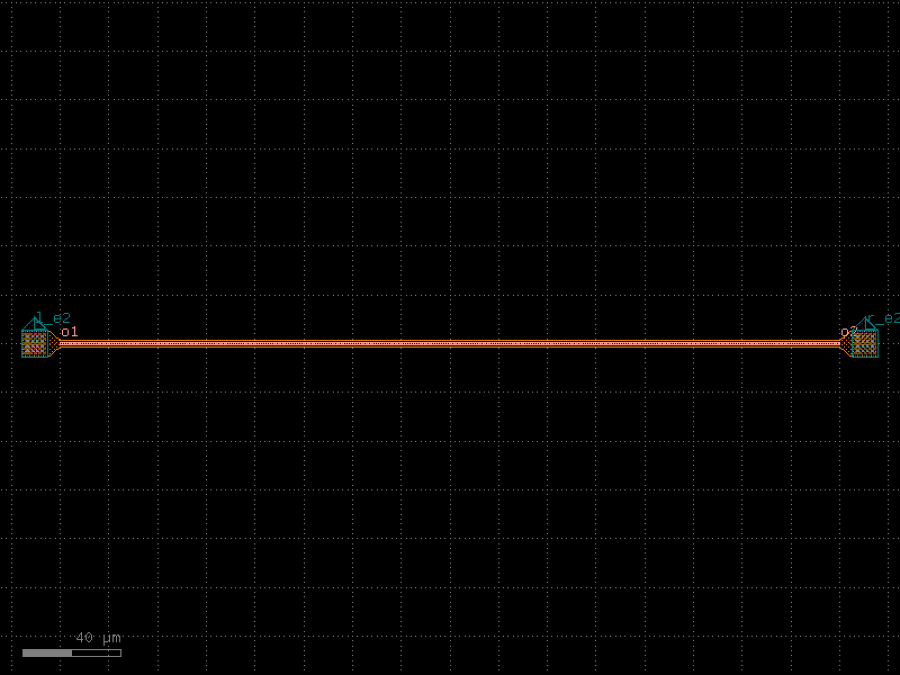
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_heater_metal_simple(length: float = 320.0, cross_section_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'heater_metal', cross_section_waveguide_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_heater_metal', via_stack: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_heater_mtop', port_orientation1: int | None = None, port_orientation2: int | None = None, heater_taper_length: float = 5.0, ohms_per_square: float | None = None)Component
Returns a thermal phase shifter that has properly fixed electrical connectivity to extract a suitable electrical netlist and models.
dimensions from Jacques et al. (2019).
- Parameters
length– of the waveguide.length_undercut– length of each undercut section.cross_section_heater– for heated sections. heater metal only.cross_section_waveguide_heater– for heated sections.via_stack– via stack.port_orientation1– left via stack port orientation. None adds all orientations.port_orientation2– right via stack port orientation. None adds all orientations.heater_taper_length– minimizes current concentrations from heater to via_stack.ohms_per_square– to calculate resistance.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_heater_metal_simple(length=320, cross_section_heater='heater_metal', cross_section_waveguide_heater='strip_heater_metal', via_stack='via_stack_heater_mtop', heater_taper_length=5).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()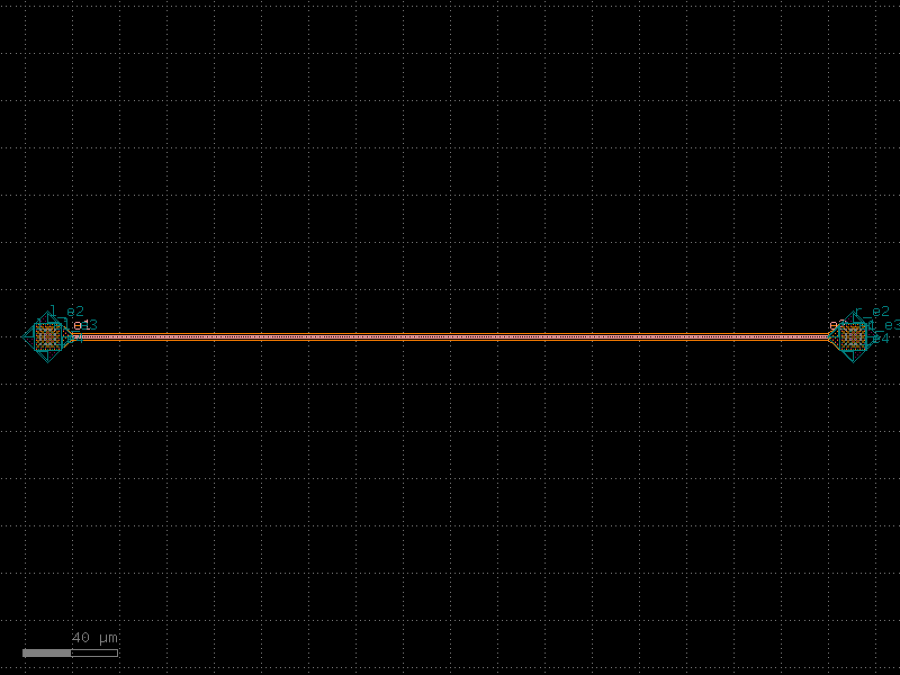
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_heater_metal_undercut(length: float = 320.0, length_undercut_spacing: float = 6.0, length_undercut: float = 30.0, length_straight: float = 0.1, length_straight_input: float = 15.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'heater_metal', cross_section_waveguide_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_heater_metal', cross_section_heater_undercut: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_heater_metal_undercut', with_undercut: bool = True, via_stack: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_heater_mtop', port_orientation1: int | None = None, port_orientation2: int | None = None, heater_taper_length: float = 5.0, ohms_per_square: float | None = None)Component
Returns a thermal phase shifter.
dimensions from Jacques et al. (2019)
- Parameters
length– of the waveguide.length_undercut_spacing– from undercut regions.length_undercut– length of each undercut section.length_straight– length of the straight waveguide.length_straight_input– from input port to where trenches start.cross_section– for waveguide ports.cross_section_heater– for heated sections. heater metal only.cross_section_waveguide_heater– for heated sections.cross_section_heater_undercut– for heated sections with undercut.with_undercut– isolation trenches for higher efficiency.via_stack– via stack.port_orientation1– left via stack port orientation. None adds all orientations.port_orientation2– right via stack port orientation. None adds all orientations.heater_taper_length– minimizes current concentrations from heater to via_stack.ohms_per_square– to calculate resistance.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_heater_metal_undercut(length=320, length_undercut_spacing=6, length_undercut=30, length_straight=0.1, length_straight_input=15, cross_section='strip', cross_section_heater='heater_metal', cross_section_waveguide_heater='strip_heater_metal', cross_section_heater_undercut='strip_heater_metal_undercut', with_undercut=True, via_stack='via_stack_heater_mtop', heater_taper_length=5).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_heater_metal_undercut_90_90(length: float = 320.0, length_undercut_spacing: float = 6.0, length_undercut: float = 30.0, length_straight: float = 0.1, length_straight_input: float = 15.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip', cross_section_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'heater_metal', cross_section_waveguide_heater: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_heater_metal', cross_section_heater_undercut: CrossSectionSpec = 'strip_heater_metal_undercut', with_undercut: bool = True, via_stack: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_heater_mtop', *, port_orientation1: int | None = 90, port_orientation2: int | None = 90, heater_taper_length: float = 5.0, ohms_per_square: float | None = None)Component
Returns a thermal phase shifter.
dimensions from Jacques et al. (2019)
- Parameters
length– of the waveguide.length_undercut_spacing– from undercut regions.length_undercut– length of each undercut section.length_straight– length of the straight waveguide.length_straight_input– from input port to where trenches start.cross_section– for waveguide ports.cross_section_heater– for heated sections. heater metal only.cross_section_waveguide_heater– for heated sections.cross_section_heater_undercut– for heated sections with undercut.with_undercut– isolation trenches for higher efficiency.via_stack– via stack.port_orientation1– left via stack port orientation. None adds all orientations.port_orientation2– right via stack port orientation. None adds all orientations.heater_taper_length– minimizes current concentrations from heater to via_stack.ohms_per_square– to calculate resistance.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_heater_metal_undercut_90_90(length=320, length_undercut_spacing=6, length_undercut=30, length_straight=0.1, length_straight_input=15, cross_section='strip', cross_section_heater='heater_metal', cross_section_waveguide_heater='strip_heater_metal', cross_section_heater_undercut='strip_heater_metal_undercut', with_undercut=True, via_stack='via_stack_heater_mtop', port_orientation1=90, port_orientation2=90, heater_taper_length=5).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()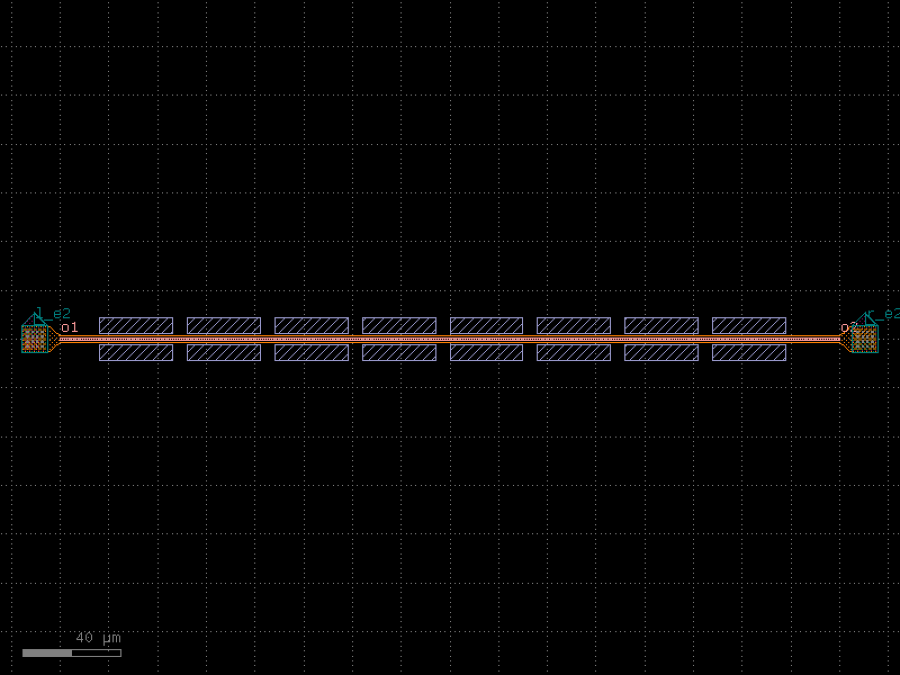
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_piecewise(x: Sequence[float] | Path, widths: Sequence[float], layer: tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum, sections: Sequence[Section] | None = None, port_names: tuple[str | None, str | None] = ('o1', 'o2'), name: str = 'core', **kwargs: Any)Component
Create a component with a piecewise-defined straight waveguide.
- Parameters
x– X coordinates or a custom Path object.widths– Waveguide widths at each corresponding x.layer– Layer to extrude.sections– Additional cross-section sections to extrude.port_names– Port names for the waveguide.name– Name for the core (main) Section.**kwargs– Additional keyword arguments for the Section.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_piecewise(port_names=('o1', 'o2'), name='core').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_pin(length: float = 500.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = <function pin>, via_stack: ComponentSpec = 'via_stack_slab_m3', via_stack_width: float = 10.0, via_stack_spacing: float = 2, taper: ComponentSpec | None = 'taper_strip_to_ridge')Component
Returns rib waveguide with doping and via_stacks used for PN and PIN modulators.
For PIN: Fatemi et al. (2018)
500um length for PI phase shift https://
ieeexplore .ieee .org /document /8268112 to go beyond 2PI, you will need at least 1mm https://
ieeexplore .ieee .org /document /8853396/ For PN: Typical lengths in practice are 2-5mm depending on doping,engineering and application: https://
opg .optica .org /oe /fulltext .cfm ?uri = oe -21 -25 -30350 & id = 275107 https:// opg .optica .org /oe /fulltext .cfm ?uri = oe -20 -11 -12014 & id = 233271 - Parameters
length– of the waveguide.cross_section– for the waveguide.via_stack– for the via_stacks.via_stack_width– width of the via_stack.via_stack_spacing– spacing between via_stacks.taper– optional taper.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_pin(length=500, via_stack='via_stack_slab_m3', via_stack_width=10, via_stack_spacing=2, taper='taper_strip_to_ridge').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_pin_slot(length: float = 500.0, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'pin', via_stack: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_m1_mtop', via_stack_width: float = 10.0, via_stack_slab: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_slab_m1_horizontal', via_stack_slab_top: ComponentSpec | None = None, via_stack_slab_bot: ComponentSpec | None = None, via_stack_slab_width: float | None = None, via_stack_spacing: float = 3.0, via_stack_slab_spacing: float = 2.0, taper: ComponentSpec | None = 'taper_strip_to_ridge', width: float | None = None)Component
Returns a PIN straight waveguide with slotted via.
500um length for PI phase shift https://
ieeexplore .ieee .org /document /8268112 to go beyond 2PI, you will need at least 1mm https://
ieeexplore .ieee .org /document /8853396/ - Parameters
length– of the waveguide.cross_section– for the waveguide.via_stack– for via_stacking the metal.via_stack_width– in um.via_stack_slab– function for the component via_stacking the slab.via_stack_slab_top– Optional, defaults to via_stack_slab.via_stack_slab_bot– Optional, defaults to via_stack_slab.via_stack_slab_width– defaults to via_stack_width.via_stack_spacing– spacing between via_stacks.via_stack_slab_spacing– spacing between via_stacks slabs.taper– optional taper.width– width of the waveguide. If None, it will use the width of the cross_section.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_pin_slot(length=500, cross_section='pin', via_stack='via_stack_m1_mtop', via_stack_width=10, via_stack_slab='via_stack_slab_m1_horizontal', via_stack_spacing=3, via_stack_slab_spacing=2, taper='taper_strip_to_ridge').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()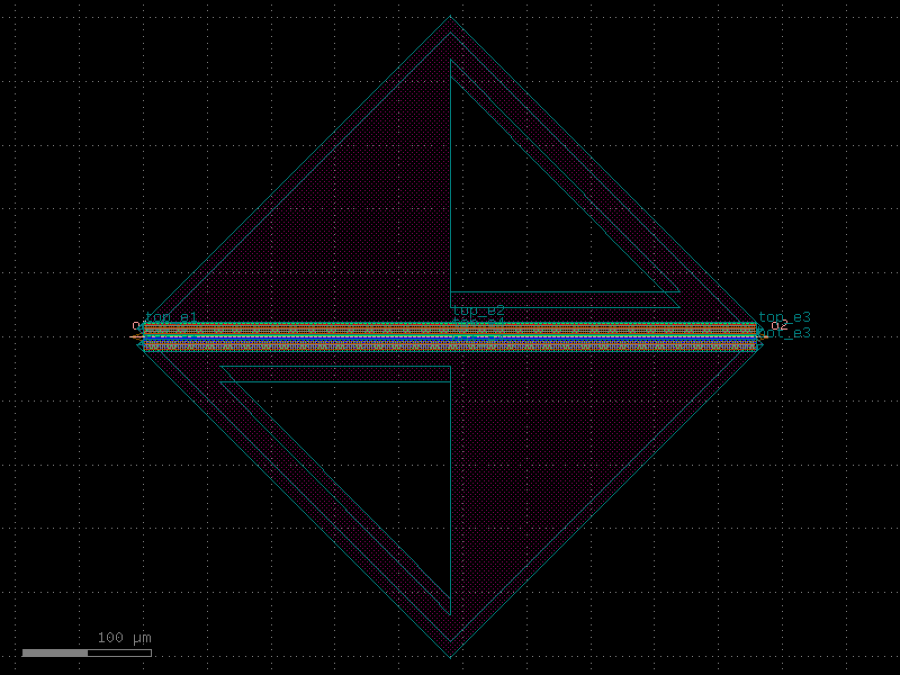
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_pn(*, length: float = 2000, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'pn', via_stack: ComponentSpec = 'via_stack_slab_m3', via_stack_width: float = 10.0, via_stack_spacing: float = 2, taper: ComponentSpec | None = 'taper_strip_to_ridge')Component
Returns rib waveguide with doping and via_stacks used for PN and PIN modulators.
For PIN: Fatemi et al. (2018)
500um length for PI phase shift https://
ieeexplore .ieee .org /document /8268112 to go beyond 2PI, you will need at least 1mm https://
ieeexplore .ieee .org /document /8853396/ For PN: Typical lengths in practice are 2-5mm depending on doping,engineering and application: https://
opg .optica .org /oe /fulltext .cfm ?uri = oe -21 -25 -30350 & id = 275107 https:// opg .optica .org /oe /fulltext .cfm ?uri = oe -20 -11 -12014 & id = 233271 - Parameters
length– of the waveguide.cross_section– for the waveguide.via_stack– for the via_stacks.via_stack_width– width of the via_stack.via_stack_spacing– spacing between via_stacks.taper– optional taper.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_pn(length=2000, cross_section='pn', via_stack='via_stack_slab_m3', via_stack_width=10, via_stack_spacing=2, taper='taper_strip_to_ridge').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()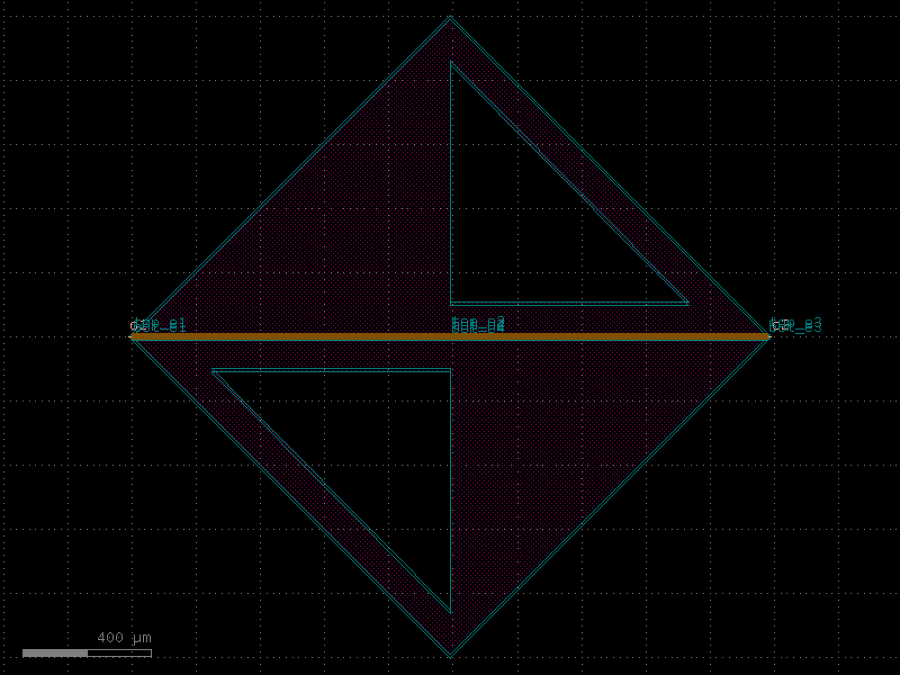
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.straight_pn_slot(length: float = 500.0, *, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = <function pn>, via_stack: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_m1_mtop', via_stack_width: float = 10.0, via_stack_slab: ComponentSpec | None = 'via_stack_slab_m1_horizontal', via_stack_slab_top: ComponentSpec | None = None, via_stack_slab_bot: ComponentSpec | None = None, via_stack_slab_width: float | None = None, via_stack_spacing: float = 3.0, via_stack_slab_spacing: float = 2.0, taper: ComponentSpec | None = 'taper_strip_to_ridge', width: float | None = None)Component
Returns a PIN straight waveguide with slotted via.
500um length for PI phase shift https://
ieeexplore .ieee .org /document /8268112 to go beyond 2PI, you will need at least 1mm https://
ieeexplore .ieee .org /document /8853396/ - Parameters
length– of the waveguide.cross_section– for the waveguide.via_stack– for via_stacking the metal.via_stack_width– in um.via_stack_slab– function for the component via_stacking the slab.via_stack_slab_top– Optional, defaults to via_stack_slab.via_stack_slab_bot– Optional, defaults to via_stack_slab.via_stack_slab_width– defaults to via_stack_width.via_stack_spacing– spacing between via_stacks.via_stack_slab_spacing– spacing between via_stacks slabs.taper– optional taper.width– width of the waveguide. If None, it will use the width of the cross_section.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.straight_pn_slot(length=500, via_stack='via_stack_m1_mtop', via_stack_width=10, via_stack_slab='via_stack_slab_m1_horizontal', via_stack_spacing=3, via_stack_slab_spacing=2, taper='taper_strip_to_ridge').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()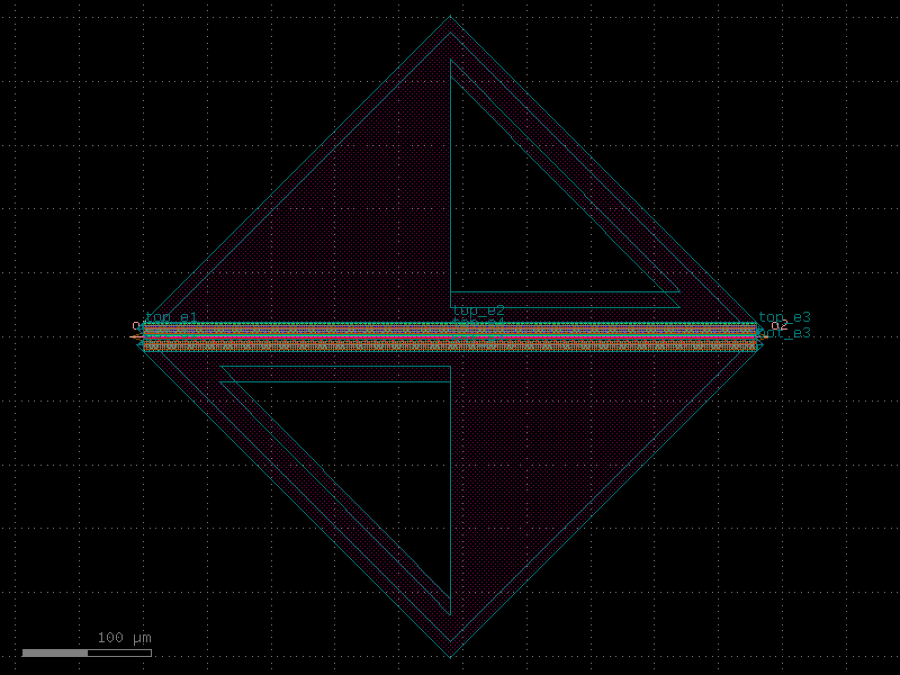
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.wire_corner(cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'metal_routing', port_names: PortNames = ('e1', 'e2'), port_types: PortTypes = ('electrical', 'electrical'), width: float | None = None, radius: None | float = None)Component
Returns 45 degrees electrical corner wire.
- Parameters
cross_section– spec.port_names– port names.port_types– port types.width– optional width. Defaults to cross_section width.radius– ignored.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.wire_corner(cross_section='metal_routing', port_names=('e1', 'e2'), port_types=('electrical', 'electrical')).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()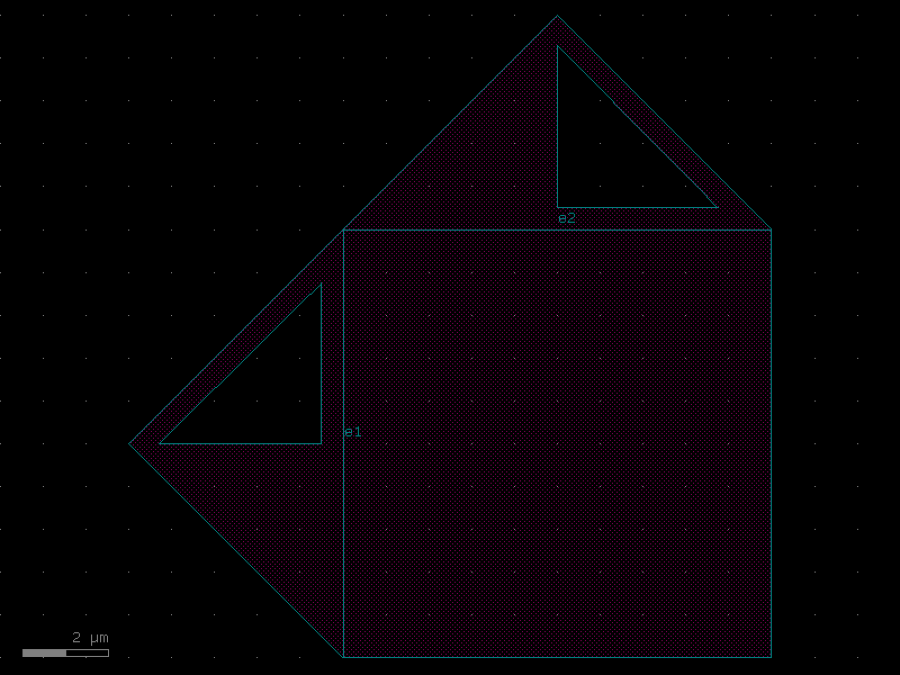
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.wire_corner45(cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'metal_routing', radius: float = 10, width: float | None = None, layer: LayerSpec | None = None, with_corner90_ports: bool = True)Component
Returns 90 degrees electrical corner wire.
- Parameters
cross_section– spec.radius– in um.width– optional width.layer– optional layer.with_corner90_ports– if True adds ports at 90 degrees.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.wire_corner45(cross_section='metal_routing', radius=10, with_corner90_ports=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.wire_corner_sections(cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'metal_routing')Component
Returns 90 degrees electrical corner wire, where all cross_section sections properly represented.
Works well with symmetric cross_sections, not quite ready for asymmetric.
- Parameters
cross_section– spec.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.wire_corner_sections(cross_section='metal_routing').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- gdsfactory.components.waveguides.wire_straight(length: float = 10.0, npoints: int = 2, cross_section: CrossSectionSpec = 'metal_routing', width: float | None = None)Component
Returns a Straight waveguide.
- Parameters
length– straight length (um).npoints– number of points.cross_section– specification (CrossSection, string or dict).width– width of the waveguide. If None, it will use the width of the cross_section.
o1 -------------- o2 length
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.wire_straight(length=10, npoints=2, cross_section='metal_routing').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
- Zhu, L., & Wu, K. (2000). Accurate circuit model of interdigital capacitor and its application to design of new quasi-lumped miniaturized filters with suppression of harmonic resonance. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 48(3), 347–356. 10.1109/22.826833
- Cao, L., Elshaari, A., Aboketaf, A., & Preble, S. (2010). Adiabatic couplers in SOI waveguides. Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics 2010, CThAA2. 10.1364/cleo.2010.cthaa2
- Xu, L., Wang, Y., Patel, D., El-Fiky, E., Xing, Z., Li, R., Saber, M. G., Jacques, M., & Plant, D. V. (2017). Polarization Independent Adiabatic 3-dB Coupler for Silicon-on-Insulator. Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, SF1I.5. 10.1364/cleo_si.2017.sf1i.5
- Tamazin, H., El-Fiky, E., Wang, Y., D’Mello, Y., Patel, D., Kumar, A., & Plant, D. V. (2018). Ultra-broadband Compact Adiabatic Coupler in Silicon-on-Insulator for Joint Operation in the C- and O-Bands. Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, STh4B.4. 10.1364/cleo_si.2018.sth4b.4
- Chen, G. F. R., Ong, J. R., Ang, T. Y. L., Lim, S. T., Png, C. E., & Tan, D. T. H. (2017). Broadband Silicon-On-Insulator directional couplers using a combination of straight and curved waveguide sections. Scientific Reports, 7(1). 10.1038/s41598-017-07618-6
- Chen, H. T., Verheyen, P., De Heyn, P., Lepage, G., De Coster, J., Absil, P., Roelkens, G., & Van Campenhout, J. (2015). High-Responsivity Low-Voltage 28-Gb/s Ge p-i-n Photodetector With Silicon Contacts. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 33(4), 820–824. 10.1109/jlt.2014.2367134
- Shu, H., Shen, B., Deng, Q., Jin, M., Wang, X., & Zhou, Z. (2019). A Design Guideline for Mode (DE) Multiplexer Based on Integrated Tapered Asymmetric Directional Coupler. IEEE Photonics Journal, 11(5), 1–12. 10.1109/jphot.2019.2941742
- Versnel, W. (1979). Analysis of the Greek cross, a Van der Pauw structure with finite contacts. Solid-State Electronics, 22(11), 911–914. 10.1016/0038-1101(79)90061-3
- Hornibrook, J. M., Colless, J. I., Mahoney, A. C., Croot, X. G., Blanvillain, S., Lu, H., Gossard, A. C., & Reilly, D. J. (2014). Frequency multiplexing for readout of spin qubits. Applied Physics Letters, 104(10). 10.1063/1.4868107
- Qiu, H., Liu, Y., Luan, C., Kong, D., Guan, X., Ding, Y., & Hu, H. (2020). Energy-efficient thermo-optic silicon phase shifter with well-balanced overall performance. Optics Letters, 45(17), 4806. 10.1364/ol.400230
- Clem, J. R., & Berggren, K. K. (2011). Geometry-dependent critical currents in superconducting nanocircuits. Physical Review B, 84(17). 10.1103/physrevb.84.174510
- Jacques, M., Samani, A., El-Fiky, E., Patel, D., Xing, Z., & Plant, D. V. (2019). Optimization of thermo-optic phase-shifter design and mitigation of thermal crosstalk on the SOI platform. Optics Express, 27(8), 10456. 10.1364/oe.27.010456
- Fatemi, R., Abiri, B., Khachaturian, A., & Hajimiri, A. (2018). High sensitivity active flat optics optical phased array receiver with a two-dimensional aperture. Optics Express, 26(23), 29983. 10.1364/oe.26.029983